Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
[Numerical Analysis] It is numerical analysis. please use Matlab language !! Consider the one-dimensional, transient (i.e. time-dependent) heat conduction equation without heat generating sources where
[Numerical Analysis]
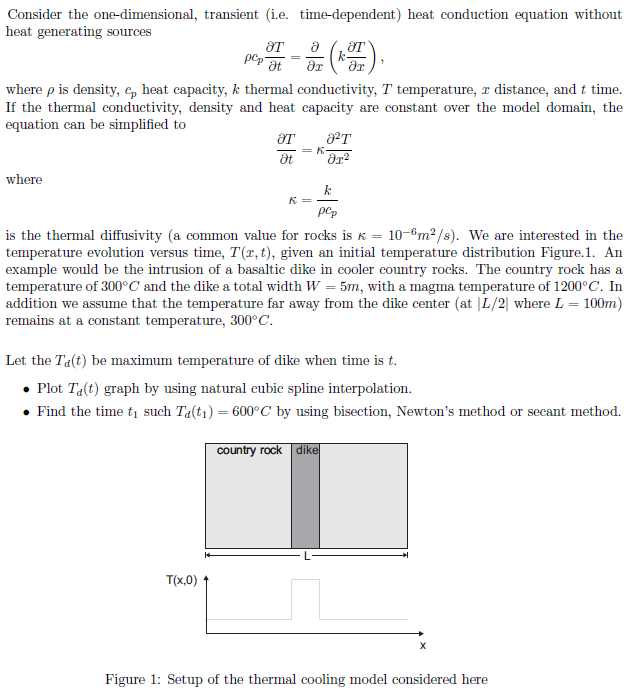
It is numerical analysis. please use Matlab language !!
Consider the one-dimensional, transient (i.e. time-dependent) heat conduction equation without heat generating sources where ? is density, Cp heat capacity, k thermal conductivity, T temperature, distance, and t time If the thermal conductivity, density and heat capacity are constant over the model domain, the equation can be simplified to OT 2T where pCp is the thermal diffusivity (a common value for rocks is K 10-6m2/s). We are interested in the temperature evolution versus time, T(r, t), given an initial temperature distribution Figure.1. An example would be the intrusion of a basaltic dike in cooler country rocks. The country rock has a temperature of 300C and the dike a total width W -5m, with a magma temperature of 1200C. In addition we assume that the temperature far away from the dike center (at L/2 where L = 100m) remains at a constant temperature, 300C Let the Td(t) be maximum temperature of dike when time is t . Plot Ta t) graph by using natural cubic spline interpolation. . Find the time t1 such Ta(t1) 600C by using bisection, Newton's method or secant method. country T(x,0) Figure 1: Setup of the thermal cooling model considered here Consider the one-dimensional, transient (i.e. time-dependent) heat conduction equation without heat generating sources where ? is density, Cp heat capacity, k thermal conductivity, T temperature, distance, and t time If the thermal conductivity, density and heat capacity are constant over the model domain, the equation can be simplified to OT 2T where pCp is the thermal diffusivity (a common value for rocks is K 10-6m2/s). We are interested in the temperature evolution versus time, T(r, t), given an initial temperature distribution Figure.1. An example would be the intrusion of a basaltic dike in cooler country rocks. The country rock has a temperature of 300C and the dike a total width W -5m, with a magma temperature of 1200C. In addition we assume that the temperature far away from the dike center (at L/2 where L = 100m) remains at a constant temperature, 300C Let the Td(t) be maximum temperature of dike when time is t . Plot Ta t) graph by using natural cubic spline interpolation. . Find the time t1 such Ta(t1) 600C by using bisection, Newton's method or secant method. country T(x,0) Figure 1: Setup of the thermal cooling model considered hereStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


