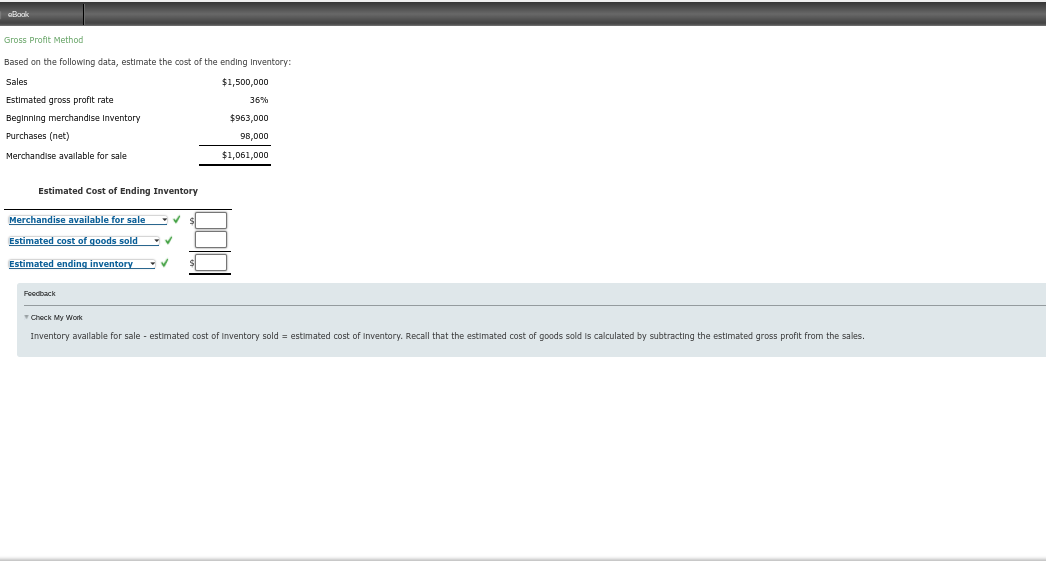
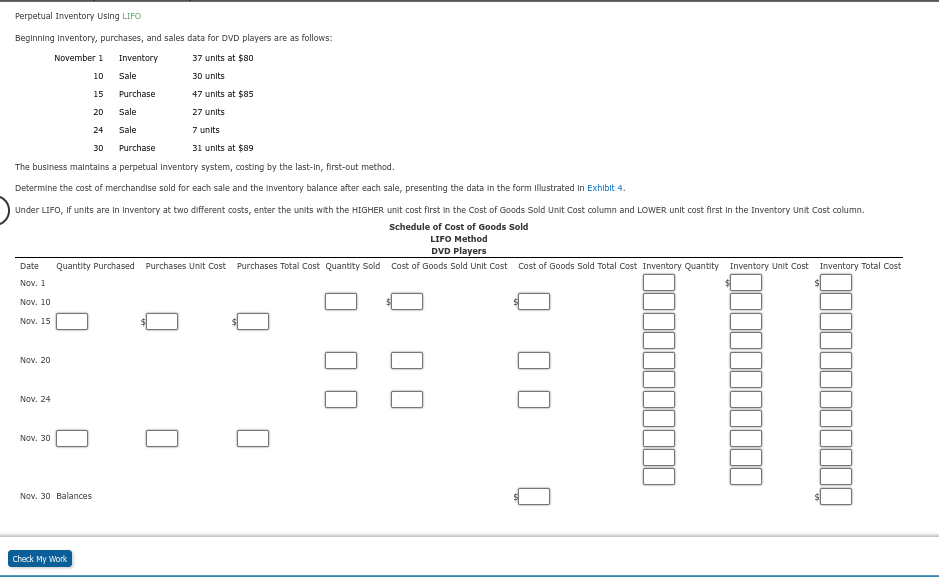
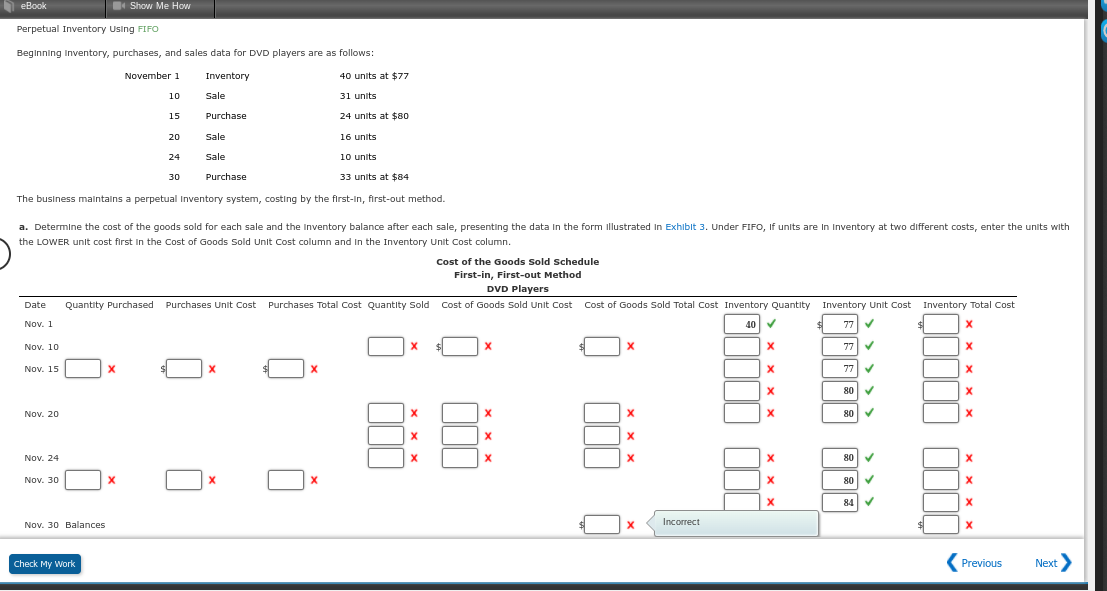
oBook Gross Profit Method Based on the following data, estimate the cost of the ending Inventory: Sales $1,500,000 Estimated gross profit rate 36% Beginning merchandise Inventory $963,000 Purchases (net) 98,000 Merchandise available for sale $1,061,000 Estimated cost Ending Inventory Merchandise available for sale Estimated cost of goods sold Estimated ending inventory Feedback Check My Work Inventory available for sale - estimated cost of Inventory sold = estimated cost of Inventory. Recall that the estimated cost of goods sold is calculated by subtracting the estimated gross profit from the sales. 20 Perpetual Inventory Using LIFO Beginning Inventory, purchases, and sales data for DVD players are as follows: November 1 Inventory 37 units at $80 10 Sale 30 units 15 Purchase 47 units at $85 Sale 27 units 24 Sale 7 units 30 Purchase 31 units at $89 The business maintains a perpetual Inventory system, costing by the last-In, first-out method. Determine the cost of merchandise sold for each sale and the Inventory balance after each sale, presenting the data in the form illustrated In Exhibit 4. Under LIFO, If units are in Inventory at two different costs, enter the units with the HIGHER unit cost first in the cost of Goods Sold Unit Cost column and LOWER unit cost first in the Inventory Unit Cost column. Schedule of cost of Goods Sold LIFO Method DVD Players Quantity Purchased Purchases Unit Cost Purchases Total Cost Quantity Sold cost of Goods Sold Unit Cost Cost of Goods Sold Total Cost Inventory Quantity Inventory Unit Cost Inventory Total Cost Date Nov. 1 Nov. 10 Nov. 15 Nov. 20 II Nov. 24 Nov. 30 Nov. 30 Balances Check My Work eBook Show Me How Perpetual Inventory Using FIFO Beginning Inventory, purchases, and sales data for DVD players are as follows: November 1 Inventory 40 units at $77 10 Sale 31 units 15 Purchase 24 units at $80 20 Sale 16 units 24 Sale 10 units 30 Purchase 33 units at $84 The business maintains a perpetual Inventory system, costing by the first-in, first-out method. a - a. Determine the cost of the goods sold for each sale and the Inventory balance after each sale, presenting the data in the form illustrated In Exhibit 3. Under FIFO, If units are in Inventory at two different costs, enter the units with the LOWER unit cost first in the cost of Goods Sold Unit Cost column and in the Inventory Unit Cost column. Cost of the Goods Sold Schedule First-in, First-out Method - DVD Players Date Quantity Purchased Purchases Unit Cost Purchases Total Cost Quantity Sold cost of Goods Sold Unit Cost Cost of Goods Sold Total Cost Inventory Quantity Inventory Unit Cost Inventory Total Cost Inventory Unit Cost 40 77 Nov. 1 Nov. 10 X X X 77 Nov. 15 X X X 77 X 80 Nov. 20 X X 80 EE Nov. 24 X 80 X Nov. 30 Ox 80 84 7 Nov. 30 Balances X Incorrect Check My Work (Previous Next >









