Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
ocaml language Library functions: You can use any library functions in the List module for this assignment (please do not use library functions in any
ocaml language 
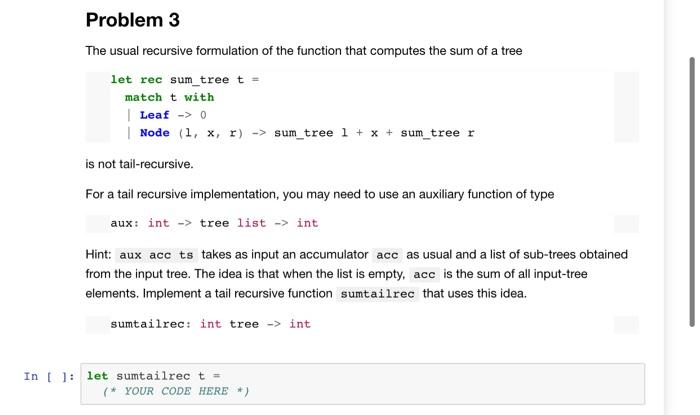
Library functions: You can use any library functions in the List module for this assignment (please do not use library functions in any other modules). You may find the following functions particularly useful, e.g., List.mapi, List.mem_assoc, and List.assoc. Datatypes: Problems 1-3 are about manipulating tree data structures. In OCaml, you can define a tree data structure using datatype: type 'a tree = Leaf Node of 'a tree * 'a * 'a tree We will assume binary search trees in this assignment and can define a bineary search tree insertion function as the following: let rec insert tree x match tree with Leaf -> Node (Leaf, x, Leaf) Node(1, y, r) -> if x = y then tree else if x insert acc x) Leaf 1 Problem 3 The usual recursive formulation of the function that computes the sum of a tree let rec sum_tree t = match t with Leaf -> 0 Node (1, x, r) -> sum_tree 1 + x + sum_treer is not tail-recursive. For a tail recursive implementation, you may need to use an auxiliary function of type aux: int -> tree list -> int Hint: aux acc ts takes as input an accumulator acc as usual and a list of sub-trees obtained from the input tree. The idea is that when the list is empty, acc is the sum of all input-tree elements. Implement a tail recursive function sumtailrec that uses this idea. sumtailrec: int tree -> int In [ ]: let sumtailrec t (* YOUR CODE HERE *) Library functions: You can use any library functions in the List module for this assignment (please do not use library functions in any other modules). You may find the following functions particularly useful, e.g., List.mapi, List.mem_assoc, and List.assoc. Datatypes: Problems 1-3 are about manipulating tree data structures. In OCaml, you can define a tree data structure using datatype: type 'a tree = Leaf Node of 'a tree * 'a * 'a tree We will assume binary search trees in this assignment and can define a bineary search tree insertion function as the following: let rec insert tree x match tree with Leaf -> Node (Leaf, x, Leaf) Node(1, y, r) -> if x = y then tree else if x insert acc x) Leaf 1 Problem 3 The usual recursive formulation of the function that computes the sum of a tree let rec sum_tree t = match t with Leaf -> 0 Node (1, x, r) -> sum_tree 1 + x + sum_treer is not tail-recursive. For a tail recursive implementation, you may need to use an auxiliary function of type aux: int -> tree list -> int Hint: aux acc ts takes as input an accumulator acc as usual and a list of sub-trees obtained from the input tree. The idea is that when the list is empty, acc is the sum of all input-tree elements. Implement a tail recursive function sumtailrec that uses this idea. sumtailrec: int tree -> int In [ ]: let sumtailrec t (* YOUR CODE HERE *) 

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


