Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Old MathJax webview Identify cash flow sequences that are arithmetic gradients and use financial tables (Appendix C) to convert arithmetic gradient cash flows into their
Old MathJax webview
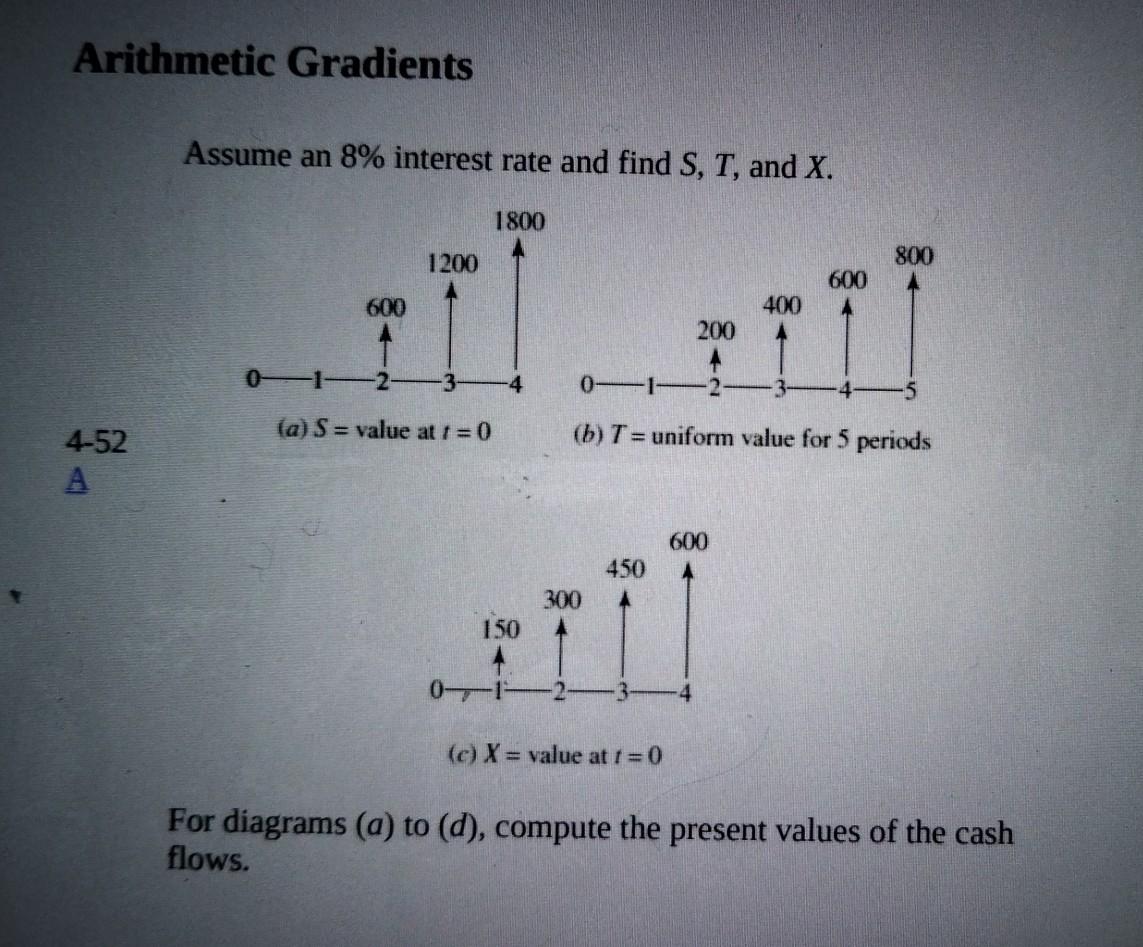
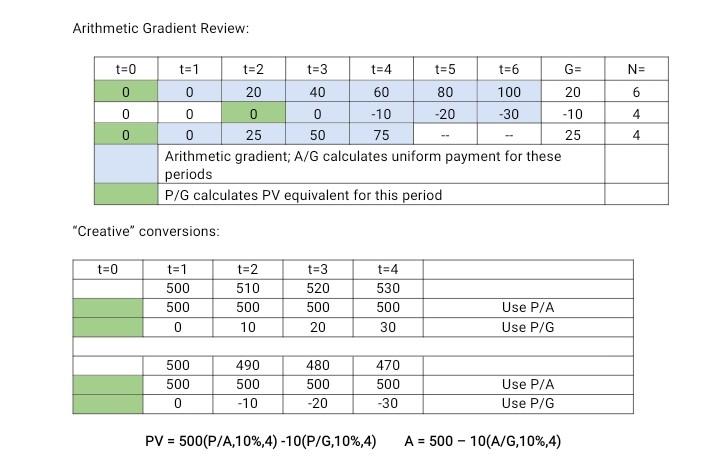
Identify cash flow sequences that are arithmetic gradients and use financial tables (Appendix C) to convert arithmetic gradient cash flows into their present value and uniform payment equivalents. [Reminder: a $0 cash flow is considered part of the gradient and P/G calculates PV one period prior to the period with that $0 cash flow.]
Arithmetic Gradients Assume an 8% interest rate and find S, T, and X. 1800 1200 800 600 600 400 A 200 0 0E +2 3 (a) S = value at i = 0 (b) T= uniform value for 5 periods 4-52 600 450 300 150 01 (c) X = value at i = 0 For diagrams (a) to (d), compute the present values of the cash flows. Arithmetic Gradient Review: t=0 V= N= 80 0 0 0 4 t=1 t=2 t=3 t=4 t=5 t=6 G= 0 20 40 60 100 20 0 0 0 -10 -20 -30 -10 0 25 50 75 25 Arithmetic gradient: A/G calculates uniform payment for these periods P/G calculates PV equivalent for this period 4 "Creative" conversions: t=0 t=1 500 500 0 t=2 510 500 10 t=3 520 500 20 t=4 530 500 30 Use P/A Use P/G 500 500 0 490 500 -10 480 500 -20 470 500 -30 Use P/A Use P/G PV = 500(P/A,10%,4) -10(P/G,10%,4) A = 500 - 10(A/G,10%,4)Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


