Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Old MathJax webview make project report on all question is full CVP Analysis and Decision Making Sale Decision (a) Manufactured XY 200 (for 6,000 hrs)
Old MathJax webview
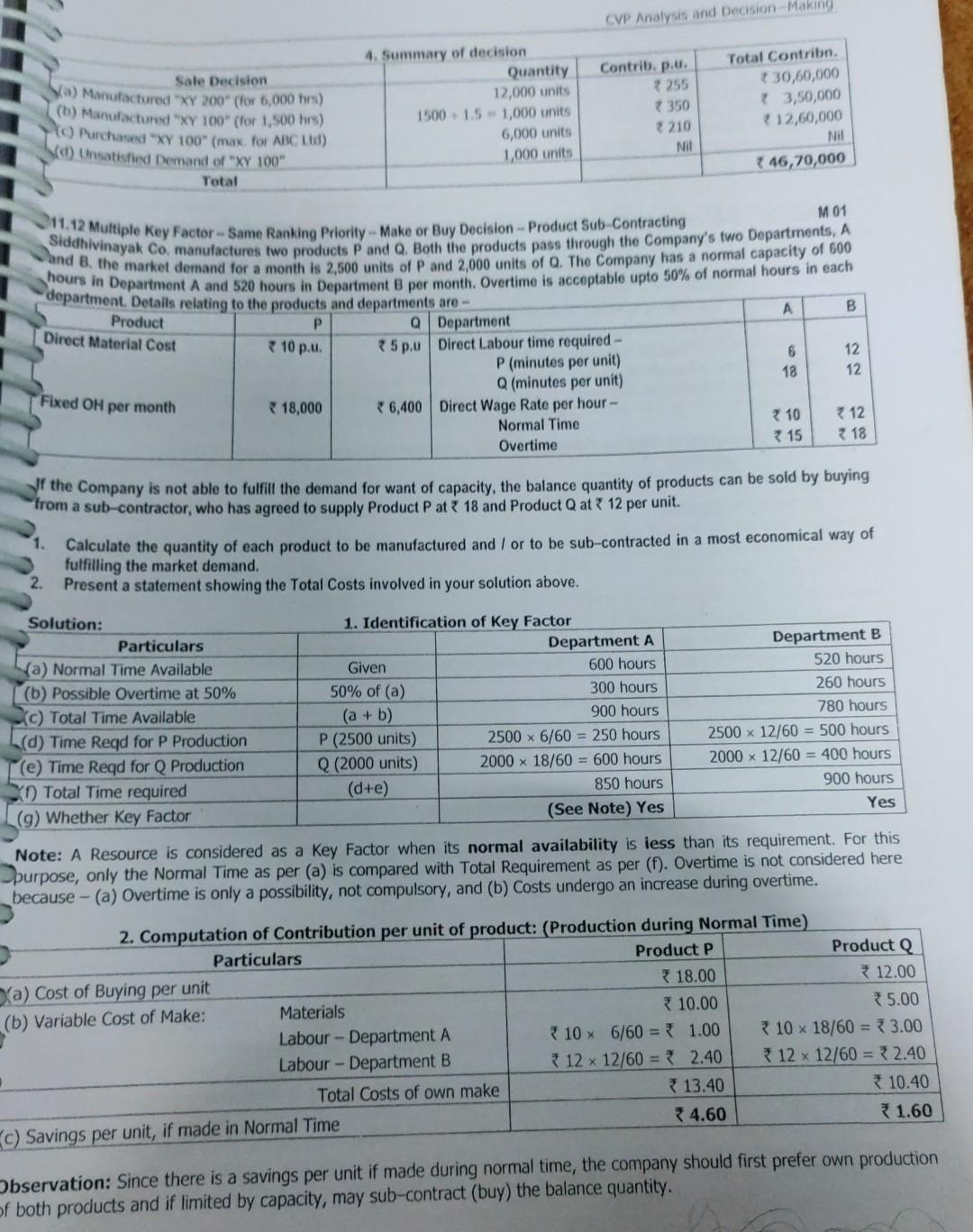
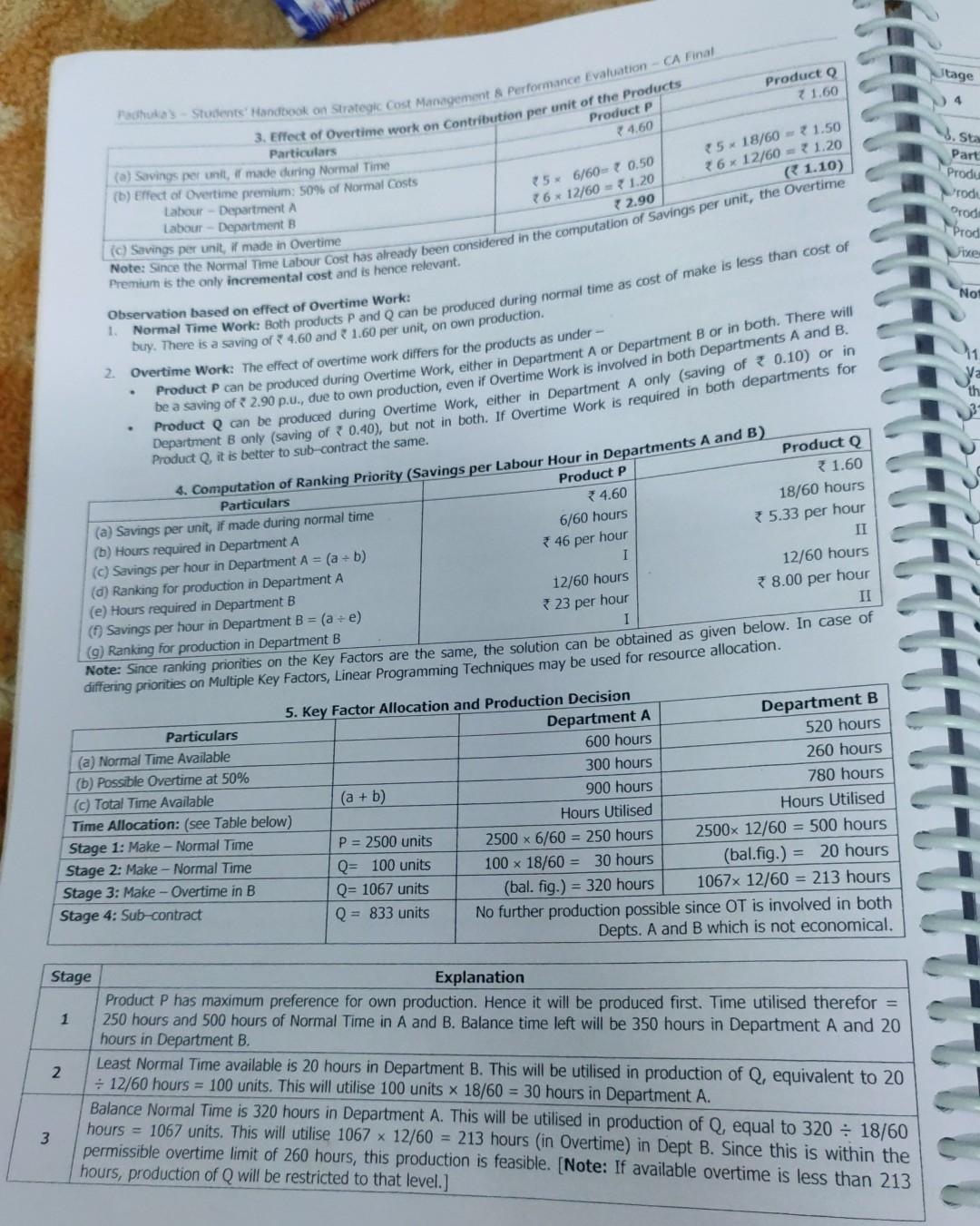
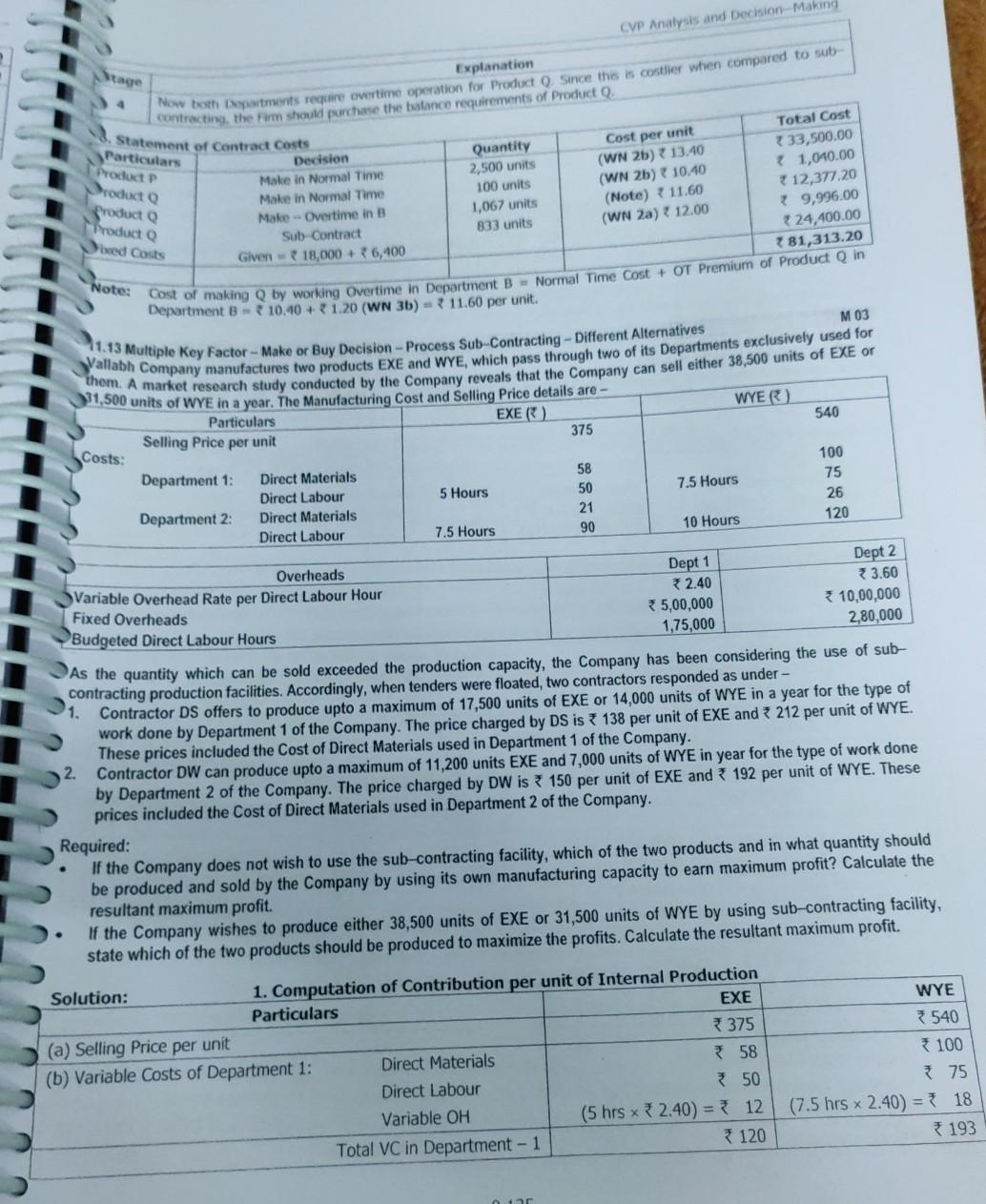
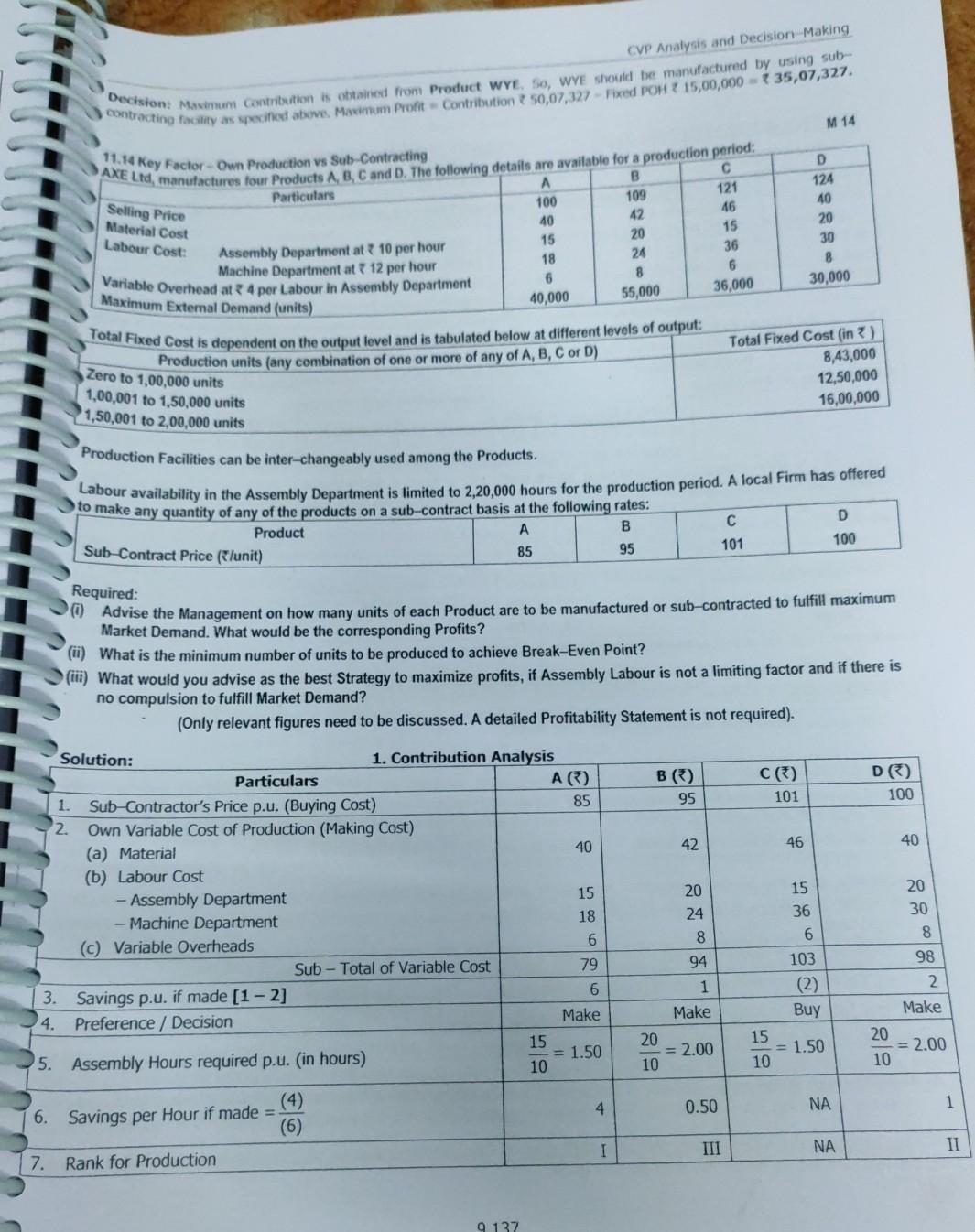
make project report on all
question is full
CVP Analysis and Decision Making Sale Decision (a) Manufactured "XY 200" (for 6,000 hrs) (b) Manufactured "XY 100" (for 1,500 hrs) Purchased "XY 100" (max. for ABC Ld) Sco) Unsatisfied Demand of "XY 100" Total 4. Summary of decision Quantity 12,000 units 1500-1.5 -1,000 units 6,000 units 1,000 units Contrib. p.u. 7255 350 210 Nil Total Contribn. 30,60,000 13,50,000 12,60,000 Nil 46,70,000 M 01 Sh.22 Multiple Key Factor -- Same Ranking Priority -- Make or Buy Decision -- Product Sub Contracting Siddhivinayak co manufactures to producer and she both o products pass through the company's two Departments, A department. Detalls relating to the products and departments are - hours in Department A and 520 hours in Department per month. Overtime is acceptable upto 50% of normal hours in each A B Product Direct Material Cost P ( 10 p.. 6 18 12 12 Q Department * 5p.u Direct Labour time required - P (minutes per unit) Q (minutes per unit) * 6,400 Direct Wage Rate per hour - Normal Time Overtime Fixed OH per month 18,000 10 12 7 18 315 If the Company is not able to fulfill the demand for want of capacity, the balance quantity of products can be sold by buying from a sub-contractor, who has agreed to supply Product Pat 18 and Product Q at 12 per unit. 1. Calculate the quantity of each product to be manufactured and / or to be sub-contracted in a most economical way of fulfilling the market demand. Present a statement showing the Total Costs involved in your solution above. 2. Solution: Particulars (a) Normal Time Available (b) Possible Overtime at 50% c) Total Time Available (d) Time Reqd for P Production (e) Time Reqd for Q Production XO) Total Time required (g) Whether Key Factor 1. Identification of Key Factor Department A Given 600 hours 50% of (a) 300 hours (a + b) 900 hours P (2500 units) 2500 x 6/60 = 250 hours Q (2000 units) 2000 x 18/60 = 600 hours (d+e) 850 hours (See Note) Yes Department B 520 hours 260 hours 780 hours 2500 x 12/60 = 500 hours 2000 x 12/60 = 400 hours 900 hours Yes Note: A Resource is considered as a Key Factor when its normal availability is less than its requirement. For this purpose, only the Normal Time as per (a) is compared with Total Requirement as per (f). Overtime is not considered here because - (a) Overtime is only a possibility, not compulsory, and (b) Costs undergo an increase during overtime. 2. Computation of Contribution per unit of product: (Production during Normal Time) Particulars Product P Product Q 18.00 a) Cost of Buying per unit 12.00 Materials 10.00 35.00 (b) Variable Cost of Make: Labour - Department A * 10 x 6/60 = 1.00 10 x 18/60 = 3.00 Labour - Department B 312 x 12/60 = 2.40 * 12 x 12/60 = 32.40 Total Costs of own make 13.40 10.40 4.60 1.60 C) Savings per unit, if made in Normal Time Observation: Since there is a savings per unit if made during normal time, the company should first prefer own productio of both products and if limited by capacity, may sub-contract (buy) the balance quantity. tage Producto 21.60 Product P 4.60 . Sta Fadhukas Students' Handbook on Strategic Cost Management & Performance Evaluation CA Final 3. Effect of Overtime work on Contribution per unit of the Products Particulars (a) Savings per unit, made during Normal Time (6) Effect of Overtime premium: 50% of Normal Costs Labour - Department A Labour - Department B (Savings per unit, if made in Overtime Note: Since the Normal Time Labour Cost has already been considered in the computation of Savings per unit, the Overtime 5* 18/60 = 1.50 36 x 12/60 = 1.20 (1.10) 15 6/60= { 0.50 7612/60 = 1.20 2.90 Part Produ rode Prode "Prod Whe No1 Premium is the only incremental cost and is hence relevant, Observation based on effect of Overtime Work: 1. Normal Time Work: Both products P and Q can be produced during normal time as cost of make is less than cost of 1 th be a saving of 2.90 p.U., due to own production, even if Overtime Work is involved in both Departments A and B. Product can be produced during Overtime Work, either in Department A only (saving of 30.10) or in buy. There is a saving of * 4.60 and 1.60 per unit, on own production. 2. Overtime Work: The effect of overtime work differs for the products as under - beroduct P can be produced during Overtime work, either in Department A or Department B or in both. There will Department B only (saving of 7 0.40), but not in both. If Overtime work is required in both departments for Product Q, it is better to sub-contract the same. 4. Computation of Ranking Priority (Savings per Labour Hour in Departments A and B) Product Q Particulars Product P (a) Savings per unit, if made during normal time 31.60 * 4.60 (b) Hours required in Department A 18/60 hours 6/60 hours (c) Savings per hour in Department A = (a + b) 46 per hour 5.33 per hour (d) Ranking for production in Department A 1 II (e) Hours required in Department B 12/60 hours 12/60 hours Savings per hour in Department B = (a +e) 38.00 per hour 23 per hour (9) Ranking for production in Department B II Note: Since ranking priorities on the Key Factors are the same, the solution can be obtained as given below. In case of differing priorities on Multiple Key Factors, Linear Programming Techniques may be used for resource allocation. 5. Key Factor Allocation and Production Decision Particulars Department A Department B (a) Normal Time Available 600 hours 520 hours (b) Possible Overtime at 50% 300 hours 260 hours (c) Total Time Available (a + b) 900 hours 780 hours Time Allocation: (see Table below) Hours Utilised Hours Utilised Stage 1: Make - Normal Time P = 2500 units 2500 x 6/60 = 250 hours 2500x 12/60 = 500 hours Stage 2: Make - Normal Time Q= 100 units 100 x 18/60 = 30 hours (bal.fig.) = 20 hours Stage 3: Make-Overtime in B Q= 1067 units (bal. fig.) = 320 hours 1067x 12/60 = 213 hours Stage 4: Sub-contract Q = 833 units No further production possible since OT is involved in both Depts. A and B which is not economical. 1 Stage Explanation Product P has maximum preference for own production. Hence it will be produced first. Time utilised therefor = 250 hours and 500 hours of Normal Time in A and B. Balance time left will be 350 hours in Department A and 20 hours in Department B. Least Normal Time available is 20 hours in Department B. This will be utilised in production of , equivalent to 20 + 12/60 hours = 100 units. This will utilise 100 units x 18/60 = 30 hours in Department A. Balance Normal Time is 320 hours in Department A. This will be utilised in production of Q, equal to 320 = 18/60 hours = 1067 units. This will utilise 1067 ~ 12/60 = 213 hours (in Overtime) in Dept B. Since this is within the 3 permissible overtime limit of 260 hours, this production is feasible. (Note: If available overtime is less than 213 hours, production of Q will be restricted to that level.] 2 CVP Analysis and Decision-Making Stage 4 Explanation Now both partnerits require overtime operation for product 0. Since this is contier wien compared to sub- contracting the form should purchase the balance requirements of Product Q. Statement of Contract costs Particulars Product P Producto Producto Product Dixed Costs Note: Total Cost Decision Quantity Cost per unit Make in Normal Time 2,500 units (WN 2b) 13.40 33,500.00 Make in Normal Time 100 units (WN 2b) 10.40 { 1,040.00 Make-Overtime in B 1,067 units (Note) 11.60 12,377.20 Sub Contract 833 units (WN 2a) 12.00 79,996.00 Glven - 18,000 + 6,400 24,400.00 781,313.20 Cost of making Q by working Overtime in Department B - Normal Time Cost + OT Premium of Product Q in Department - 10.40 + 1.20 (WN 3b) - 11.60 per unit. 113 Multiple Key Factor - Make or Buy Decision - Process Sub-Contracting - Different Alternatives M 03 allabh Company manufactures to products exe and wees, which has incroughouwen of its Departments exclusively used for 31,500 units of WYE in a year. The Manufacturing Cost and Selling Price details are - Particulars EXE) WYER) 375 540 them. A market research study conducted by the Company reveals that the Company can sell either 38,500 units of EXE or Selling Price per unit Costs: Department 1: 7.5 Hours Direct Materials Direct Labour Direct Materials Direct Labour 5 Hours 100 75 26 120 58 50 21 90 Department 2 10 Hours 7.5 Hours 1. Overheads Dept 1 Dept 2 Variable Overhead Rate per Direct Labour Hour 2.40 *3.60 Fixed Overheads 5,00,000 10,00,000 Budgeted Direct Labour Hours 1,75,000 2,80,000 As the quantity which can be sold exceeded the production capacity, the Company has been considering the use of sub- contracting production facilities. Accordingly, when tenders were floated, two contractors responded as under - Contractor DS offers to produce upto a maximum of 17,500 units of EXE or 14,000 units of WYE in a year for the type of work done by Department 1 of the Company. The price charged by DS is 138 per unit of EXE and 3 212 per unit of WYE. These prices included the Cost of Direct Materials used in Department 1 of the Company. 2. Contractor DW can produce upto a maximum of 11,200 units EXE and 7,000 units of WYE in year for the type of work done by Department 2 of the Company. The price charged by DW is 150 per unit of EXE and 192 per unit of WYE. These prices included the Cost of Direct Materials used in Department 2 of the Company. Required: If the Company does not wish to use the sub-contracting facility, which of the two products and in what quantity should be produced and sold by the Company by using its own manufacturing capacity to earn maximum profit? Calculate the resultant maximum profit. If the Company wishes to produce either 38,500 units of EXE or 31,500 units of WYE by using sub-contracting facility, state which of the two products should be produced to maximize the profits. Calculate the resultant maximum profit. . Solution: 1. Computation of Contribution per unit of Internal Production Particulars EXE 375 (a) Selling Price per unit (b) Variable Costs of Department 1: Direct Materials 58 Direct Labour 50 Variable OH (5 hrs x 2.40) = 12 Total VC in Department - 1 120 WYE 7540 * 100 75 (7.5 hrs x 2.40) = 18 193 CVP Analysis and Decision Making Decision: Maximum Contribution is obtained from Product WYE 5, WYE should be manufactured by using sub- contracting facility as specified above. Maximum Profit Contribution 50,07,327 Fixed POH ? 15,00,000 - 35,07,327. M 14 B A 100 121 Selling Price Material Cost Labour Cost: 11.14 Key Factor-Own Production vs Sub-Contracting AXE Ltd, manufactures four Products A, B, C and D. The following details are available for a production period: Particulars 109 46 40 42 15 20 15 Assembly Department at 10 per hour 24 18 Machine Department at 12 per hour Variable Overhead at 4 por Labour in Assembly Department 6 8 Maximum External Demand (units) 40,000 Total Fixed Cost is dependent on the output tovel and is tabulated below at different levels of output: Production units (any combination of one or more of any of A, B, C or D) D 124 40 20 30 B 30,000 36 6 36,000 55,000 Zero to 1,00,000 units 1,00,001 to 1,50,000 units 1,50,001 to 2,00,000 units Total Fixed Cost (in) 8,43,000 12,50,000 16,00,000 D A B 95 101 85 Production Facilities can be inter-changeably used among the Products. tabour availability in the Assembly Department is limited to 2,20,000 hours for the production period. A local Firm has offered to make any quantity of any of the products on a sub-contract basis at the following rates: Product Sub-Contract Price (lunit) 100 Required: Advise the Management on how many units of each Product are to be manufactured or sub-contracted to fulfill maximum Market Demand. What would be the corresponding Profits? (ii) What is the minimum number of units to be produced to achieve Break-Even Point? (iii) What would you advise as the best Strategy to maximize profits, if Assembly Labour is not a limiting factor and if there is no compulsion to fulfill Market Demand? (Only relevant figures need to be discussed. A detailed profitability Statement is not required). B) 95 CE) 101 D) 100 42 46 40 Solution: 1. Contribution Analysis Particulars A) 1. Sub-Contractor's Price p.u. (Buying Cost) 85 2. Own Variable Cost of Production (Making Cost) (a) Material 40 (b) Labour Cost - Assembly Department 15 - Machine Department 18 (c) Variable Overheads 6 Sub - Total of Variable Cost 79 3. Savings p.u. if made [1 -2] 6 4. Preference / Decision Make 15 5. Assembly Hours required p.u. (in hours) = 1.50 10 20 24 8 15 36 20 30 8 98 6 94 1 Make 103 (2) Buy 15 = 1.50 10 2 Make 20 = 2.00 10 20 = 2.00 10 4 0.50 1 NA U-0. (4) 6. Savings per Hour if made = (6) I III NA 7. Rank for Production 9137Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


