Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Old MathJax webview need project report on all question is full Colgate Product Note: Since the Normal Time Labour cost has already been considered in
Old MathJax webview
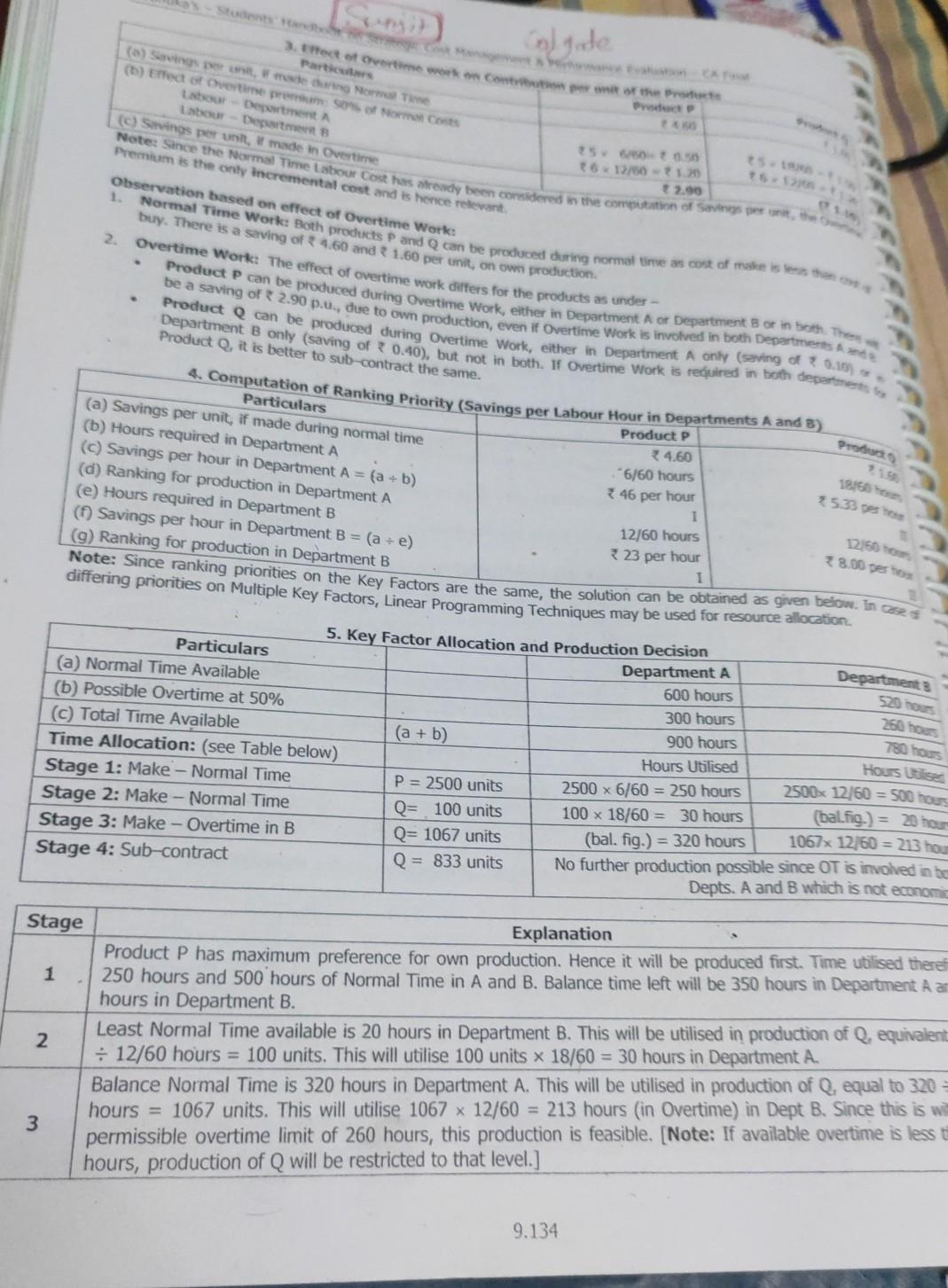
need project report on all
question is full
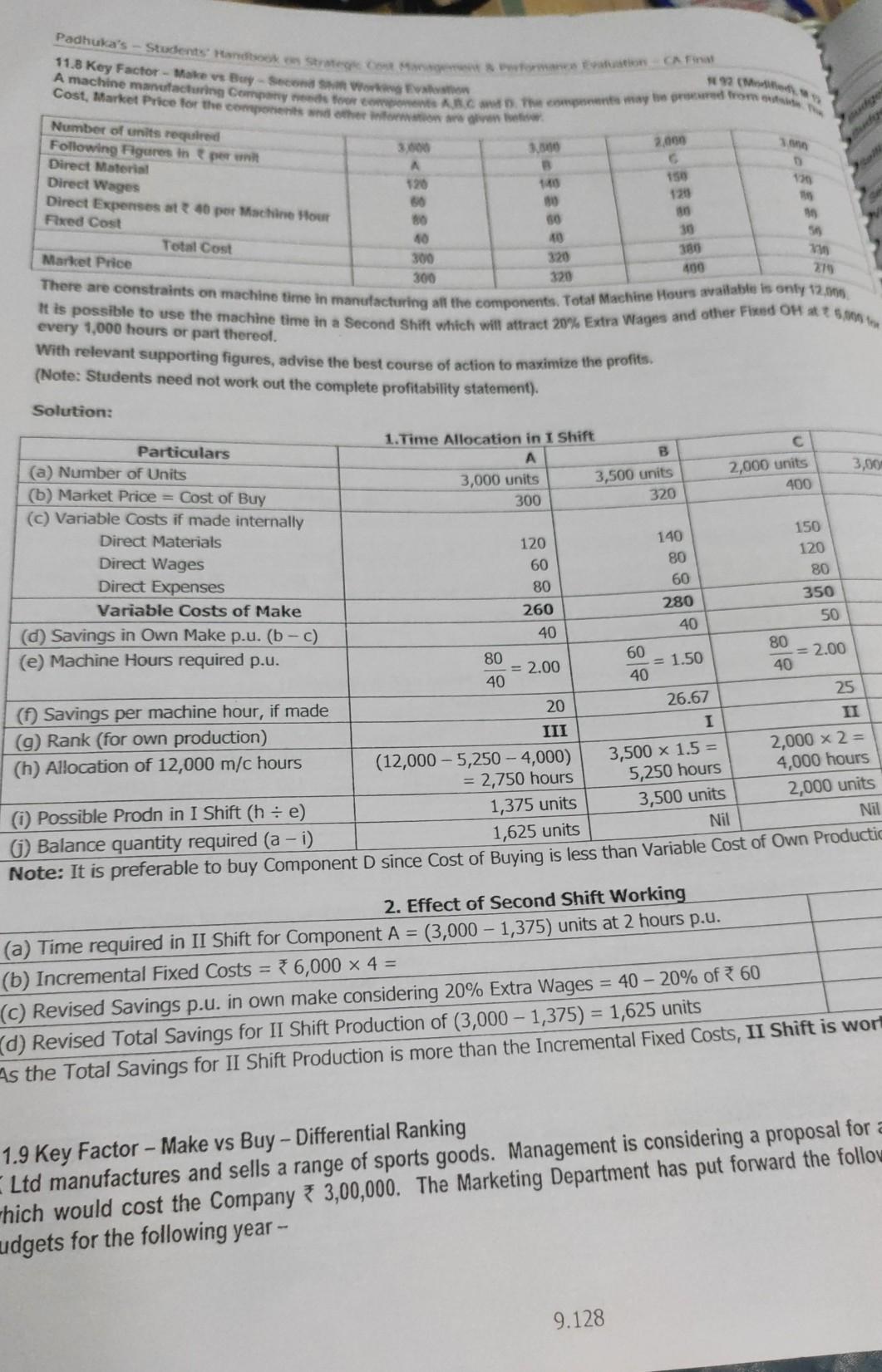
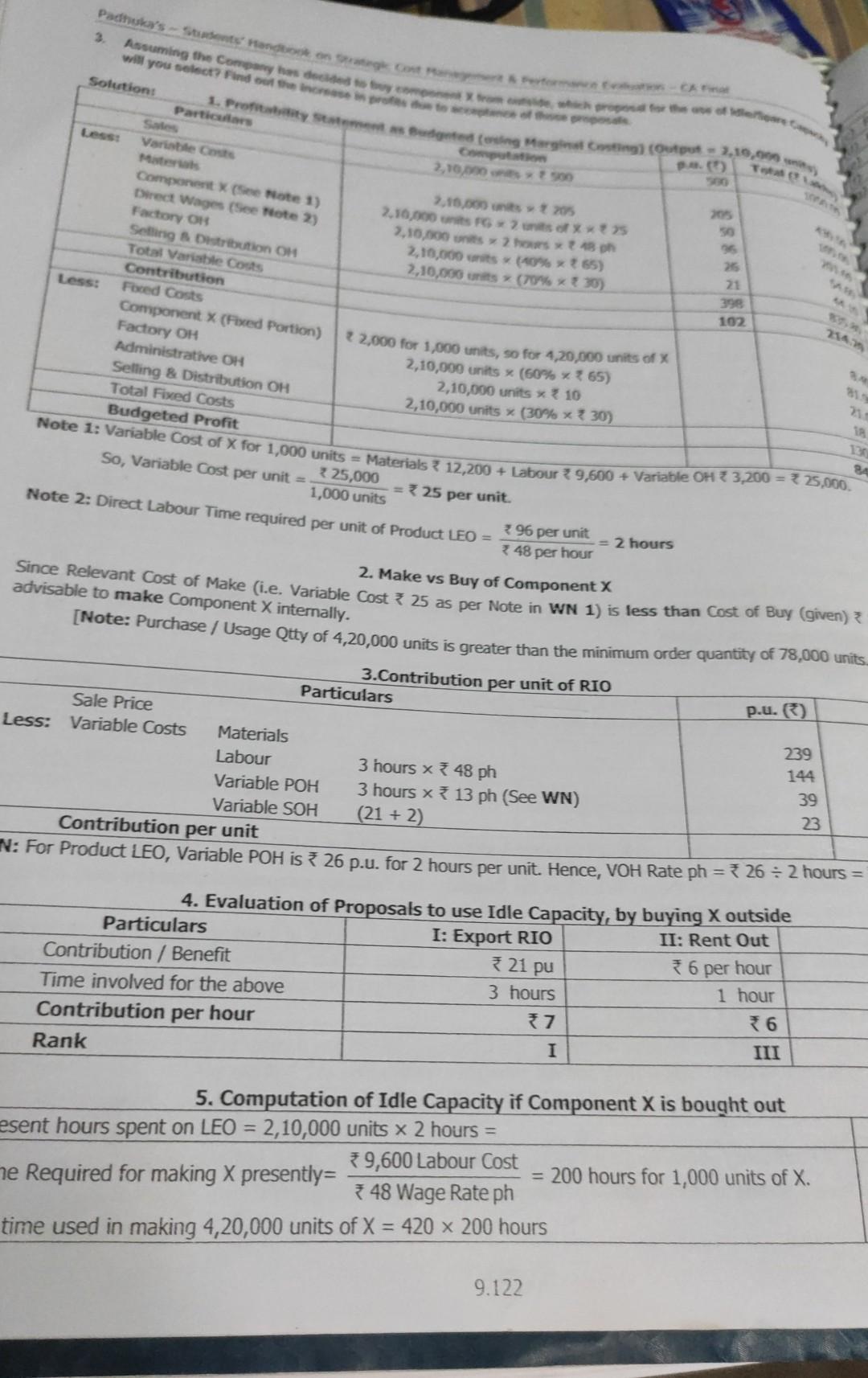
Colgate Product Note: Since the Normal Time Labour cost has already been considered in the computation of Sants per the 3. Hect of overtime work on the norther Parties (a) SW made ang Normal Time (1) Effect of Ovestme proof No Cost Labour Department Lab Department (c) Savings per unit, made in Overtime Premium is the only incremental cost and is hence relevant Observation based on effect of Overtime Work: 1. buy. There is a saving of 460 and 1.60 per unit, on own production 2. Overtime Work: The effect of overtime work differs for the products as under 26 12750 1.0 2.90 6 Normal Time Work: Both products P and Q can be produced during normal time as cost of me Product P can be produced during Overtime Work, either in Department A or Department B or in both. The be a saving Product can be produced during Overtime work, either in Department A anly (saving of 2014 Department B only (saving of 0.40), but noe in both the overtime work is required in both departner Product Q, it is better to sub-contract the same. Pro 18166 35.33 e *8.00 peso 4. Computation of Ranking Priority (Savings per Labour Hour in Departments A and 3) Particulars (a) Savings per unit, if made during normal time Product P (b) Hours required in Department A 4.60 (c) Savings per hour in Department A = (a + b) *6/60 hours (d) Ranking for production in Department A * 46 per hour (e) Hours required in Department B 1 (Savings per hour in Department B = (a +e) 12/60 hours (9) Ranking for production in Department B 23 per hour 1 Note: Since ranking priorities on the Key Factors are the same, the solution can be obtained as given below. In case differing priorities on Multiple Key Factors, Linear Programming Techniques may be used for resource allocation 5. Key Factor Allocation and Production Decision Particulars Department A Departments (a) Normal Time Available 600 hours (b) Possible Overtime at 50% 300 hours (c) Total Time Available (a + b) 900 hours Time Allocation: (see Table below) Hours Utilised Hours Used Stage 1: Make - Normal Time P = 2500 units 2500 x 6/60 = 250 hours 2500x12/60 = 500 hours Stage 2: Make - Normal Time Q= 100 units 100 x 18/60 = 30 hours (bal.fig.) = 20 hour 1067x 12160 = 213 hou Stage 3: Make - Overtime in B Q= 1067 units (bal. fig.) = 320 hours Stage 4: Sub-contract Q = 833 units No further production possible since OT is involved in be Depts. A and B which is not economic 520 hours 260 hours 780 hours Stage Explanation Product P has maximum preference for own production. Hence it will be produced first. Time utilised there 1 250 hours and 500 hours of Normal Time in A and B. Balance time left will be 350 hours in Department Aan hours in Department B. Least Normal Time available is 20 hours in Department B. This will be utilised in production of Q. equivalent 2 12/60 hours = 100 units. This will utilise 100 units x 18/60 = 30 hours in Department A. Balance Normal Time is 320 hours in Department A. This will be utilised in production of Q. equal to 320 hours = 1067 units. This will utilise 1067 x 12/60 = 213 hours (in Overtime) in Dept B. Since this is wi 3 permissible overtime limit of 260 hours, this production is feasible. [Note: If available overtime is less hours, production of Q will be restricted to that level.] 9.134 11.8 Key Factor - Makes Buy - Second Worstwo Cost, Market Price for the components wider information are given Padhuka's - Students and Strategoston CA Final A machine manufacturing Company for the compensated from the * More 150 120 an 30 180 400 Number of units required Following Figures in per writ 3.000 2.000 Direct Material Direct Wages 120 1.00 13 Direct Expenses at 46 per Machine Hout 50 Fixed Cost 50 36 Total Cost 40 40 Market Price 300 320 There are constraints on machine time in manufacturing all the components. Total Machine Hours available is only 12.79 300 320 279 It is possible to use the machine time in a Second Shift which will attract 20% Extra Wages and other Fixed OH every 1,000 hours or part thereof. With relevant supporting figures, advise the best course of action to maximize the profits. (Note: Students need not work out the complete profitability statement). Solution: Particulars 1. Time Allocation in I Shift B (a) Number of Units 2,000 units 3,00 3,000 units 3,500 units (6) Market Price = Cost of Buy 400 300 320 (c) Variable Costs if made internally Direct Materials 150 120 140 Direct Wages 120 80 60 Direct Expenses 80 80 60 Variable Costs of Make 350 280 260 (0) Savings in Own Make p.u. (b-c) 50 40 40 (e) Machine Hours required p.u. 80 80 = 2.00 = 2.00 40 40 25 ( Savings per machine hour, if made 20 26.67 II (9) Rank (for own production) III I 2,000 x 2 = (h) Allocation of 12,000 m/c hours (12,000 - 5,250 -- 4,000) 3,500 x 1.5 = 4,000 hours = 2,750 hours 5,250 hours 2,000 units (i) Possible Prodn in I Shift (h: e) 1,375 units 3,500 units Nil Nil 6) Balance quantity required (a - i) 1,625 units Note: It is preferable to buy Component D since Cost of Buying is less than Variable Cost of Own Productic 60 = 1.50 40 2. Effect of Second Shift Working (a) Time required in II Shift for Component A = (3,000 - 1,375) units at 2 hours p.u. (b) Incremental Fixed Costs = 76,000 x 4 = (C) Revised Savings p.u. in own make considering 20% Extra Wages = 40 - 20% of 60 d) Revised Total Savings for II Shift Production of (3,000 - 1,375) = 1,625 units As the Total Savings for II Shift Production is more than the Incremental Fixed Costs, II Shift is wort 1.9 Key Factor - Make vs Buy - Differential Ranking Ltd manufactures and sells a range of sports goods. Management is considering a proposal for a which would cost the Company 3,00,000. The Marketing Department has put forward the follow udgets for the following year -- 9.128 Padhuka's - Sentando conto Assuming the Company will you select Find the Inc Solutions Particular Sale Less Varble Cut 1. Proty Studentin Marging (output 2.19,90 pa 2,19,00 500 2.15.000 205 2,10,000 ofxx25 7,10,000 2 hours 48h 2,10,000 its (40% +65) 2,10,000 units (70% x 30) so Less: Component See Note 1) Direct Wages (See Note 2) Factory ON Setting & Distribution OH Total Variable costs Contribution Fixed Costs Component X (Fixed Portion) Factory OH Administrative OH Selling & Distribution OH Total Fixed Costs Budgeted Profit 25 21 398 102 22,000 for 1,000 units, so for 4,20,000 units of 2,10,000 units x (50% x 765) 2,10,000 units x 10 2,10,000 units X (30% x 30) 21 Note 1: Variable Cost of X for 1,000 units = Materials 3 12,200 + Labour 39,600 + Variable OH 3,200 = 325,000. 12 So, Variable Cost per unit = 225,000 = 325 per unit. 1,000 units Note 2: Direct Labour Time required per unit of Product LEO = 396 per unit 348 per hour = 2 hours P.u. ) Since Relevant Cost of Make (i.e. Variable cost * 25 as per Note in WN 1) is less than cost of Buy (given)? 2. Make vs Buy of Component X advisable to make Component X internally. [Note: Purchase / Usage Qtty of 4,20,000 units is greater than the minimum order quantity of 78,000 units. 3.Contribution per unit of RIO Particulars Sale Price Less: Variable Costs Materials 239 Labour 3 hours x 48 ph 144 Variable POH 3 hours x 13 ph (See WN) 39 Variable SOH (21 + 2) 23 Contribution per unit N: For Product LEO, Variable POH is 326 p.u. for 2 hours per unit. Hence, VOH Rate ph = 3 26 = 2 hours = 4. Evaluation of Proposals to use Idle Capacity, by buying X outside Particulars I: Export RIO II: Rent Out Contribution / Benefit 6 per hour Time involved for the above 3 hours 1 hour Contribution per hour 77 6 Rank I 321 pu III 5. Computation of Idle Capacity if Component X is bought out esent hours spent on LEO = 2,10,000 units x 2 hours = ne Required for making X presently= 79,600 Labour Cost = 200 hours for 1,000 units of X. * 48 Wage Rate ph time used in making 4,20,000 units of X = 420 x 200 hours 9.122Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


