Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Old MathJax webview Project note on all question is full Target Contados con New Singh Target Poft 15% on Cost, 15/115 on SP = 3.25
Old MathJax webview
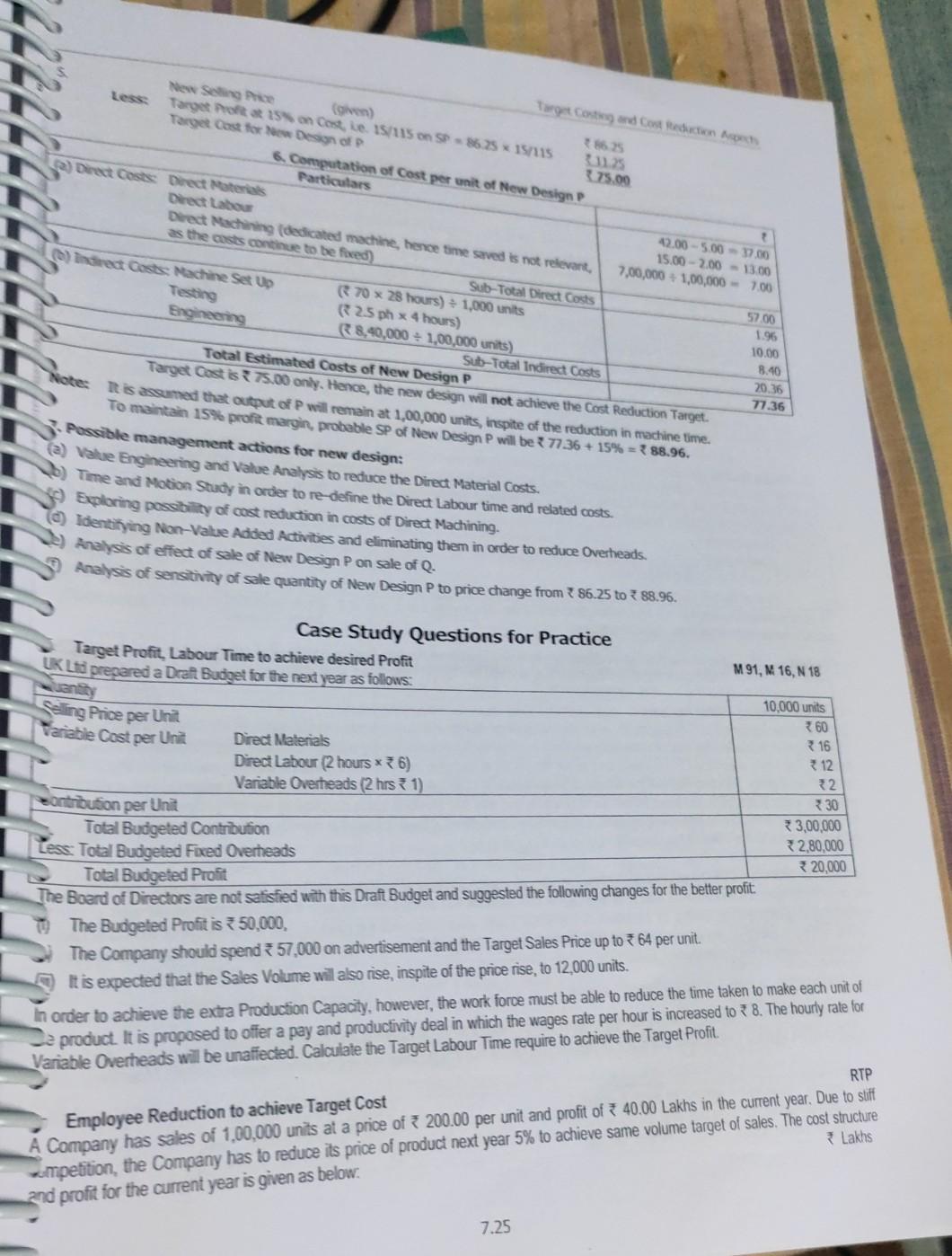


Project note on all
question is full
Target Contados con New Singh Target Poft 15% on Cost, 15/115 on SP = 3.25 157115 Target Cost for New Design 375.00 6. Computation of Cost per unit of New Design Particulars a) Direct Costs Direct Materials 42.00 -5.00 - 17.00 Direct labour 15.00 -2.00 - 13.00 Direct Machining (dedicated machine, hence time saved is not relevant, 7,00,000 + 1,00,000 - 700 as the costs continue to be forced) Sub-Total Direct Costs (0) Indirect Costs Machine Set Up 70 x 28 hours) 1,000 units Testing 25 ph x 4 hours) 10.00 Engineering R8,40,000 = 1,00,000 units) Sub-Total Indirect Costs Total Estimated Costs of New Design P Target Costis 75.00 only. Hence, the new design will not achieve the Cost Reduction Target Note Ris assumed that output of P will remain at 1,00,000 units, inspite of the reduction in machine time. To maintain 15% profit margin, probable SP of New Design P will be 77.36 + 15% = 88.96. Possible management actions for new design: a) Value Engineering and Value Analysis to reduce the Direct Material Costs. 5) Time and Motion Study in order to re-define the Direct Labour time and related costs. D) Exploring possibility of cost reduction in costs of Direct Machining. 57.00 1.96 8.40 20.36 77.36 identifying Non-Value Added Activities and eliminating them in order to reduce Overheads. Analysis of effect of sale of New Design P on sale of Q. Analysis of senstivity of sale quantity of New Design P to price change from 86.25 to 88.96. M 91, M. 16, N 18 Case Study Questions for Practice Target Profit, Labour Time to achieve desired Profit UK Lis prepared a Draft Bugget for the next year as follows: uenity Seling Price per Unit Variable Cost per Unit Direct Materials Direct Labour (2 hours *36) Variable Overheads (2 hrs 1) 10,000 units 360 16 12 contribution per Unit 2. *30 Total Budgeted Contribution 3,00,000 Less: Total Budgeted Fixed Overheads 32,80,000 Total Budgeted Profit 20,000 The Board of Directors are not satisfied with this Draft Budget and suggested the following changes for the better profit. The Budgeted Profit is 750,000, The Company should spend 57,000 on advertisement and the Target Sales Price up to 64 per unit. It is expected that the Sales Volume will also rise, inspite of the price rise, to 12,000 units. In order to achieve the extra Production Capacity, however, the work force must be able to reduce the time taken to make each unit of product. It is proposed to offer a pay and productivity deal in which the wages rate per hour is increased to 38. The hourly rate for Variable Overheads will be unaffected. Calculate the Target Labour Time require to achieve the Target Profit. RTP Employee Reduction to achieve Target Cost A Company has sales of 1,00,000 units at a price of 200.00 per unit and profit of 40.00 Lakhs in the current year. Due to stuff Lakhs wompetition, the Company has to reduce its price of product next year 5% to achieve same volume target of sales. The cost structure and profit for the current year is given as below. 7.25 Padhuka's - Students' Handbook on Strategic Cost Management & Performance Evaluation - CA Final anoner: Produd N Note 1: In the Growth Stage, the Firm will maintain prices at high levels, in order to realise maximum profits, Price Reduction will not be undertaken unless - (a) the low prices will lead to market penetration, (b) the Firm has sufficient production capacity to absorb the increased sales volume, and (c) Competitors enter the market. Note 2: Sometimes, the above broad stages may be sub-classified into sub stages as under - 1. Market Research 4. Prototype Manufacture 8. Selling 2. Design Specification 5. Development 9. Distribution 3. Design 6. Tooling 10. Product Support 7. Manufacture 11. Decommissioning or Replacement Concep Rao MATURITY GROWTH SALES DECLINE Rs. INTRODUCTION TIME RTP Answer Valid Valid Invalid Concept Illustration: Examine the validity of the following statements under Life Cycle Costing - Statement 1. In the Introduction Stage, usual marketing strategy is to strengthen the Supply Chain Relationships to make the product easily accessible by target customers. 2 In the Introduction Stage, Competitors will purchase the product to carry out Reverse Engineering and understand how the product works, so that they can develop the own similar, but different product. 3. In the Introduction Phase, the Firm will seek to avoid this competition by maintaining its Selling Price at the end of the Introductory Stage. 4. in the Growth Stage, if the product cannot be differentiated in other ways, the Firm may need further reduction in Selling Price to maintain growth. 5. In the Maturity Stage, Firms are tempted to engage in costly promotional price wars to wean away market share from Competitors. 6. In the Decline Stage, falling Sales may induce Firms to slash marketing expenditure. Brand Loyalty will be exploited to create profits. 7. The Concept of Product Life Cycle is applicable only for well-established products. Valid Valid Valid Invalid Concept Illustration: A Company's four products, M, N,O & P are in the market. Identify the phase of Product Life Cycle for each product with brief reasons. N 10 1. M: There is a lot of competition. Quantity sold has been increasing at 10%, 8% and 7% in the last 3 years. 2. N: Until last year, N had no competition. Suddenly the company finds 4 new products very similar to N in the market. However, N continues to have good sales. 3. 0: There is intense competition. Achieving targeted sales is becoming increasingly difficult. Hence the Company is introducing slightly modified features in the market. 4. P: Huge Inventory of P is available. P is being sold but there are many products in the market which are priced lesser than P, but have the same utility as P. 8.2 Padhuka's - Students' Handbook on Strategic Cost Management & Performance Evaluation - CA Final Beer Ded Maturity Introduction Long Run Aspect Growth Product Extensions & Add-ons, Service, Warranty features, Control over Product Quality to ensure customer satisfaction Brand Diversification, More Models & Versions, Improved Features Decline Phasing out weak products at lower prices Use this as Replacement Product for a new one. Uited Product Product Strategies Basic Product only - No product refinements or add- ons sbene Review Engine PLC a . Customer Strategies b) . on Acquisition of Customers, Motivating Product Trials, Focus on Customers who are most ready to buy. Create Product / Brand Awareness and Visibility, Inform Product Features, Inform Dealers/Customers a Adver- tising Suategies . Customer Retention, Preserve Loyalty of Repeat Purchases, existing customers and Preserve Loyalty of switch-over encourage existing customers for Building Brand Loyalty from Competitors. next product version Create Product Conviction, Focus Create interest in the core Brand Maintain hard product in the mass Quality & Benefits, etc. Differences Superior loyalty of customers for next product version market, Create Brand identity Extensive Expanding Supply Distri- Selective Distribution, bution, Chain Relationships, Close down Make product more Higher Incentives unprofitable distribution to to Dealers, available & visible. outlets / channels handle competition Reduce al Leveraging the products Incentives for - Promotional Expenses, "perceived" differen- Brand Switching, and spend only for tiation advantages for Higher buying from reducing inventory securing market position loyal customers, etc. levels. . Distri bution Strategies Selective Distribution to Focus Group Customers who are Early Adopters Establish Channels and Supply Chain Relationships Heavy Sales Promotion, Free Trials to Customers, Sale or Return Offers, Motivating Distributors to promote the Brand Promotion Strategies 8.5 Life Cycle Costing 1. Life Cyde Costing, aims at cost ascertainment of a product, project, etc. over its projected life. 2. It is a system that tracks and accumulates the actual costs and revenues attributable to cost object (i.e, product) from its inception to its abandonment. 3. Sometimes the terms, "cradle-to-grave costing" and "womb-to-tomb costing convey the meaning of fully capturing all costs associated with the product from its initial to final stages. 8.6 Importance of Life Cycie Costing Product Life Cyde Costing (PLC Costing) is considered important due to the following reasons- 1. Time based analysis: PLC Costing involves tracing of costs and revenues of each product over several calendar periods throughout their PLC. Costs and revenues can be analysed by time periods. The total magnitude of costs for each individual product can be reported and compared with product revenues generated in various time periods. 2. Overall Cost Analysis: Production Costs are accounted and recognised by the routine accounting system. However non-production costs like R&D, Design, Marketing, Distribution, Customer Service, etc. are less visible on a product-by product basis. PLC Costing focusses on recognising both production and non-production costs. 3. Pre-Production Costs Analysis: The development period for R&D and Design is long and costly. A high percentag of Total Product Costs may be incurred before commercial production begins. Hence, the Company needs accura information on such costs for deciding whether to continue with the R&D or not. 4. Effective Pricing Decisions: Pricing Decisions, in order to be effective, should include market considerations on one hand and cost considerations on the other. PLC Costing and Target Costing help analyse both these considerati and arrive at optimal price decisions. 8.4Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


