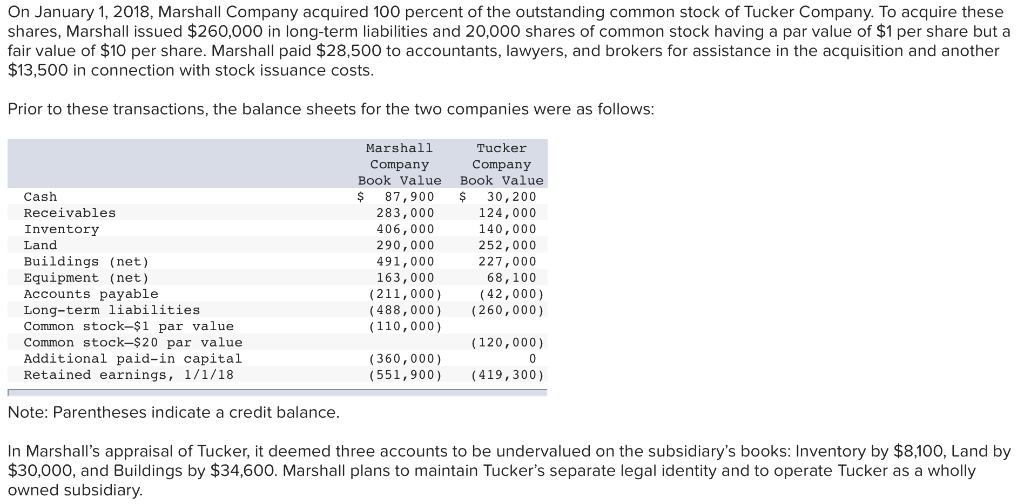

On January 1, 2018, Marshall Company acquired 100 percent of the outstanding common stock of Tucker Company. To acquire these shares, Marshall issued $260,000 in long-term liabilities and 20,000 shares of common stock having a par value of $1 per share but a fair value of $10 per share. Marshall paid $28,500 to accountants, lawyers, and brokers for assistance in the acquisition and another $13,500 in connection with stock issuance costs Prior to these transactions, the balance sheets for the two companies were as follows Marshall Company Tucker Company Book Value Book Value Cash Receivables Inventory Land Buildings (net) Equipment (net) Accounts payable Long-term liabilities Common stock-$1 par value Common stock-$20 par value Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings, 1/1/18 $ 87,900 $ 30,200 124,000 140,000 252,000 227,000 68,100 283,000 406, 000 290,000 491,000 163,000 (211,000) 42,000) (488,000) (260,000) (120, 000) (551,900) (419,300) (110,000) (360,000) Note: Parentheses indicate a credit balance In Marshall's appraisal of Tucker, it deemed three accounts to be undervalued on the subsidiary's books: Inventory by $8,100, Land by $30,000, and Buildings by $34,600. Marshall plans to maintain Tucker's separate legal identity and to operate Tucker as a wholly owned subsidiary a. Determine the amounts that Marshall Company would report in its postacquisition balance sheet. In preparing the postacquisition balance sheet, any required adjustments to income accounts from the acquisition should be closed to Marshall's retained earnings Other accounts will also need to be added or adjusted to reflect the journal entries Marshall prepared in recording the acquisition b. To verify the answers found in part (a), prepare a worksheet to consolidate the balance sheets of these two companies as of January 1, 2018. Consolidated Totals Cash Receivables Inventory Land Buildings (net) Equipment (net) 0 Total assets Accounts payable Long-term liabilities Common stock Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings Total liabilities and equities $ 0 MARSHALL COMPANY AND CONSOLIDATED SUBSIDIARY Worksheet January 1, 2018 Consolidation Entries Marshall Company Tucker Company Consolidated Totals Accounts Debit Credit Cash Receivables Inventory Land Buildings (net) Equipment (net) Investment in Tucker 0 Total assets Accounts payable Long-term liabilities Common stock Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings, 1/1/18 Total liabilities and owners' equities $ 0










