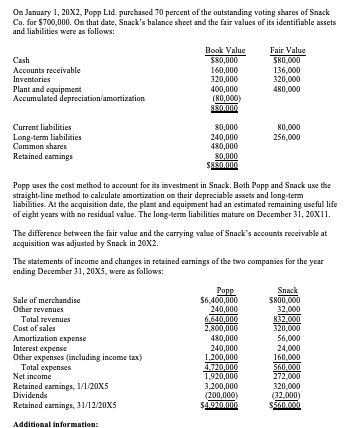

On January 1, 20X2, Popp Ltd. purchased 70 percent of the outstanding voting shares of Snack Co. for $700,000. On that date, Snack's balance sheet and the fair values of its identifiable assets and liabilities were as follows: Book Value Fair Value Cash $80,000 $80,000 Accounts receivable 160,000 136,000 Inventories 320,000 320,000 Plant and equipment 400,000 480,000 Accumulated depreciation/amortization (80,000) 880.000 Current liabilities 80,000 80.000 Long-term liabilities 240,000 256,000 Common shares 480,000 Retained earnings 80,000 $880.000 Popp uses the cost method to account for its investment in Snack. Both Popp and Snack use the straight-line method to calculate amortization on their depreciable assets and long-term liabilities. At the acquisition date, the plant and equipment had an estimated remaining useful life of eight years with no residual value. The long-term liabilities mature on December 31, 20x11. The difference between the fair value and the carrying value of Snack's accounts receivable at acquisition was adjusted by Snack in 20x2. The statements of income and changes in retained earnings of the two companies for the year ending December 31, 20X5, were as follows: Papp Snack Sale of merchandise $6,400,000 $800,000 Other revenues 240,000 32,000 Total revenues 6.640,000 Cost of sales 2,800,000 320,000 Amortization expense 480,000 56,000 Interest expense 240,000 24,000 Other expenses (including income tax) 1.200,000 160.000 Total expenses 4.720,000 560.000 Net income 1.920,000 272,000 Retained earnings, 1/1/20X5 3,200,000 320,000 Dividends (200,000) (32.000 Retained camings, 31/12/20X5 S4220.000 $560.000 Additional information: During 20x4, Snack sold merchandise that it had purchased for $80,000 to Papp for $120,000. None of this merchandise had been resold by Popp by December 31, 20X4. Popp had sales of $160,000 to Snack during 20X4, which produced a gross profit of 560,000. All of this inventory was resold by Snack during 20x4 for $188,000 During November 20X5, Snack sold merchandise that had been purchased for $160,000 to Popp for $240,000. All of this merchandise remained in the December 31, 20x5, inventories of Popp. During September 20X5, Popp had sales of $192,000 to Snack, which increased Popp's gross profit by $96,000. By December 31, 20X5, one-half of this merchandise had been sold to the public by Snack. On January 1, 20X5, Popp sold equipment to Snack for $29,000. Popp had originally acquired this equipment for $32,000. On January 1, 20X5, it had been amortized for six years of its estimated 10-year life. During 20X5, Popp charged Snack $40,000 for management fees. Goodwill impairment tests resulted in losses and were recorded as follows: 20X3: $4,000 20X4: $25,000 20x5: $8,000 Assume a 30 percent corporate tax rate. Required: Prepare a consolidated statement of income for the year ending December 31, 20Xs. b. Prepare a consolidated statement of changes in equity-retained earnings section for the year ending December 31, 20X5. Compute the balances that would appear in the consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 20X5, for the following accounts: i. goodwill non-controlling interest Be sure to show all supporting calculations, as partial arts may be awarded. On January 1, 20X2, Popp Ltd. purchased 70 percent of the outstanding voting shares of Snack Co. for $700,000. On that date, Snack's balance sheet and the fair values of its identifiable assets and liabilities were as follows: Book Value Fair Value Cash $80,000 $80,000 Accounts receivable 160,000 136,000 Inventories 320,000 320,000 Plant and equipment 400,000 480,000 Accumulated depreciation/amortization (80,000) 880.000 Current liabilities 80,000 80.000 Long-term liabilities 240,000 256,000 Common shares 480,000 Retained earnings 80,000 $880.000 Popp uses the cost method to account for its investment in Snack. Both Popp and Snack use the straight-line method to calculate amortization on their depreciable assets and long-term liabilities. At the acquisition date, the plant and equipment had an estimated remaining useful life of eight years with no residual value. The long-term liabilities mature on December 31, 20x11. The difference between the fair value and the carrying value of Snack's accounts receivable at acquisition was adjusted by Snack in 20x2. The statements of income and changes in retained earnings of the two companies for the year ending December 31, 20X5, were as follows: Papp Snack Sale of merchandise $6,400,000 $800,000 Other revenues 240,000 32,000 Total revenues 6.640,000 Cost of sales 2,800,000 320,000 Amortization expense 480,000 56,000 Interest expense 240,000 24,000 Other expenses (including income tax) 1.200,000 160.000 Total expenses 4.720,000 560.000 Net income 1.920,000 272,000 Retained earnings, 1/1/20X5 3,200,000 320,000 Dividends (200,000) (32.000 Retained camings, 31/12/20X5 S4220.000 $560.000 Additional information: During 20x4, Snack sold merchandise that it had purchased for $80,000 to Papp for $120,000. None of this merchandise had been resold by Popp by December 31, 20X4. Popp had sales of $160,000 to Snack during 20X4, which produced a gross profit of 560,000. All of this inventory was resold by Snack during 20x4 for $188,000 During November 20X5, Snack sold merchandise that had been purchased for $160,000 to Popp for $240,000. All of this merchandise remained in the December 31, 20x5, inventories of Popp. During September 20X5, Popp had sales of $192,000 to Snack, which increased Popp's gross profit by $96,000. By December 31, 20X5, one-half of this merchandise had been sold to the public by Snack. On January 1, 20X5, Popp sold equipment to Snack for $29,000. Popp had originally acquired this equipment for $32,000. On January 1, 20X5, it had been amortized for six years of its estimated 10-year life. During 20X5, Popp charged Snack $40,000 for management fees. Goodwill impairment tests resulted in losses and were recorded as follows: 20X3: $4,000 20X4: $25,000 20x5: $8,000 Assume a 30 percent corporate tax rate. Required: Prepare a consolidated statement of income for the year ending December 31, 20Xs. b. Prepare a consolidated statement of changes in equity-retained earnings section for the year ending December 31, 20X5. Compute the balances that would appear in the consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 20X5, for the following accounts: i. goodwill non-controlling interest Be sure to show all supporting calculations, as partial arts may be awarded








