Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
On January 1, Paisley, Inc., paid $560,000 for all of Skyler Corporation's outstanding stock. This cash payment was based on a price of $180 per
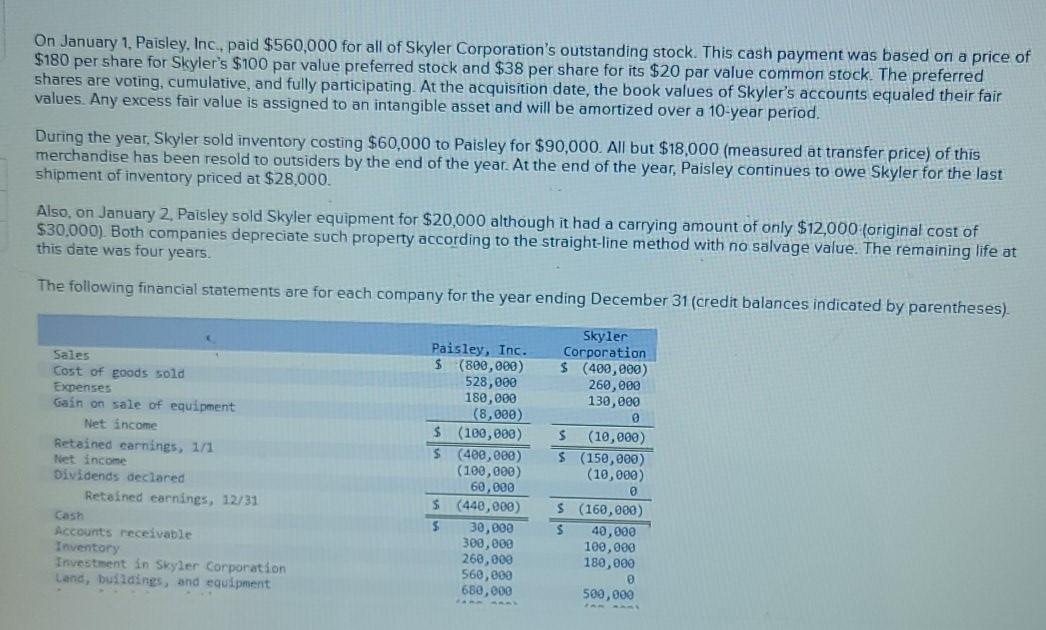
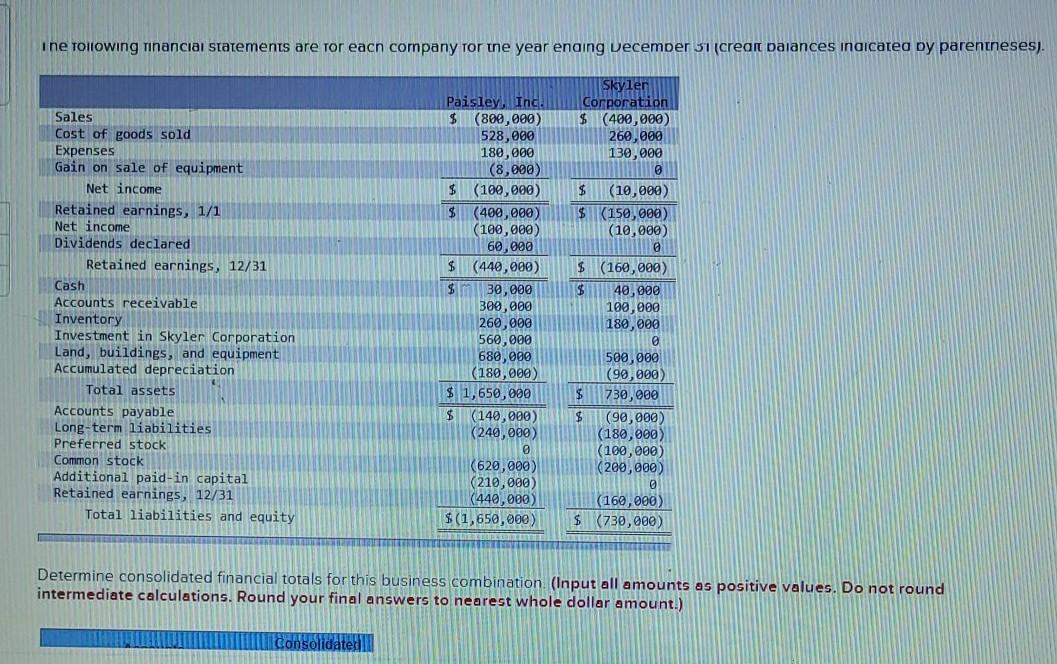
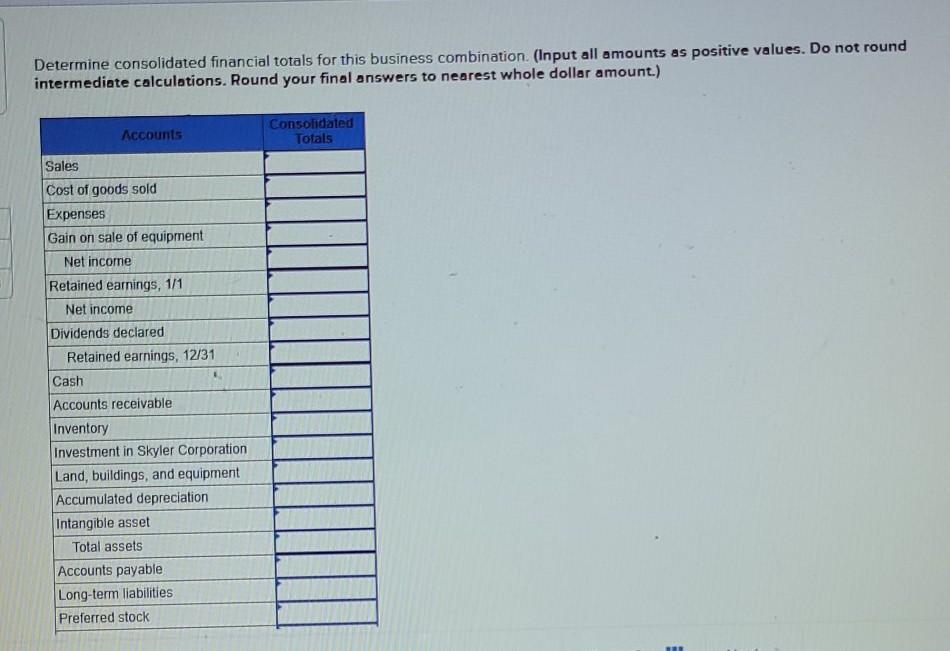
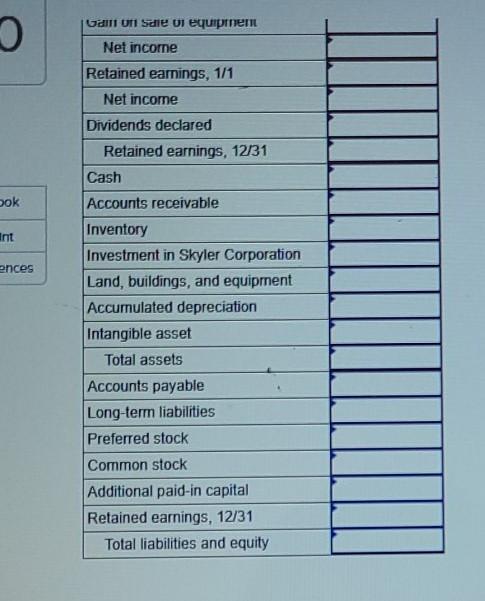
On January 1, Paisley, Inc., paid $560,000 for all of Skyler Corporation's outstanding stock. This cash payment was based on a price of $180 per share for Skyler's $100 par value preferred stock and $38 per share for its $20 par value common stock. The preferred shares are voting, cumulative, and fully participating. At the acquisition date, the book values of Skyler's accounts equaled their fair values. Any excess fair value is assigned to an intangible asset and will be amortized over a 10-year period. During the year, Skyler sold inventory costing $60,000 to Paisley for $90,000. All but $18,000 (measured at transfer price) of this merchandise has been resold to outsiders by the end of the year. At the end of the year, Paisley continues to owe Skyler for the last shipment of inventory priced at $28.000. Also, on January 2, Paisley sold Skyler equipment for $20,000 although it had a carrying amount of only $12,000 (original cost of $30,000). Both companies depreciate such property according to the straight-line method with no salvage value. The remaining life at this date was four years. The following financial statements are for each company for the year ending December 31 (credit balances indicated by parentheses). Skyler Corporation $ (400,000) 260,000 130,000 Sales Cost of goods sold Expenses Gain on sale of equipment Net income Retained earnings, 1/1 Net income Dividends declared Retained earnings, 12/31 Paisley, Inc. $(800,000) 528,000 180,000 (8,000) $ (100,000) 5 (480,000) (100,000) 60,000 $ (440,000) $ 30,800 300,000 268,000 560,000 680,000 $ (10,000) $ (150,000) (10,000) Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Investment in Skyler Corporation Land, buildings, and equipment $ (160,000) $ 40,000 100,000 180,000 500,000 i ne tollowing ninancial statements are for each company for the year enaing December 31 (creant balances indicated by parentheses). Sales Cost of goods sold Expenses Gain on sale of equipment Net income Retained earnings, 1/1 Net income Dividends declared Retained earnings, 12/31 Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Investment in Skyler Corporation Land, buildings, and equipment Accumulated depreciation Total assets Accounts payable Long-term liabilities Preferred stock Common stock Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings, 12/31 Total liabilities and equity Paisley Inc. $ (800,000) 528,000 180,000 (8,000) $ (100,000) $ (400,000) (100,000) 60,000 $ (440,000) $ 30,000 300,000 260,000 560,000 680,000 (180,000) $ 1,650,000 $ (140,000) (240,000) 0 (620,000) (210,000 (440,000) $(1,650,000) Skyler Corporation $ (400,000) 260,000 130,000 @ $ (10,000) $ 150,000) (10,000) a $ (160,000) $ 40,990 100,000 180,000 500,000 (90,000) 730,000 (90,000) (180,000) (100,000) (200,000) 0 (160,000) $ (730,000) Determine consolidated financial totals for this business combination (Input all amounts as positive values. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to nearest whole dollar amount.) consolidaterin Determine consolidated financial totals for this business combination (Input all amounts as positive values. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to nearest whole dollar amount.) Accounts Consolidated Totals Sales Cost of goods sold Expenses Gain on sale of equipment Net income Retained earnings, 1/1 Net income Dividends declared Retained earnings, 12/31 Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Investment in Skyler Corporation Land, buildings, and equipment Accumulated depreciation Intangible asset Total assets Accounts payable Long-term liabilities Preferred stock Gal uti Sale di equipmen Net income Retained earnings, 1/1 Net income Dividends declared Retained earnings, 12/31 Cash ok Accounts receivable int ences Inventory Investment in Skyler Corporation Land, buildings, and equipment Accumulated depreciation Intangible asset Total assets Accounts payable Long-term liabilities Preferred stock Common stock Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings, 12/31 Total liabilities and equity
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


