Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
On January 1,2024 , when its $30 par value common stock was selling for $80 per share, Windsor Corp. issued $10,800,000 of 8% convertible debentures
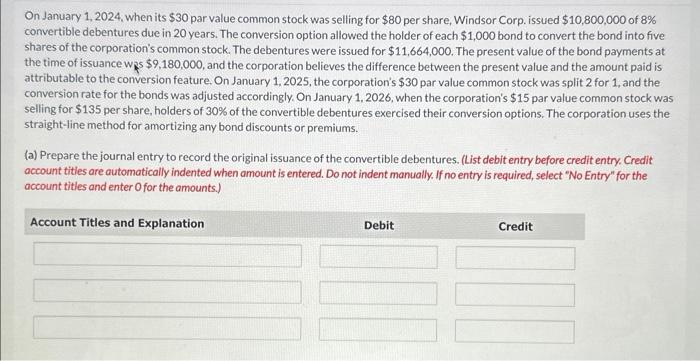
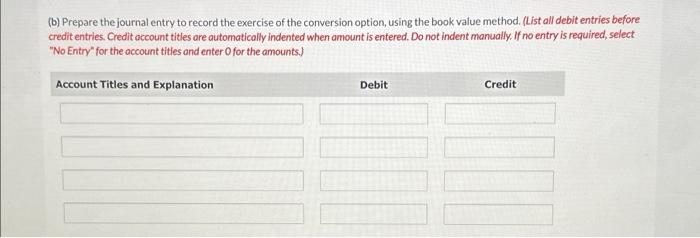
 On January 1,2024 , when its $30 par value common stock was selling for $80 per share, Windsor Corp. issued $10,800,000 of 8% convertible debentures due in 20 years. The conversion option allowed the holder of each $1,000 bond to convert the bond into five shares of the corporation's common stock. The debentures were issued for $11,664,000. The present value of the bond payments at the time of issuance ws $9,180,000, and the corporation believes the difference between the present value and the amount paid is attributable to the conversion feature. On January 1,2025, the corporation's $30 par value common stock was split 2 for 1 , and the conversion rate for the bonds was adjusted accordingly, On January 1, 2026, when the corporation's $15 par value common stock was selling for $135 per share, holders of 30% of the convertible debentures exercised their conversion options. The corporation uses the straight-line method for amortizing any bond discounts or premiums. (a) Prepare the journal entry to record the original issuance of the convertible debentures. (List debit entry before credit entry. Credit account tities are automatically indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter 0 for the amounts.) (b) Prepare the journal entry to record the exercise of the conversion option, using the book value method. (List all debit entries before credit entrles. Credit occount titles are automatically Indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the occount tities and enter O for the amounts.) Assistance Used Bond Conversion Expense Bond Interest Expense Bonds Payable Cash Compensation Expense Common Stock Convertible Preferred Stock Debt Conversion Expense Discount on Bonds Payable Income Summary Incremental Cash Insurance Expense Interest Expense Interest Payable Interest Receivable Liability under Stock Appreciation Plan No Entry Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par - Common Stock Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par - Preferred Stock Paid-in Capital-Expired Stock Options Paid-in Capital-Restricted Stock Units Paid-in Capital-Stock Options Paid-in Capital-Stock Warrants Premium on Bonds Payable Preferred Stock Retained Earnings Share Capital-Ordinary Share Premium-Conversion Equity Share Premium-Ordinary Share Premium-Share Options
On January 1,2024 , when its $30 par value common stock was selling for $80 per share, Windsor Corp. issued $10,800,000 of 8% convertible debentures due in 20 years. The conversion option allowed the holder of each $1,000 bond to convert the bond into five shares of the corporation's common stock. The debentures were issued for $11,664,000. The present value of the bond payments at the time of issuance ws $9,180,000, and the corporation believes the difference between the present value and the amount paid is attributable to the conversion feature. On January 1,2025, the corporation's $30 par value common stock was split 2 for 1 , and the conversion rate for the bonds was adjusted accordingly, On January 1, 2026, when the corporation's $15 par value common stock was selling for $135 per share, holders of 30% of the convertible debentures exercised their conversion options. The corporation uses the straight-line method for amortizing any bond discounts or premiums. (a) Prepare the journal entry to record the original issuance of the convertible debentures. (List debit entry before credit entry. Credit account tities are automatically indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter 0 for the amounts.) (b) Prepare the journal entry to record the exercise of the conversion option, using the book value method. (List all debit entries before credit entrles. Credit occount titles are automatically Indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the occount tities and enter O for the amounts.) Assistance Used Bond Conversion Expense Bond Interest Expense Bonds Payable Cash Compensation Expense Common Stock Convertible Preferred Stock Debt Conversion Expense Discount on Bonds Payable Income Summary Incremental Cash Insurance Expense Interest Expense Interest Payable Interest Receivable Liability under Stock Appreciation Plan No Entry Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par - Common Stock Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par - Preferred Stock Paid-in Capital-Expired Stock Options Paid-in Capital-Restricted Stock Units Paid-in Capital-Stock Options Paid-in Capital-Stock Warrants Premium on Bonds Payable Preferred Stock Retained Earnings Share Capital-Ordinary Share Premium-Conversion Equity Share Premium-Ordinary Share Premium-Share Options




Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


