Only do the ones that are blank or empty
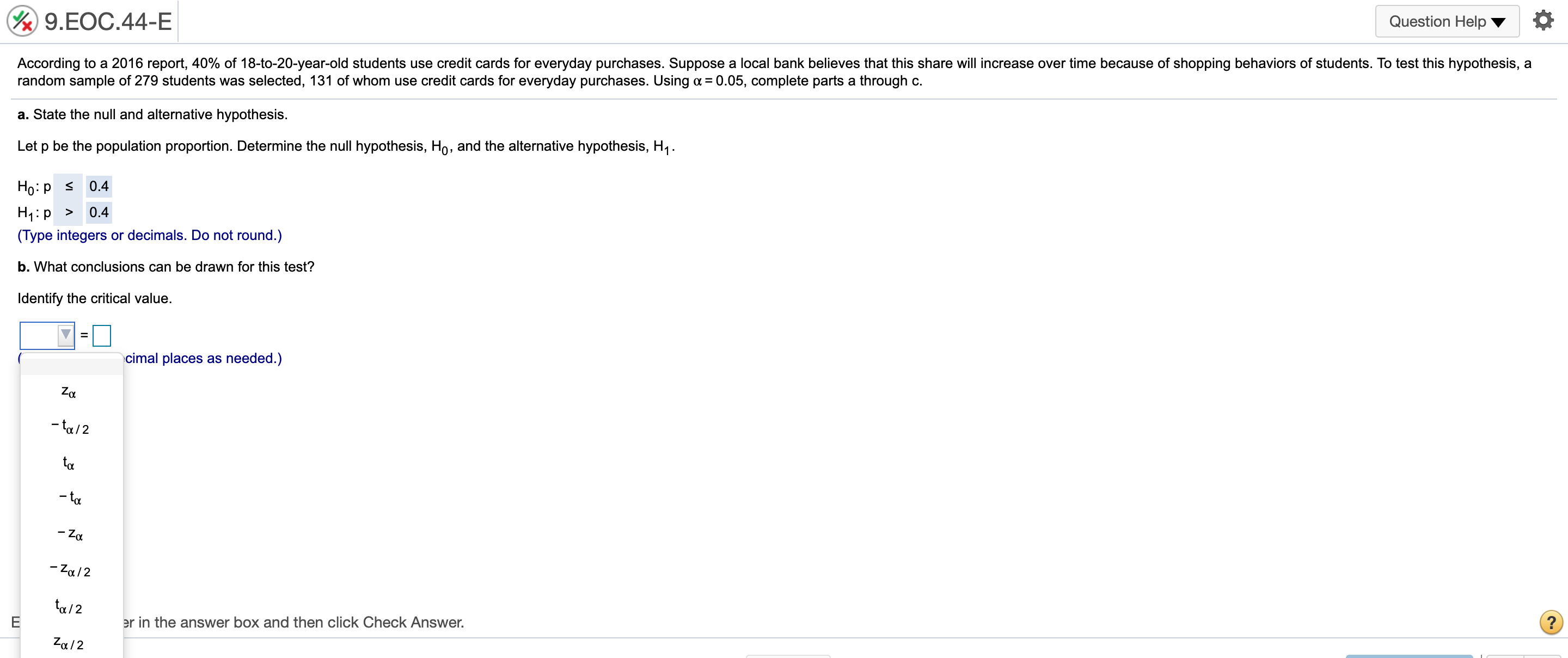
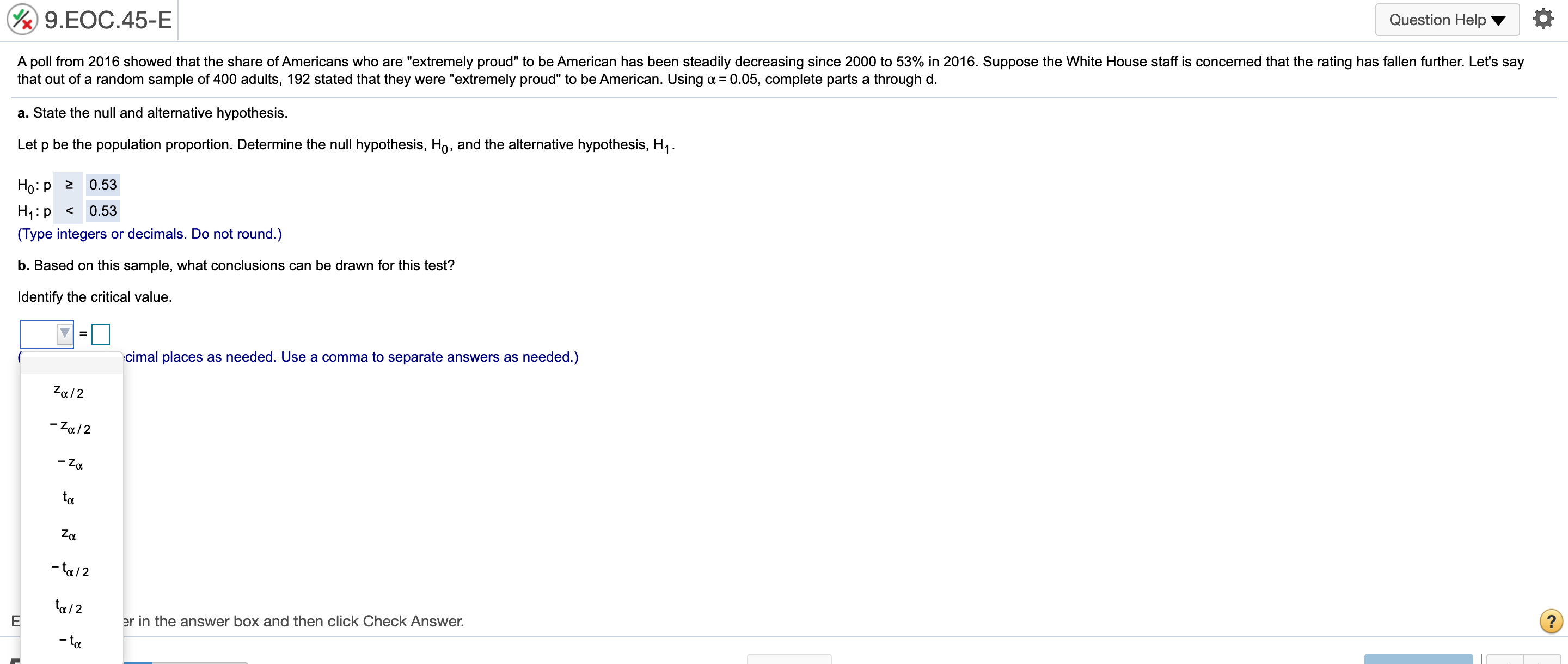
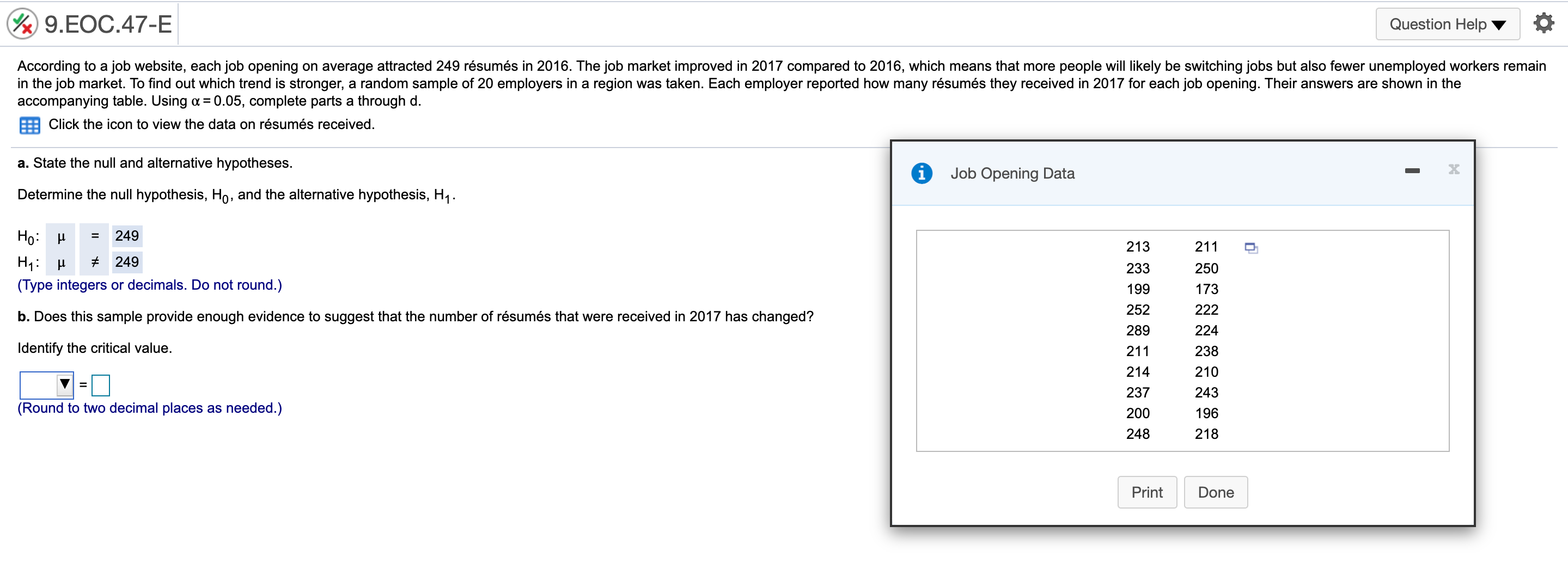
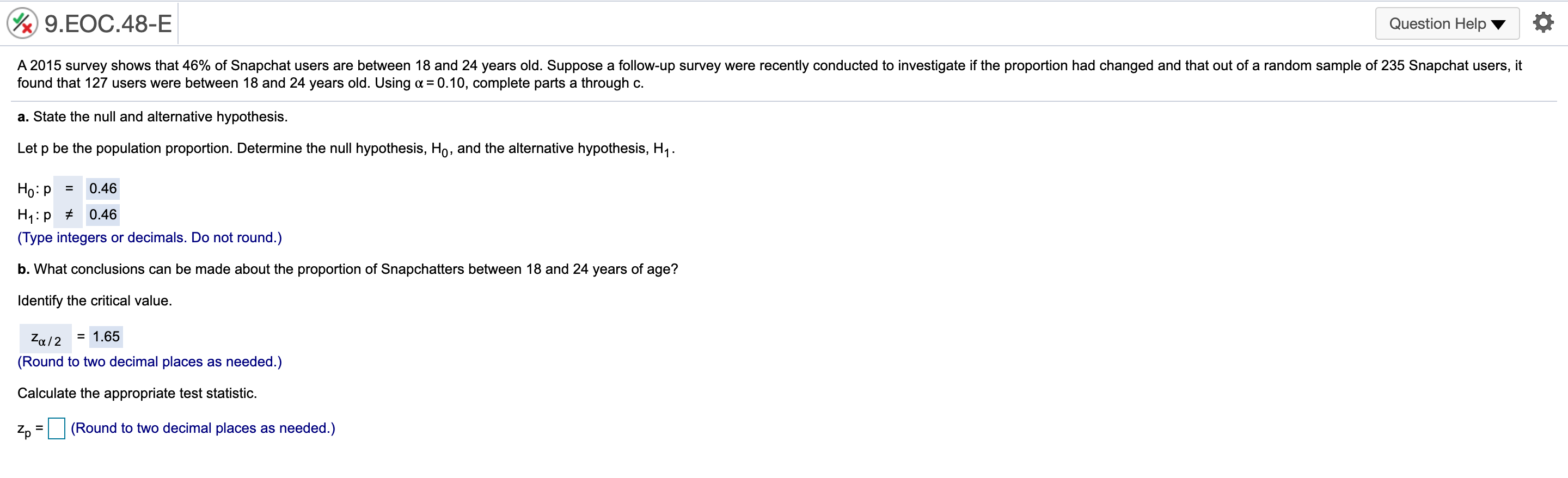
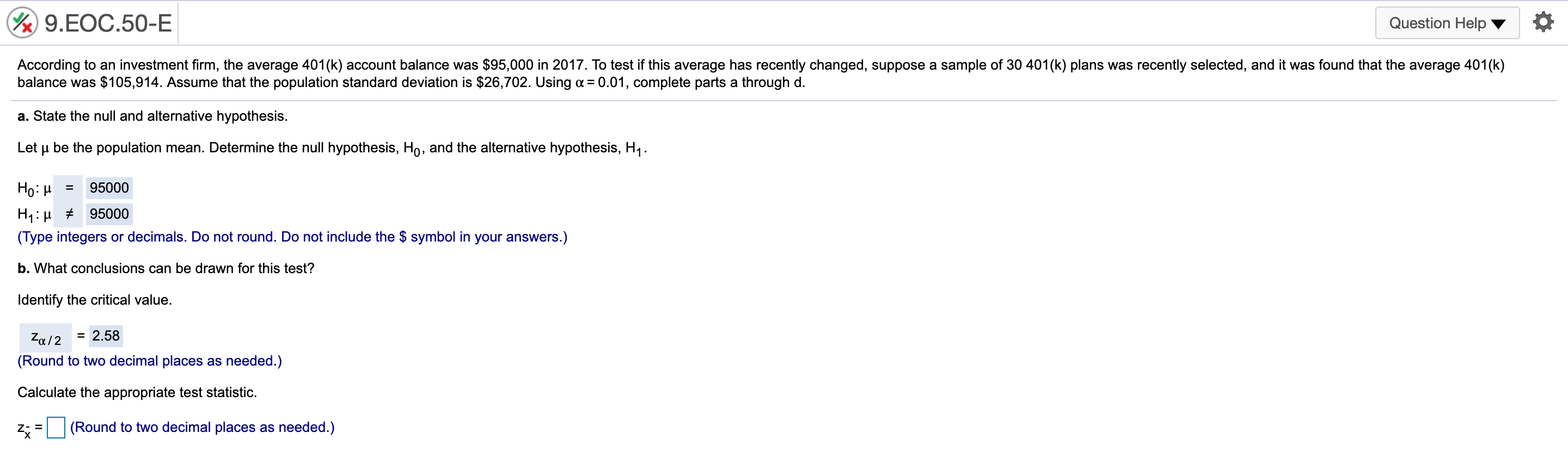
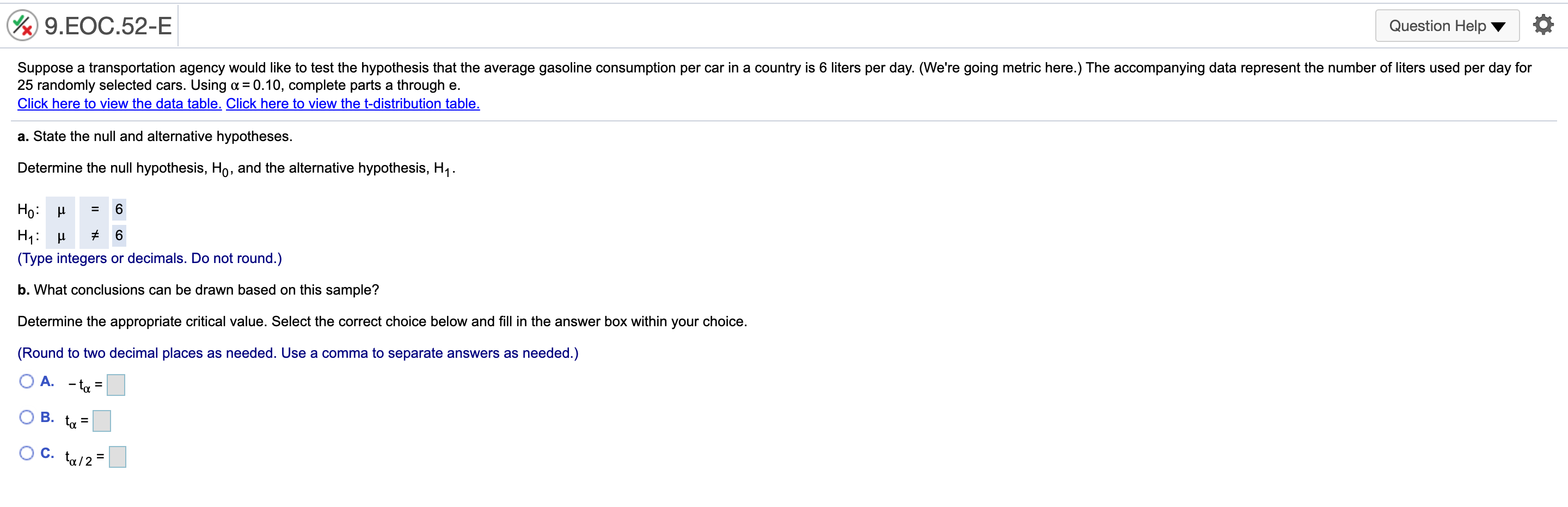
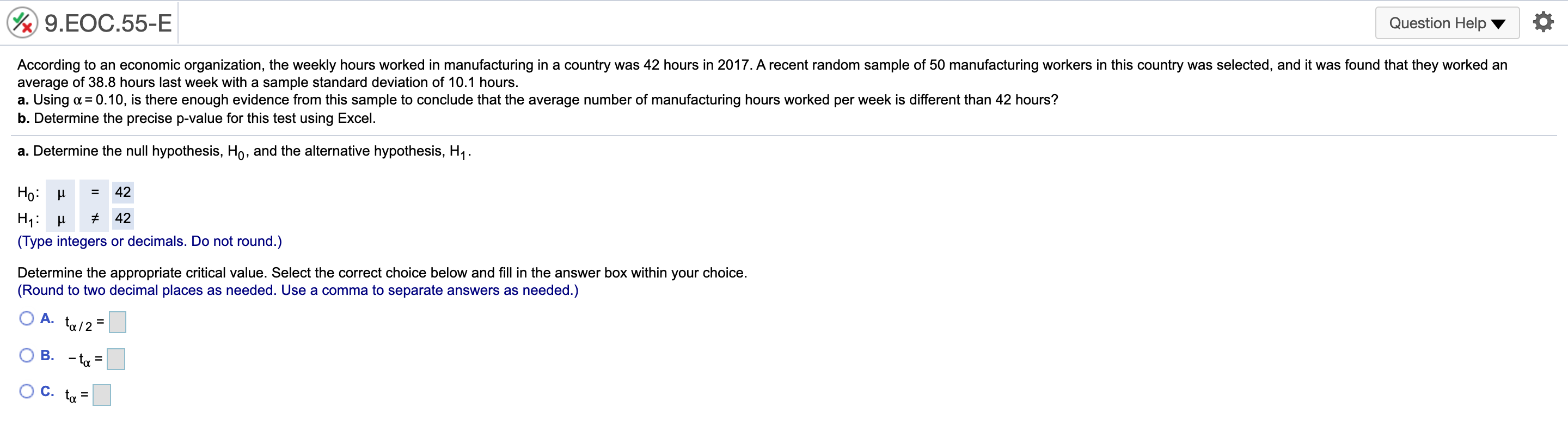
@ 9..EOC44-E Question Helpv '6 According to a 2016 report, 40% of 18-io-20-yearold students use credit cards for everyday purchases. Suppose a local bank believes that this share will increase over time because of shopping behaviors of students. To test this hypothesis, a random sample of 279 students was selected, 131 of Mom use credit cards for everyday purchases. Using ot= 0.05, complete parts a through c. a. State the null and alternative hypothesis. Let p be the population proportion. Determine the null hypothesis, H0, and the alternative hypothesis, H1. H0: p s 0.4 H1:p > 0.4 (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) b. What conclusions can be drawn for this test? Identify the critical value. V: ( vcimal places as needed.) '2': 'Zulz km E er in the answer box and then click Check Answer. ' Zu/Z ' @ 9..EOC45-E 1 Question HelpV a A poll from 2016 showed that the share of Americans who are "extremely proud" to be American has been steadily decreasing since 2000 to 53% in 2016. Suppose the White House staff is concerned that the rating has fallen further. Let's say that out of a random sample of 400 adults, 192 stated that they were "extremely proud\" to be American. Using a = 0.05, complete parts a through d. a. State the null and alternative hypothesis. Let p be the population proportion. Determine the null hypothesis, Ho, and the alternative hypothesis, H1. H0: p 2 0.53 H1: p 0.30 (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) h. Determine the p-value for this test and interpret its meaning. Identify the critical value. 2\" = 2.33 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Calculate the appropriate test statistic. zp = (Round to two decimal places as needed.) 9HE0655-E Question Help V a According to an economic organization, the weekly hours worked in manufacturing in a country was 42 hours in 2017. A recent random sample of 50 manufacturing workers in this country was selected, and it was found that they worked an average of 38.8 hours last week with a sample standard deviation of 10.1 hours. 3. Using u= 0.10, is there enough evidence from this sample to conclude that the average number of manufacturing hours worked per week is different than 42 hours? [1. Determine the precise p-value for this test using Excel. a. Determine the null hypothesis, Ho, and the alternative hypothesis, H1. Ho: [1 = 42 H1: p # 42 (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) Determine the appropriate critical value. Select the correct choice below and ll in the answer box within your choice, (Round to two decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) 0 A' tall = O B. 4\": O 0.1\": @ 9.EOC.58-E Question Help Y Q During 2016, the average monthly bill for digital cable in a country was $105. Suppose a cable company would like to test the hypothesis that the average monthly bill is higher than $105 this year. A random sample of 48 households was chosen. Assume the standard deviation of monthly cable bills in the country is $19. Complete parts a through d. Explain how a Type | enor can occur. Choose the correct answer below. A. The average monthly cable bill is greater than $105, but based on the sample it is incorrectly concluded that the average monthly cable bill is less than or equal to $105. 3 B. The average monthly cable bill is less than or equal to $105, but based on the sample it is incorrectly concluded that the average monthly cable bill is greater than $105. C. The average monthly cable bill has changed from $105, but based on the sample it is incorrectly concluded that the average monthly cable bill has not changed from $105. D. The average monthly cable bill is equal to $105, but based on the sample it is inconecy concluded that the average monthly cable bill has changed from $105. Explain how a Type II error can occur. Choose the correct answer below. A. The average monthly cable bill is equal to $105, but based on the sample it is incorrectly concluded that the average monthly cable bill has changed from $105. 3 B. The average monthly cable bill is greater than $105, but based on the sample it is incorrectly concluded that the average monthly cable bill is less than or equal to $105. C. The average monthly cable bill has changed from $105, but based on the sample it is incorrectly concluded that the average monthly cable bill has not changed from $105. D. The average monthly cable bill is less than or equal to $105, but based on the sample it is incorrectly concluded that the average monthly cable bill is greater than $105. b. Using a = 0,05, compute the probability of a Type II error occurring if the actual average monthly cable bill is $113. The probability is 0.102 . (Round to three decimal places as needed.) c. Using a: 0.10, compute the probability of a Type II error occurring if the actual average monthly cable bill is $113. The probability is . (Round to three decimal places as needed.) @ 9..EOC61-E Question HeIpV O According to a country's department of labor, 11.4% of the country's workforce was unionized in 2017. Suppose the department would like to test the hypothesis that the proportion of union workers decreased in 2018 by randomly sampling 177 employees. Complete parts a through d. Explain how a Type I error can occur. Choose the correct answer below. A. The percentage of unionized employees is less than 11.4%, but based on the sample it is incorrectly concluded that the percentage of unionized employees is not less than 11.4%. B. The percentage of unionized employees has changed from 11.4%, but based on the sample it is incorrectly concluded that the percentage of unionized employees has not changed from 11.4%, C. The percentage of unionized employees is equal to 11.4%, but based on the sample it is incorrectly concluded that the percentage of unionized employees has changed from 11.4%. s" D. The percentage of unionized employees is greater than or equal to 11.4%, but based on the sample iti incorrectly concluded that the percentage of unionized employees is less than 11.4%. Explain how a Type II error can occur. Choose the correct answer below. A. The percentage of unionized employees has changed from 11.4%, but based on the sample it is incorrectly concluded that the percentage of unionized employees has not changed from 11.4%, B. The percentage of unionized employees is greater than or equal to 11.4%, but based on the sample iti incorrectly concluded that the percentage of unionized employees is less than 11.4%. s" C. The percentage of unionized employees is less than 11.4%, but based on the sample it is incorrectly concluded that the percentage of unionized employees is not less than 114%. D The percentage of unionized employees is equal to 11.4%, but based on the sample it is incorrectly concluded that the percentage of unionized employees has changed from 11.4%. b. Using n: = 0,05, compute the probability of a Type II error occurring if the actual proportion of unionized employees in the workforce is 8%. The probability is 0.603 . (Round to three decimal places as needed.) c. Using 0:: 0.05, compute the probability of a Type II error occurring if the actual proportion of unionized employees in the workforce is 4%. The probability is . (Round to three decimal places as needed.)