Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Opgaver 1. .AAU ApS M-tech. (vgtning max. 12 %) AAU ApS, Manufactures BMWs and distributes them across Denmark. Part -2.500 ccm.-218 hp. (a motor)
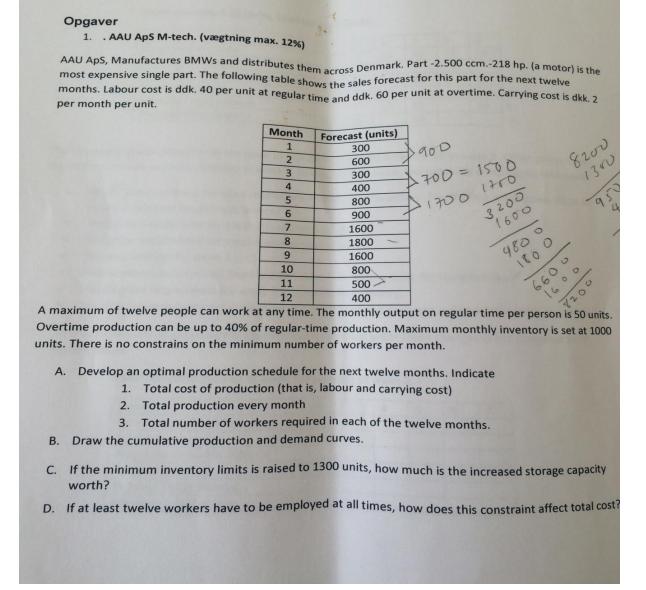
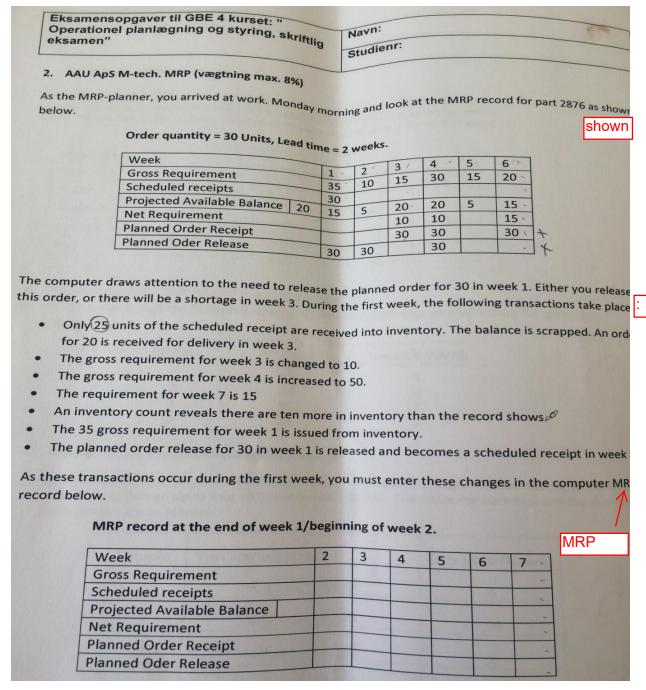
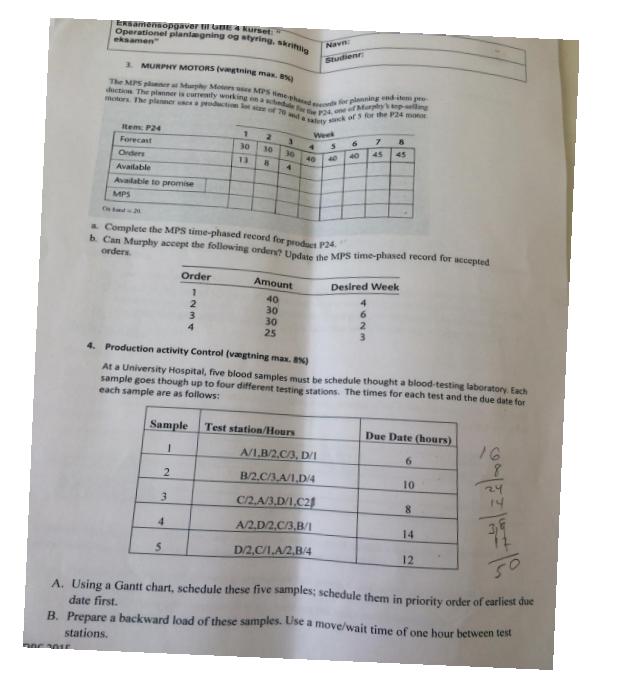

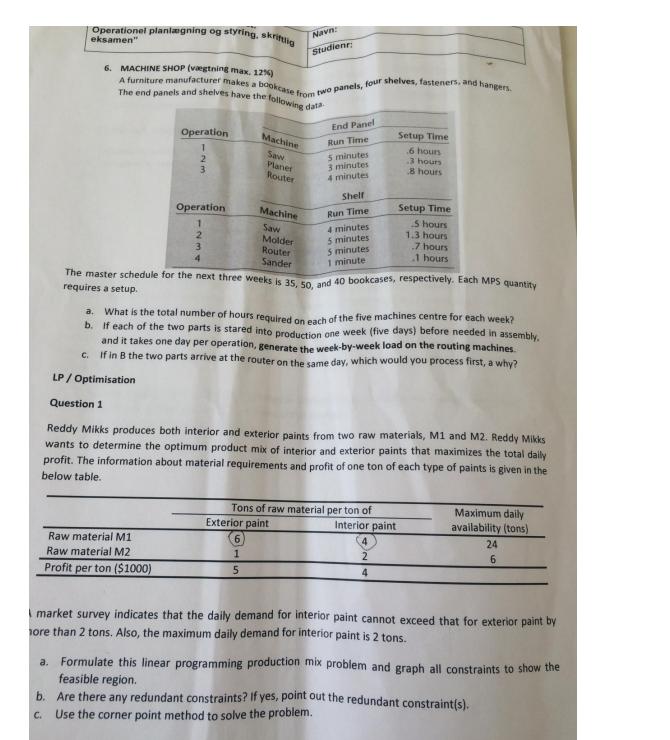


Opgaver 1. .AAU ApS M-tech. (vgtning max. 12 %) AAU ApS, Manufactures BMWs and distributes them across Denmark. Part -2.500 ccm.-218 hp. (a motor) is the most expensive single part. The following table shows the sales forecast for this part for the next twelve months. Labour cost is ddk. 40 per unit at regular time and ddk. 60 per unit at overtime. Carrying cost is dkk. 2 per month per unit. Month 1 Forecast (units) 300 600 300 400 800 900 1600 1800 1600 800 500 400 A maximum of twelve people can work at any time. The monthly output on regular time per person is 50 units. Overtime production can be up to 40% of regular-time production. Maximum monthly inventory is set at 1000 units. There is no constrains on the minimum number of workers per month. 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 90 D 700 = 1500 1700 1760 3200 1600 A. Develop an optimal production schedule for the next twelve months. Indicate 1. Total cost of production (that is, labour and carrying cost) B. Draw the cumulative production and demand curves. 2. Total production every month 3. Total number of workers required in each of the twelve months. 4800 Ito o 8200 1300 6600 1600 8200 95 C. If the minimum inventory limits is raised to 1300 units, how much is the increased storage capacity worth? D. If at least twelve workers have to be employed at all times, how does this constraint affect total cost? Eksamensopgaver til GBE 4 kurset: " Operationel planlgning og styring, skriftlig eksamen" 2. AAU APS M-tech. MRP (vgtning max. 8%) As the MRP-planner, you arrived at work. Monday morning and look at the MRP record for part 2876 as show below. shown . Order quantity 30 Units, Lead time 2 weeks. Week Gross Requirement Scheduled receipts Projected Available Balance Net Requirement Planned Order Receipt Planned Oder Release 20 1 35 30 15 Navn: Studienr: 30 Week Gross Requirement Scheduled receipts Projected Available Balance Net Requirement Planned Order Receipt Planned Oder Release 2 10 5 The gross requirement for week 4 is increased to 50. The requirement for week 7 is 15 30 2 31 3/ 15 20 10 30 3 MRP record at the end of week 1/beginning of week 2. 4 R 30 The computer draws attention to the need to release the planned order for 30 in week 1. Either you release this order, or there will be a shortage in week 3. During the first week, the following transactions take place 20 10 30 30 Only 25 units of the scheduled receipt are received into inventory. The balance is scrapped. An ord for 20 is received for delivery in week 3. The gross requirement for week 3 is changed to 10. 4 15 An inventory count reveals there are ten more in inventory than the record shows. The 35 gross requirement for week 1 is issued from inventory. The planned order release for 30 in week 1 is released and becomes a scheduled receipt in week As these transactions occur during the first week, you must enter these changes in the computer MR record below. 5 5 65 20 15 15 30 6 + X 7 MRP Examensopgaver til GBE 4 Kurset Operationel planlgning og styring, skriftlig eksamen DOC 2015 3. MURPHY MOTORS (vagtning max. 8) The MPS planner at Murphy Moters usee MPS time-phased e Motors The planner uses a production lot size of 70 wd a safety stack of 3 for the P24 duction The planner is currently working in a schedule to the P24, one of Morphy's top-selling for planning end-item pro Rem: P24 Forecast Orders Available Available to promise MPS On od 21 2 3 Order 1 2 4 3 5 1 30 13 4 2 10 8 & Complete the MPS time-phased record for product P24 b. Can Murphy accept the following orden? Update the MPS time-phased record for accepted orders. Desired Week 3 30 4 Sample Test station/Hours 1 Amount 40 30 30 25 Navn: Studien Week S 40 40 40 4. Production activity Control (vgtning max. 8%) At a University Hospital, five blood samples must be schedule thought a blood-testing laboratory. Each sample goes though up to four different testing stations. The times for each test and the due date for each sample are as follows: 6 7 45 A/1.8/2.C/3, D/1 B/2.C/3A/1,D/4 C/2A/3D/1.C2 A/2,D2,C/3,B/1 D/2,C/1.A/2,B/4 6 Due Date (hours) 6 10 8 14 12 2004/200 16 8 A. Using a Gantt chart, schedule these five samples; schedule them in priority order of earliest due date first. B. Prepare a backward load of these samples. Use a move/wait time of one hour between test stations. Eksamensopgaver til GBE 4 kurset: " Operationel planlgning og styring, skriftlig eksamen" Navn: Studienr: C. Assume that the capacity of each teat station (A, B, C and D) is doubled. Prepare a finite capacity schedule (FCS) for this station. D. What are the bottleneck work centers with reference to part A of the problem Suggest capacity additions that might be needed. situation 5. Textile ApS. (vgtning max. 12%) A small textile company makes various types of sweaters. Of course, demand is very seasonal, as shown by the following quarterly demand estimates. Demand is estimated in terms of standard hours of production required. Quarterly Forecast (units) Fall Winter Spring Summer 10.000 15.000 8000 5000 An hour of regular time costs the company 8$. Employees are paid 12$ per hour on overtime, and labour can be subcontracted from the outside at 10$ per hour. A maximum of 1000 overtime hours is available in any given month. A change in the regular level of production (either increase or decrease) incurs a one-time cost of 5$ per hour for adding or subtracting an hour of labour. It costs 2 percent per month to carry an hour of labour in inventory. Materials and overhead costs in inventory are equal to the direct labour costs. At the beginning of fall quarter, there are 5000 standard hours in inventory and the workforce level is equivalent to 10000 standard hours. E. Suppose management sets the level of regular workers the year equal to the average demand and subcontracts out the rest. What is the cost of this strategy? F. What is the cost of a chase strategy? Operationel planlgning og styring, skriftlig eksamen" 6. MACHINE SHOP (vgtning max. 12%) The end panels and shelves have the following data A furniture manufacturer makes a bookcase from two panels, four shelves, fasteners, and hangers. Operation 2 3 Raw material M1 Raw material M2 Profit per ton ($1000) a. Operation 2 Machine Saw Planer Router Machine Saw Molder Router Sander The master schedule for the next three weeks is 35, 50, and 40 bookcases, respectively. Each MPS quantity requires a setup. Navn: Studienr: 6 1 5 End Panel Run Time 5 minutes 3 minutes 4 minutes Exterior paint Shelf Run Time b. a. What is the total number of hours required on each of the five machines centre for each week? If each of the two parts is stared into production one week (five days) before needed in assembly. and it takes one day per operation, generate the week-by-week load on the routing machines. c. If in B the two parts arrive at the router on the same day, which would you process first, a why? LP / Optimisation Question 1 Reddy Mikks produces both interior and exterior paints from two raw materials, M1 and M2. Reddy Mikks wants to determine the optimum product mix of interior and exterior paints that maximizes the total daily profit. The information about material requirements and profit of one ton of each type of paints is given in the below table. 4 minutes 5 minutes 5 minutes 1 minute Tons of raw material per ton of Setup Time 6 hours 3 hours 8 hours. Interior paint 2 4 Setup Time 5 hours 1.3 hours 7 hours 1 hours Maximum daily availability (tons) 24 6 market survey indicates that the daily demand for interior paint cannot exceed that for exterior paint by more than 2 tons. Also, the maximum daily demand for interior paint is 2 tons. Formulate this linear programming production mix problem and graph all constraints to show the feasible region. b. Are there any redundant constraints? If yes, point out the redundant constraint(s). c. Use the corner point method to solve the problem. Eksamensopgaver til GBE 4 kurset: " Operationel planlgning og styring, skriftlig eksamen" Navn: Studienr: C. Assume that the capacity of each teat station (A, B, C and D) is doubled. Prepare a finite capacity schedule (FCS) for this station. D. What are the bottleneck work centers with reference to part A of the problem Suggest capacity additions that might be needed. 5. .Textile ApS. (vgtning max. 12 %) A small textile company makes various types of sweaters. Of course, demand is very seasonal, as shown by the following quarterly demand estimates. Demand is estimated in terms of standard hours of production required. Quarterly Forecast (units) Fall Winter Spring Summer 10.000 15.000 8000 5000 An hour of regular time costs the company 8$. Employees are paid 12$ per hour on overtime, and labour can be subcontracted from the outside at 10$ per hour. A maximum of 1000 overtime hours is available in any given month. A change in the regular level of production (either increase or decrease) incurs a one-time cost of 5$ per hour for adding or subtracting an hour of labour. It costs 2 percent per month to carry an hour of labour in inventory. Materials and overhead costs in inventory are equal to the direct labour costs. At the beginning of fall quarter, there are 5000 standard hours in inventory and the workforce level is equivalent to 10000 standard hours. E. Suppose management sets the level of regular workers the year equal to the average demand and subcontracts out the rest. What is the cost of this strategy? F. What is the cost of a chase strategy? Eksamensopgaver til GBE 4 kurset: " Operationel planlgning og styring, skriftlig eksamen" d. Due to trouble with raw material supply, Reddy Mikks decides that the exterior paint production should not exceed 2.5 tons per day. Formulate the additional constraint. Question 2 A report from the Marketing department revealed that the demand in both interior and exterior paints can increase. The company in Question 1 changes its goal. Instead of finding the optimal mix production, the manager decides the following goals: Navn: Studienr: The total profit should be more than $20000 Avoid producing more than the quota of exterior paint in Question 1d. Using goal programming and information from Question 1.a., formulate these problems. Question 3 The table given below is the sensitivity analysis on two constraints related to material M1 and M2 Allowable decrease Name M1 availability M2 availability Shadow price 0.75 0.5 Constraint R.H.-side 24 6 Allowable increase 12 0.666666667 4 2 a. Give a short explanation about the table? b. How much will the objective function value increase/decrease if the maximum daily availability of M1 is 28? Question 4 a. What are the differences between Linear Programming (LP) and Integer Programming (IP)? b. Suppose that the amounts of interior and exterior paints (in tons) must be integer values, how should we change the formulation in Question 1.a.? Does the optimal solution in Question 1.c. change? State the reasons if there is any change.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.31 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
To solve this problem well need to calculate the optimal production schedule total cost of production total production each month and the total number of workers required Lets start by organizing the ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


