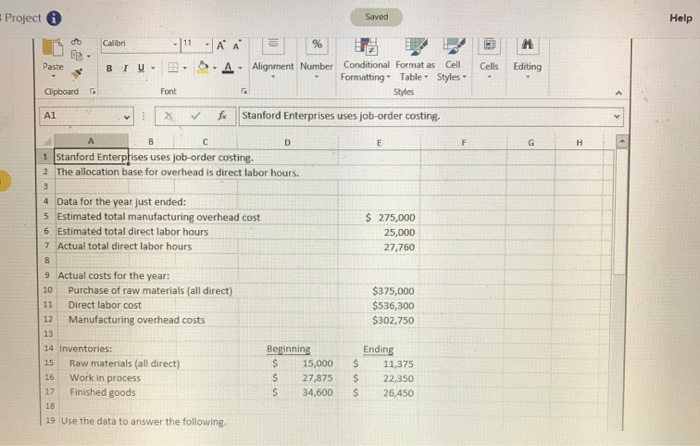
Overhead Analysis and Preparing Schedules of Cost of Goods using Excel's SUM and Basic Math Functions Stanford Enterprises has provided its manufacturing estimated and actual data for the year end. The Controller has asked you to compute the predetermined overhead rate the schedule of cost of goods manufactured, and the schedule of cost of goods sold. Use the information included in the Excel Simulation and the Excel functions described below to complete the task Cell Reference: Allows you to refer to data from another cell in the worksheet. From the Excel Simulation below, if in a blank cell," 5" was entered, the formula would output the result from cell E5, or $275,000 in this example, Basic Math functions Allows you to use the basic math symbols to perform mathematical functions. You can use the following keys: - plus sign to add). - minus sign to subtract)." (asterisk sign to multiply), and/(forward slash to divide). From the Excel Simulation below, if in a blank cell-E6E7" was entered, the formula would add the values from those cells and output the result, or 52,760 in this example, if using the other math symbols the result would output an appropriate answer for its function SUM function: Allows you to refer to multiple cells and adds all the values. You can add individual cell references or ranges to utilize this function. From the Excel Simulation below, if in a blank cell SUME10 E11, E12) was entered the formula would output the result of adding those three separate cells, or 1214,050 in this example. Similarly, if in a blank cellSUME10 E127 was entered the formula would output the same result of adding those cells, except they are expressed as a range in the formula, and the result would be 1214,050 in this example All answers must be entered as a formula. Click OK to begin. OK Project Saved Help . Paste B T U. A Cells Editing Alignment Number Conditional Format as Cell Formatting Table Styles Styles Clipboard Font Al fx Stanford Enterprises uses job-order costing. A 1 Stanford Enterphises uses job-order costing. 2 The allocation base for overhead is direct labor hours. 4 Data for the year just ended: 5 Estimated total manufacturing overhead cost 6 Estimated total direct labor hours 7 Actual total direct labor hours $ 275,000 25,000 27,760 9 Actual costs for the year: 10 Purchase of raw materials (all direct) Direct labor cost 12 Manufacturing overhead costs $375,000 $536,300 $302.750 14 Inventories: 15 Raw materials (all direct) 16 Work in process 17 Finished goods Beginning $ 15,000 $ 27,875 $ 34,600 $ $ $ Ending 11,375 22,350 26,450 19 Use the data to answer the following. 16 Calibri -111-AA 2. -A- Paste B I U . % AL Alignment Number Conditional Format as Cell Formatting Table Styles Styles Cells Editing Clipboard Al X fx Stanford Enterprises uses job-order costing. 19 Use the data to answer the following. ped 21 1. Compute applied overhead and determine the amount of underapplied or overapplied overhead: Actual manufacturing overhead cost Predetermined overhead rate Actual direct labor hours 25 Manufacturing overhead applied Underapplied (overapplied) manufacturing overhead 29 2. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured: Stanford Enterprises Schedule of Cost of Goods Manufactured 35 Direct materials: 34 Raw materials inventory, beginning 55 Add: Purchases of raw materials 36 Total raw materials available Prev 1 of 1 Next pboard fo Stanford Enterprises uses job-order costing. 33 Direct materials: 34 Raw materials inventory, beginning 35 Add: Purchases of raw materials 36 Total raw materials available 37 Deduct: Raw materials inventory, ending 38 Raw materials used in production 39 Direct labor 40 Manufacturing overhead applied to work in process 41 Total manufacturing costs 42 Add: Beginning work in process inventory 44 Deduct: Ending work in process inventory 45 Cost of goods manufactured 47 3. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods sold. Stanford Enterprises Schedule of Cost of Goods Sold A 41 Total manufacturing costs 42 Add: Beginning work in process inventory 44 Deduct: Ending work in process inventory 45 Cost of goods manufactured 47 3. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods sold. Stanford Enterprises Schedule of Cost of Goods Sold 52 Finished goods inventory, beginning 53 Add: Cost of goods manufactured 54 Cost of goods available for sale 55 Deduct: Finished goods inventory, ending 56 Unadjusted cost of goods sold S7 Underapplied (overapplied) overhead 58 Adjusted cost of goods sold Sheet1 Prev 1 of 1 !!! Next 7:02 PM 9 58% .. AT&T LTE