

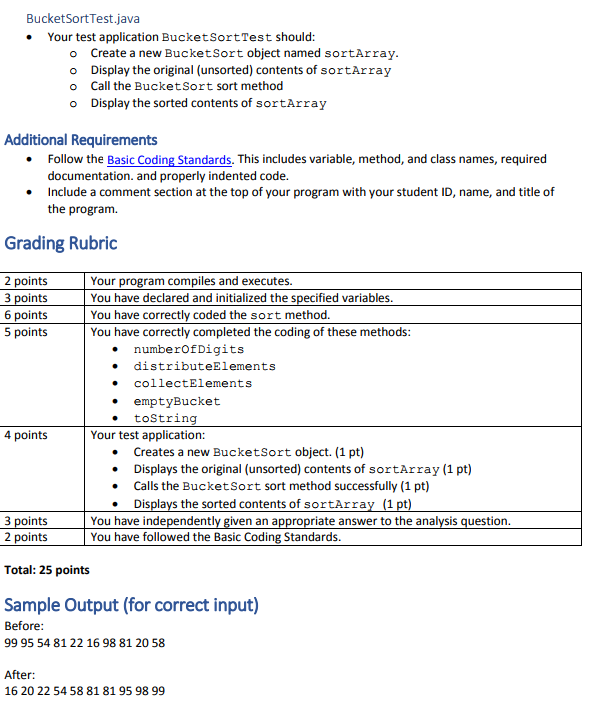
Overview Not all sorting algorithms are comparison sorts. The bucket sort is one such algorithm. Just like it sounds, a bucket sort places array items in buckets based on some formula or on a non-comparative set of steps. A security application of this type of sort involves hashing algorithms, which are used in cryptographic applications. These typically map a key to a bucket using a formula. To learn more about hashing from an algorithmic and coding perspective, visit this course site: https://opendsa server.cs.vt.edu/ODSA/Books/CS3/html/HashFuncExamp.html In this challenge, you will create a variant of the bucket sort with the BucketSort class (described below) and a BucketSortTest driver that will call the BucketSort sort method. This bucket sort begins with a one-dimensional array of positive integers to be sorted. It also uses a two- dimensional array of integers with rows indexed from 0 to 9 and columns indexed from 0 to n-1, where n is the number of values to be sorted. The rows represent the buckets; the columns that create the two-dimensional array represent the numbers that will fill any particular bucket. The digits of each integer, from right to left, will be placed in buckets 0 to 9 based on their value in passes, processing one digit placeholder at a time. After each pass, the values are placed back in the original array by copying the values, in order, from the two-dimensional array back into the original array. After the leftmost digit is processed, the original array will be in order Now, write a class named BucketSort containing a method called sort that operates as follows Place each value of the one-dimensional array into a row of the bucket array, based on the value's "ones" (rightmost) digit. For an example with three starting value (97, 3, 100), 97 is placed in row 7, 3 is placed in row 3 and 100 is placed in row 0. This procedure is called a distribution pass Loop through the bucket array row by row, and copy the values back to the original array. This procedure is called a gathering pass. The new order of the preceding values in the one- dimensional array is 100, 3 and 97 Repeat this process for each subsequent digit position (tens, hundreds, thousands, etc.). On the second (tens digit) pass, 100 is placed in row 0, 3 is placed in row 0 (because 3 has not tens digit) and 97 is placed in row 9. After the gathering pass, the order of the values in the one- dimensional array is 100, 3 and 97. On the third (hundreds digit) pass, 100 is placed in row 1, 3 is placed in row 0 and 97 is placed in row 0 (after the 3). After this last gathering pass, the original array is in sorted order a. b. c. The two-dimensional array of buckets is 10 times the length of the integer array being sorted. This sorting technique provides better performance than a bubble sort, but requires much more memory- the bubble sort requires space for only one additional element of data









