Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
package hw1; public class Runner { public static void main(String[] args) { /*print top header ID Name Gender Age CH Academic Year */ Student.printHeader(); /*
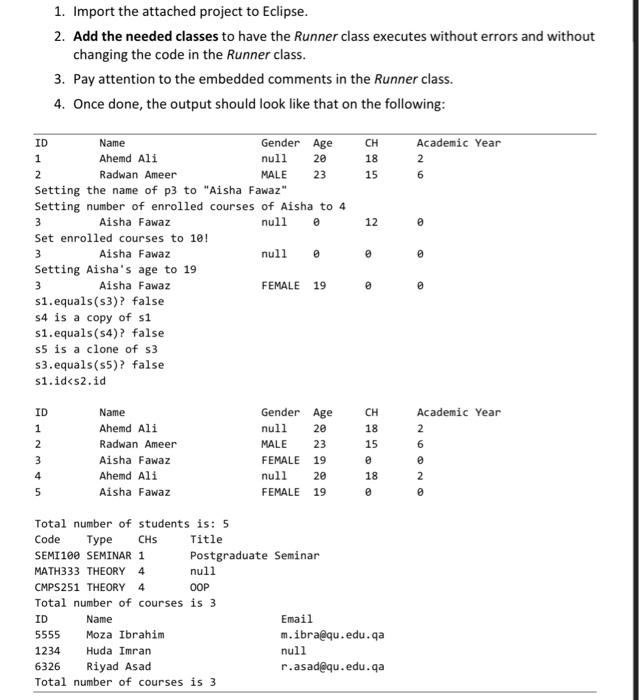
package hw1;
public class Runner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*print top header
ID Name Gender Age CH Academic Year
*/
Student.printHeader();
/* Creates a student and prints his info.
* Parameters here are: Name, age, number of courses enrolled in,
* academic year, and gender.
* Pay attention that the ID is auto generated and does not have a setter.
* valid age is [1-100] otherwise, it is set to 1
* valid academicYear is [1-10] otherwise, it is set to 1
* valid numEnrolledCourses is [1-9] otherwise, it is set to 0
*/
//You must make this constructor call the empty constructor which sets the value of the id
Student s1 = new Student("Ahemd Ali", 20, 6, 2);
/*printStudentInfo() prints the ID, name, Age, Credit Hours, Academic year, and gender.
* credit hours is the number of courses the student is enrolled in * 3
*/
s1.printStudentInfo();
//Creates a second student and prints the students' info
//You must make this constructor call the constructor that takes all attributes but not the gender
Student s2 = new Student("Radwan Ameer", 23, 5, 6, Gender.MALE);
s2.printStudentInfo();
//Creates a third student and prints the students' info
Student s3 = new Student();
//sets the name of s3 to Aisha Fawaz
System.out.println("Setting the name of p3 to \"Aisha Fawaz\"");
s3.setName("Aisha Fawaz");
//Set number of enrolled courses for Aisha to 4
System.out.println("Setting number of enrolled courses of Aisha to 4");
s3.setNumEnrolledCourses(4);
/*printStudentInfo() for s3 */
s3.printStudentInfo();
//Set number of enrolled courses of Aisha to 10!
System.out.println("Set enrolled courses to 10!");
s3.setNumEnrolledCourses(10);
/*printStudentInfo() for s3 */
s3.printStudentInfo();
//Sets the age of Aisha to 19
System.out.println("Setting Aisha's age to 19");
s3.setAge(19);
//sets the gender of Aisha to Female
s3.setGender(Gender.FEMALE);
// printStudentInfo() for s3
s3.printStudentInfo();
/*checks if s1 and s3 having the same values for all of their corresponding attributes*/
System.out.println("s1.equals(s3)? "+s1.equals(s3));
//creates student object s4
Student s4 = new Student();
/*copies data of s1 to s4*/
s1.copy(s4);
System.out.println("s4 is a copy of s1");
/*checks if s1 and s4 having the same values for all of their corresponding attributes*/
System.out.println("s1.equals(s4)? "+s1.equals(s4));
/*creates a clone of s3 and returns its reference to be saved in s5.
* s5 is a clone of s3
*/
Student s5 = s3.clone();
System.out.println("s5 is a clone of s3");
/*checks if s3 and s5 having the same values for all of their corresponding attributes*/
System.out.println("s3.equals(s5)? "+s3.equals(s5));
/*compares s1 to s2 based on the value of the attribute id.
* if the value of id of s1 is less than the value of id of s2 the method returns -1,
* if the value of id of s1 is greater than the value of id of s2 the method returns 1,
* otherwise the two values of id are equal, it returns 0.
*/
switch(s1.compareTo(s2)) {
case -1: System.out.println("s1.id
case 1: System.out.println("s1.d>s2.id");break;
case 0: System.out.println("s1.id==s2.id");break;
}
//prints all students
System.out.println();
Student.printHeader();
s1.printStudentInfo();
s2.printStudentInfo();
s3.printStudentInfo();
s4.printStudentInfo();
s5.printStudentInfo();
System.out.println(" total number of students is: " + Student.totalNumOfStudents);
/*
* creating course objects. Must make use of constructors chaining: constructor calls another
* the course type can be THEORY,LAB,SEMINAR,SDP,TRAINING
*/
Course c1 = new Course();
Course c2 = new Course("MATH333",CourseType.THEORY,4);
Course c3 = new Course("OOP","CMPS251",CourseType.THEORY,4);
c1.setChs(1);
c1.setCode("SEMI100");
c1.setTitle("Postgraduate Seminar");
c1.setType(CourseType.SEMINAR);
/*printing header of course
* Code Type CHs Title
*/
Course.printHeader();
//print all courses taking advantage of overriding toString method
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println(c3);
//print number of courses
System.out.println("Total number of courses is "+Course.totNumOfCourses);
/*
* creating instructor objects. Must make use of constructors chaining: constructor calls another
*/
Instructor i1 = new Instructor();
Instructor i2 = new Instructor("Huda Imran",1234);
Instructor i3 = new Instructor("Riyad Asad", 6326,"r.asad@qu.edu.qa");
i1.setName("Moza Ibrahim");
i1.setEmploymentId(5555);
i1.setEmail("m.ibra@qu.edu.qa");
/*printing header of Instructor
*
*/
Instructor.printHeader();
//print all instructors taking advantage of overriding toString method
System.out.println(i1);
System.out.println(i2);
System.out.println(i3);
//print number of instructors
System.out.println("Total number of courses is "+Instructor.totNumOfInstructors);
}
}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


