
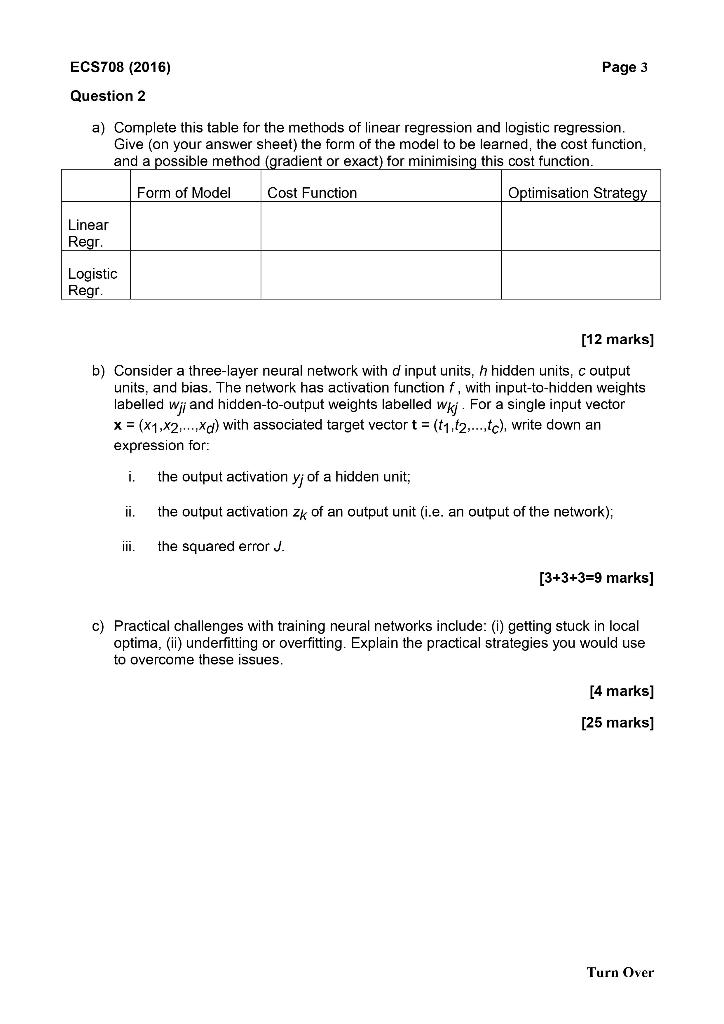

Page 2 ECS708 (2016) Question 1 a) Some emails received by users are spams, attempting to gain illicit access to employee's accounts. You are building a classifier to detect such illicit emails. You start by using the feature of whether or not an email asks for the recipients password, as this an important datum indicating if the email is in fact a hacking attempt. In particular 95% of hacking emails contain requests for a user's password, and 95% of legitimate emails do not contain requests for a user's password. 1% of emails overall are hacking attempts. i. If your classifier scans an email with a password request, what is the probability that the email is in fact a hacking attempt? ii Comment on this value that you calculate iii. What is the probability that your classifier makes an error? [7+2+3=12 marks] b) Explain the difference between Maximum Likelihood (ML) and Maximum a Posterior (MAP) methods of parameter estimation. [4 marks] c) Give the equations for ML and MAP estimates for the bias of a coin. [3 marks] d) Explain the underlying probabilistic assumptions that implicitly underlie (1) the least squares error function and (ii) weight regularization in linear regression. [6 marks] [25 marks] ECS708 (2016) Page 3 Question 2 a) Complete this table for the methods of linear regression and logistic regression. Give (on your answer sheet) the form of the model to be learned, the cost function, and a possible method (gradient or exact) for minimising this cost function. Form of Model Cost Function Optimisation Strategy Linear Regr. Logistic Regr. [12 marks] b) Consider a three-layer neural network with d input units, h hidden units, c output units, and bias. The network has activation function f, with input-to-hidden weights labelled wj; and hidden-to-output weights labelled wkj. For a single input vector x = (x1,x2,...,xd) with associated target vector t = (t1,62...,tc), write down an expression for: the output activation y; of a hidden unit; I. ii. the output activation Zk of an output unit (i.e. an output of the network); III. the squared error J. [3+3+3=9 marks] c) Practical challenges with training neural networks include: (i) getting stuck in local optima, (ii) underfitting or overfitting. Explain the practical strategies you would use to overcome these issues. [4 marks] [25 marks] Turn Over Page 4 ECS708 (2016) Question 3: (a) The probability density function of the Gaussian distribution is given by 1 y'r' x-w) P(x)= (22) Explain what each symbol represents and give its dimensionality. Sketch the probability density function in the 1 dimensional case and use it to support your explanations. [6 marks] (b) The maximum likelihood principle for density estimation states that the optimal parameters * are the ones that minimise the following quantity: N E == - In6p(x,y: 0)) n=1 i. Explain the terms in the equation above, and state what are the parameters 0 in the case of a Gaussian. ii. Explain how the derivatives of this function can be used to optimise E in the equation above and show that in the case of the mean vector u this leads to H = 1/N Xn 11=1 For simplicity you may do the derivations for the 1 dimensional case, that is, in the case that the data are scalars and the covariance matrix a scalar as well. [4+4 = 8 marks] (c) Explain how density estimation with a single Gaussian can be used in a practical application. Pick one of the two examples below or devise your own problem. Explain the steps carefully. For the example that you choose explain whether you could have used a Supervised Learning algorithm and, if not, why. i. Background modelling and subtraction in a Computer Vision application where the goal is to determine at each frame which pixels belong to the foreground and which to the background. ji Abnormality detection in any context. For example in the context of consumer buying habits in a supermarket chain. [4+4=8 marks]









