Parson Awning manufactures awnings and uses a standard cost system. The company allocates overhead based on the number of direct labor hours. The following are the company's cost and standards data:
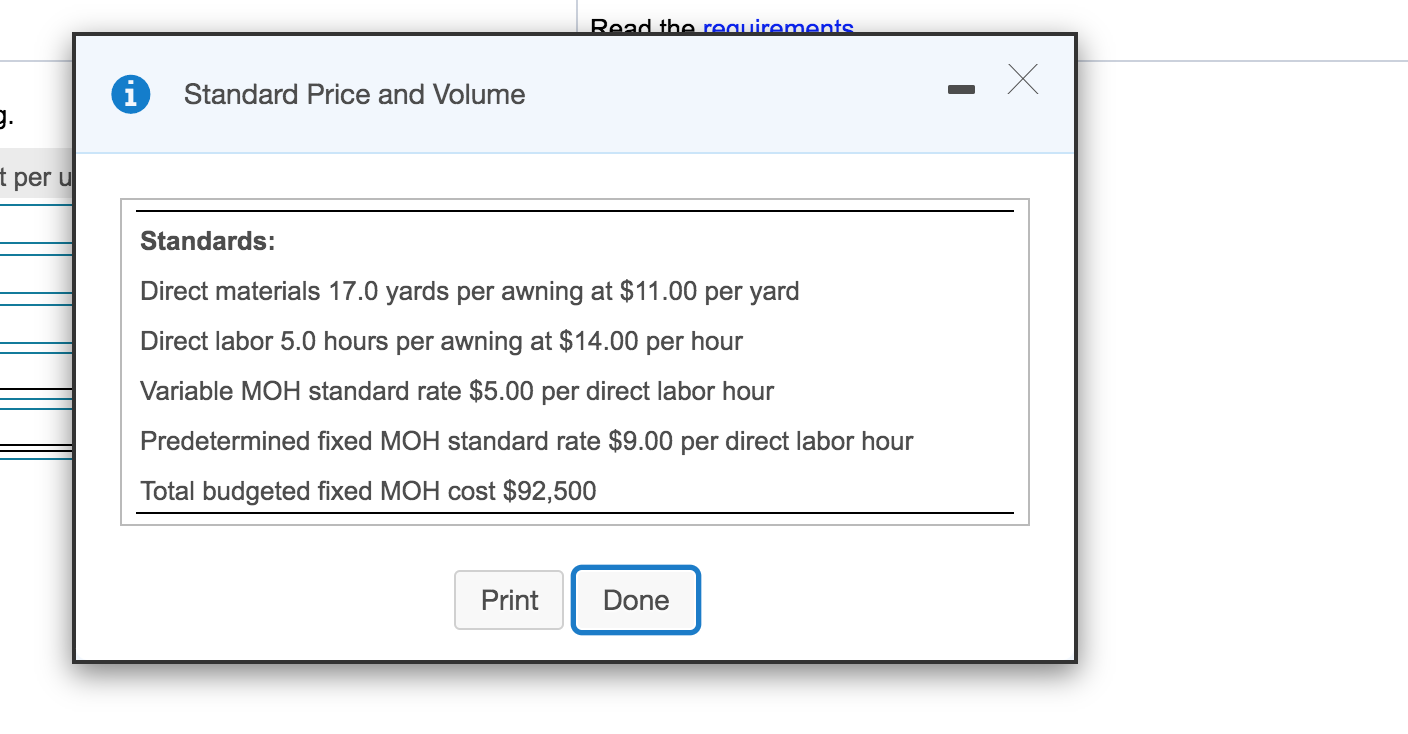
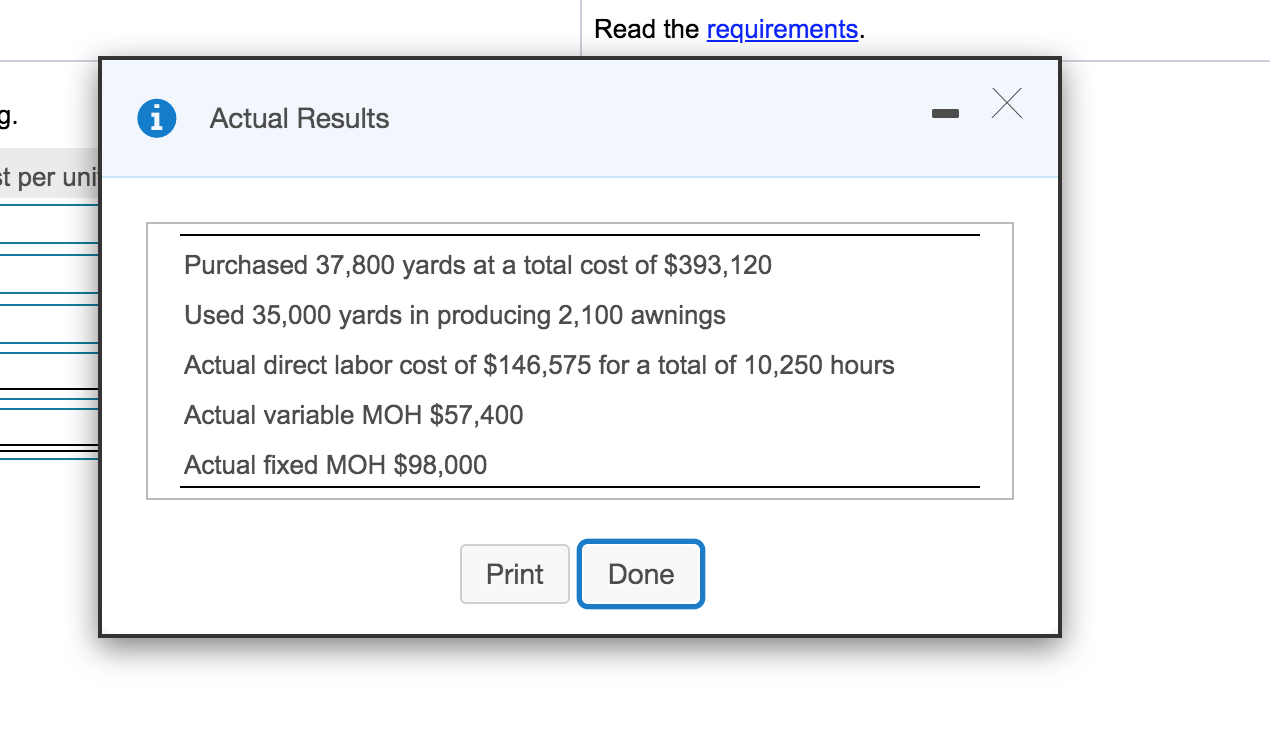
All manufacturing overhead is allocated on the basis of direct labor hours.
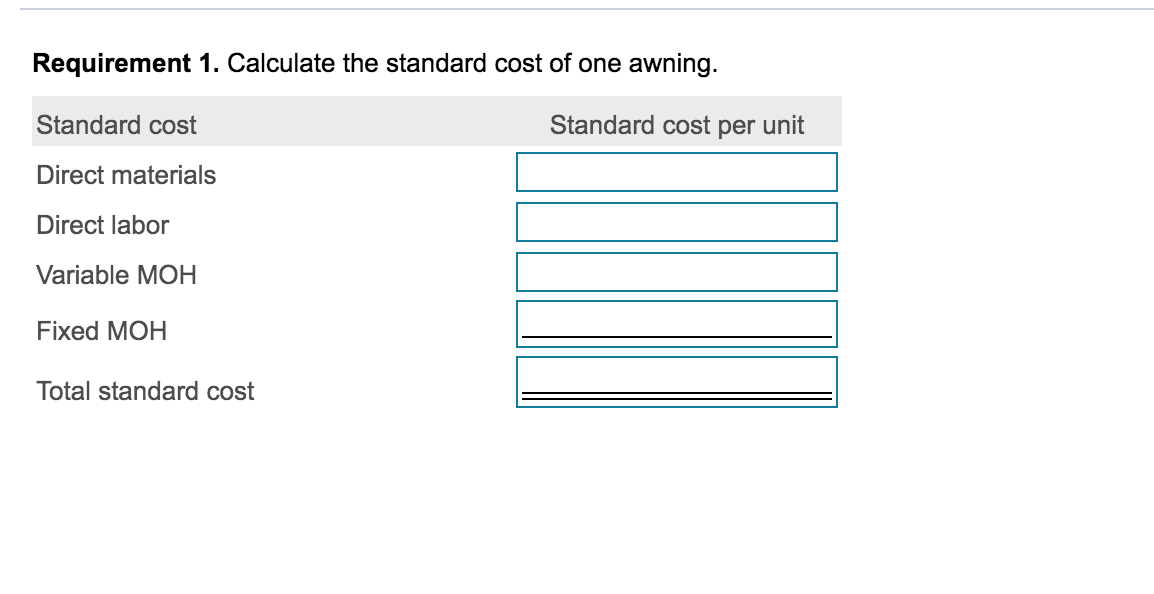
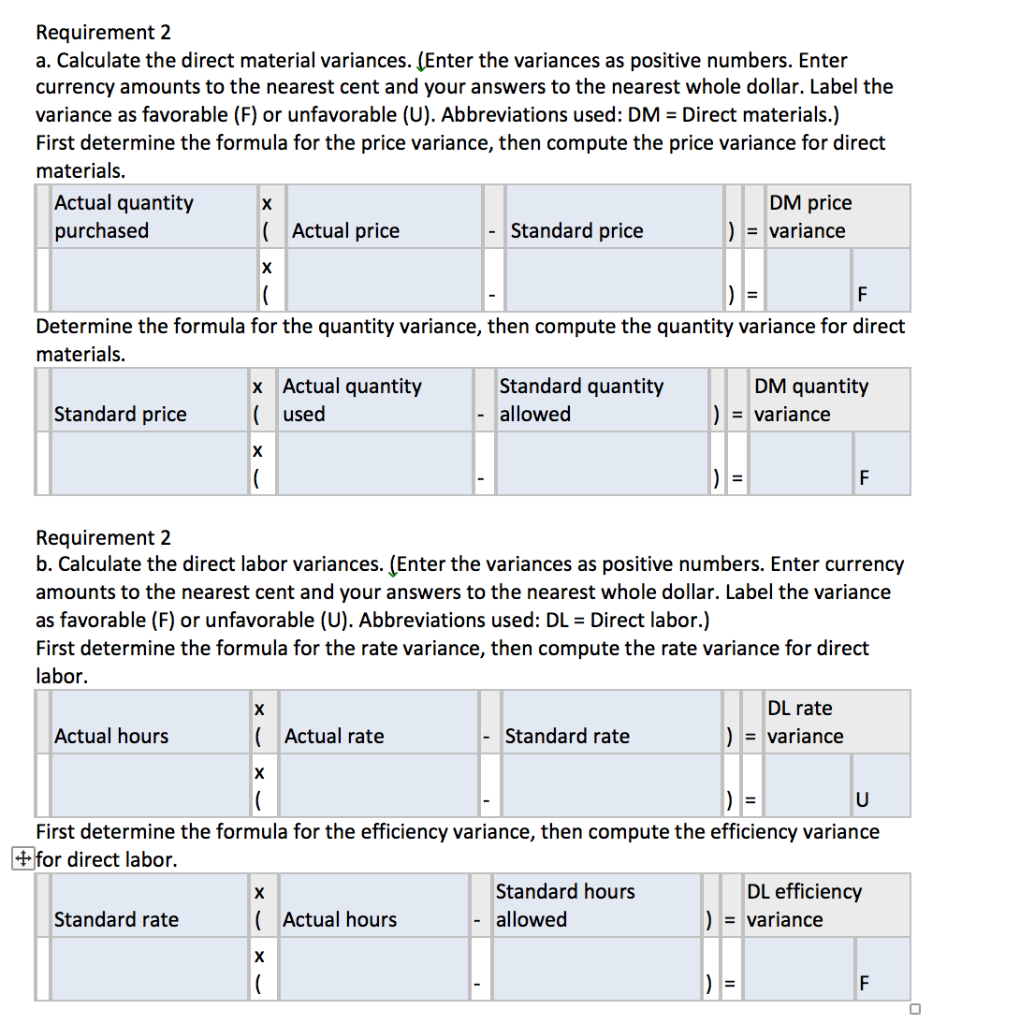
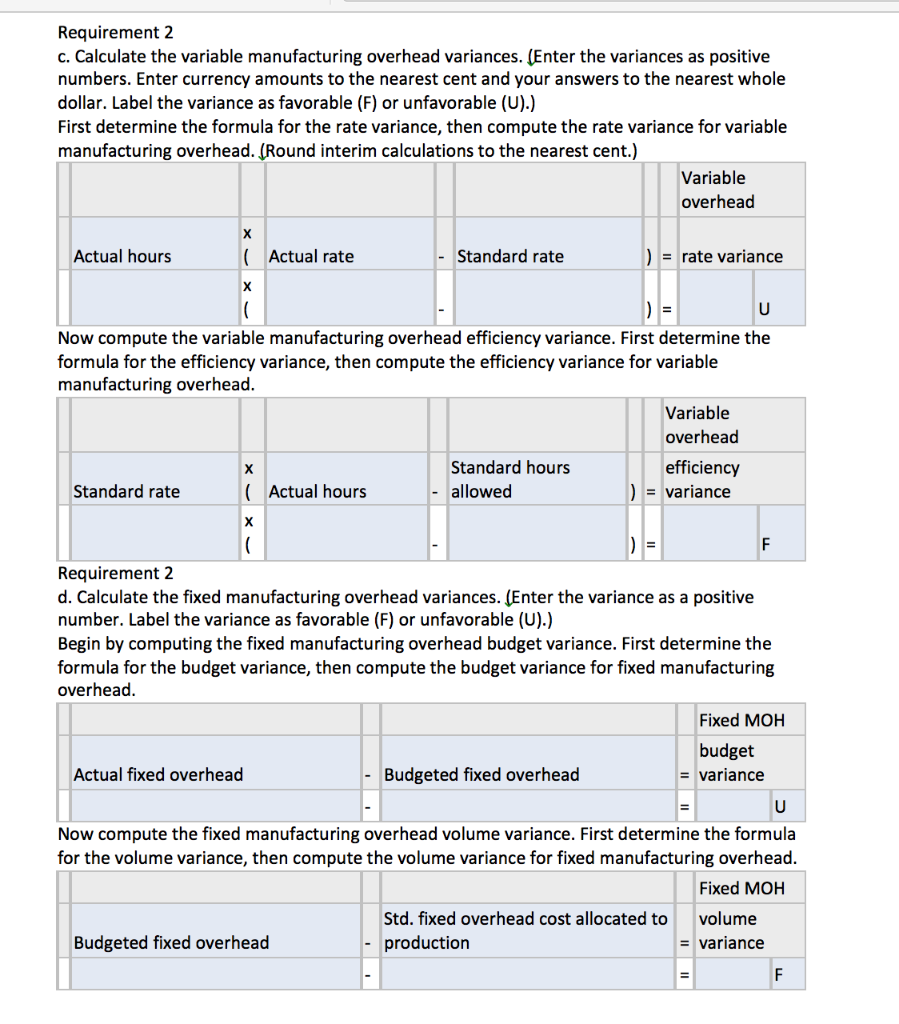
Read the requirements i Standard Price and Volume t per u Standards: Direct materials 17.0 yards per awning at $11.00 per yard Direct labor 5.0 hours per awning at $14.00 per hour Variable MOH standard rate $5.00 per direct labor hour Predetermined fixed MOH standard rate $9.00 per direct labor hour Total budgeted fixed MOH cost $92,500 Print Done Read the requirements. 9. i Actual Results per uni Purchased 37,800 yards at a total cost of $393,120 Used 35,000 yards in producing 2,100 awnings Actual direct labor cost of $146,575 for a total of 10,250 hours Actual variable MOH $57,400 Actual fixed MOH $98,000 Print Done Requirement 1. Calculate the standard cost of one awning. Standard cost Standard cost per unit Direct materials Direct labor Variable MOH Fixed MOH Total standard cost Requirement 2 a. Calculate the direct material variances. (Enter the variances as positive numbers. Enter currency amounts to the nearest cent and your answers to the nearest whole dollar. Label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). Abbreviations used: DM = Direct materials.) First determine the formula for the price variance, then compute the price variance for direct materials. Actual quantity DM price purchased ( Actual price Standard price ) = variance F Determine the formula for the quantity variance, then compute the quantity variance for direct materials. x Actual quantity Standard quantity DM quantity Standard price (used allowed = variance = F Requirement 2 b. Calculate the direct labor variances. (Enter the variances as positive numbers. Enter currency amounts to the nearest cent and your answers to the nearest whole dollar. Label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). Abbreviations used: DL = Direct labor.) First determine the formula for the rate variance, then compute the rate variance for direct labor. DL rate Actual hours (Actual rate Standard rate ) = variance = U First determine the formula for the efficiency variance, then compute the efficiency variance + for direct labor. X Standard hours DL efficiency Standard rate (Actual hours allowed = variance = F Requirement 2 c. Calculate the variable manufacturing overhead variances. (Enter the variances as positive numbers. Enter currency amounts to the nearest cent and your answers to the nearest whole dollar. Label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).) First determine the formula for the rate variance, then compute the rate variance for variable manufacturing overhead. (Round interim calculations to the nearest cent.) Variable overhead Actual hours Actual rate Standard rate ) = rate variance D = U Now compute the variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance. First determine the formula for the efficiency variance, then compute the efficiency variance for variable manufacturing overhead. Variable overhead Standard hours efficiency Standard rate ( Actual hours allowed ) = variance F Requirement 2 d. Calculate the fixed manufacturing overhead variances. (Enter the variance as a positive number. Label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).) Begin by computing the fixed manufacturing overhead budget variance. First determine the formula for the budget variance, then compute the budget variance for fixed manufacturing overhead. Fixed MOH budget = variance Actual fixed overhead - Budgeted fixed overhead Now compute the fixed manufacturing overhead volume variance. First determine the formula for the volume variance, then compute the volume variance for fixed manufacturing overhead. Fixed MOH Std. fixed overhead cost allocated to volume Budgeted fixed overhead production = variance F











