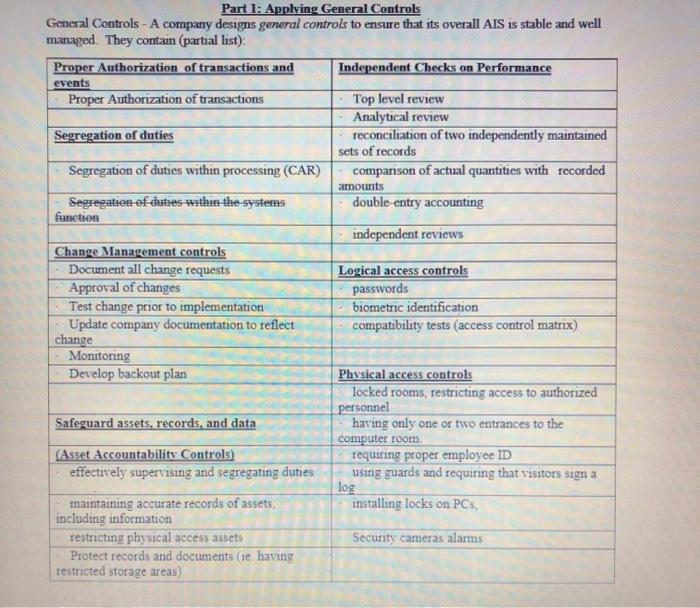
Part 1: Applying General Controls General Controls - A company designs general controls to ensure that its overall AIS is stable and well managed. They contain (partial list) Proper Authorization of transactions and Independent Checks on Performance events Proper Authorization of transactions Top level review Analytical review Segregation of duties reconciliation of two independently maintained sets of records Segregation of duties within processing (CAR) comparison of actual quantities with recorded amounts Segregation of duties within the systems double-entry accounting function independent reviews Change Management controls Document all change requests Logical access controls Approval of changes passwords Test change prior to implementation biometric identification Update company documentation to reflect compatibility tests (access control matrix) change Monitoring Develop backout plan Physical access controls locked rooms, restricting access to authorized personnel Safeguard assets, records, and data having only one or two entrances to the computer room (Asset Accountability Controls) requiring proper employee ID effectively supervising and segregating duties using guards and requiring that visitors sign a log maintaining accurate records of assets, installing locks on PCS including information restricting physical access assets Security cameras alarms Protect records and documents (ie having restricted storage areas) Required: What general controls from above would be most effective in preventing or detecting each of the following errors or undesirable practices? Your answer can have more than one general control. Use the detailed control, not the header. 1) A clerk in the personnel department lists a phantom employee in the personnel records, when the signed paychecks are received from the cashier for distribution, this clerk takes the paycheck for the fictitious employee, cashes it and keeps the proceeds. 2) A salesperson collects $500 cash on account from a customer and pockets the proceeds. 3) An accounts payable clerk prepares and submits an invoice form a fictitious supplier having the name of her mother, writes a check to the supplier and mails the check to her mother's address, the daughter and mother later split the proceeds. 4) Several employees pad the hours worked on their time cards to receive pay for overtime hours never worked 5) An accountant steals payments made by customers by writing off the receivables against the allowance for doubtful accounts 6) A salesperson using her microcomputer, which is interconnected to a local area network accesses the server containing payroll data and prints out a list of the salaries of the firm's sales personnel Part 1: Applying General Controls General Controls - A company designs general controls to ensure that its overall AIS is stable and well managed. They contain (partial list) Proper Authorization of transactions and Independent Checks on Performance events Proper Authorization of transactions Top level review Analytical review Segregation of duties reconciliation of two independently maintained sets of records Segregation of duties within processing (CAR) comparison of actual quantities with recorded amounts Segregation of duties within the systems double-entry accounting function independent reviews Change Management controls Document all change requests Logical access controls Approval of changes passwords Test change prior to implementation biometric identification Update company documentation to reflect compatibility tests (access control matrix) change Monitoring Develop backout plan Physical access controls locked rooms, restricting access to authorized personnel Safeguard assets, records, and data having only one or two entrances to the computer room (Asset Accountability Controls) requiring proper employee ID effectively supervising and segregating duties using guards and requiring that visitors sign a log maintaining accurate records of assets, installing locks on PCS including information restricting physical access assets Security cameras alarms Protect records and documents (ie having restricted storage areas) Required: What general controls from above would be most effective in preventing or detecting each of the following errors or undesirable practices? Your answer can have more than one general control. Use the detailed control, not the header. 1) A clerk in the personnel department lists a phantom employee in the personnel records, when the signed paychecks are received from the cashier for distribution, this clerk takes the paycheck for the fictitious employee, cashes it and keeps the proceeds. 2) A salesperson collects $500 cash on account from a customer and pockets the proceeds. 3) An accounts payable clerk prepares and submits an invoice form a fictitious supplier having the name of her mother, writes a check to the supplier and mails the check to her mother's address, the daughter and mother later split the proceeds. 4) Several employees pad the hours worked on their time cards to receive pay for overtime hours never worked 5) An accountant steals payments made by customers by writing off the receivables against the allowance for doubtful accounts 6) A salesperson using her microcomputer, which is interconnected to a local area network accesses the server containing payroll data and prints out a list of the salaries of the firm's sales personnel