Part 1 Traverse the directory structure from current directory (recursively, that is, to traverse left-to-right depth-first manner) and (1) to print the current path (with
Part 1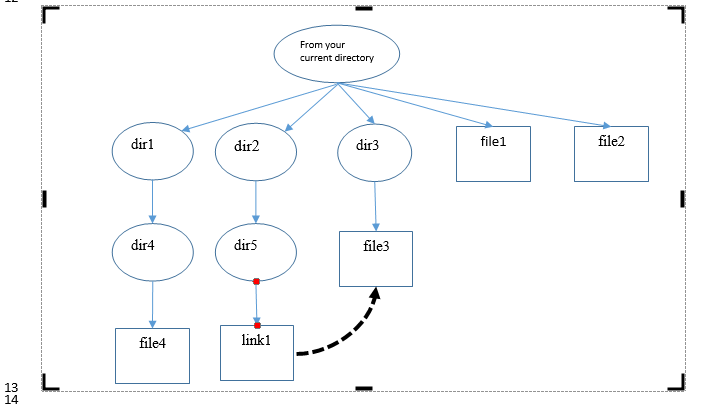
Traverse the directory structure from current directory (recursively, that is, to traverse left-to-right depth-first manner) and (1) to print the current path (with pwd command using system("pwd") call) and (2) to print any file/directory entries (with ls command, using system("ls") call). Your program should print the result of each pwd from current-directory path name, then to the path name of dir1, and then dir4 and so on.
Reference: https://www.gnu.org/software/libc/manual/html_node/Running-a-Command.html
http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man3/system.3.html
/* for example, in your program, to run time command */
#include
int main(void)
{
int rc;
rc = system("pwd");
exit(0);
}
/* Example2. to create a file using touch command */
#include
int main(void)
{
int result;
result = system("touch newfile");
}
13 diri dir4. file4 dir2 dirs linki From your current directory dir3 file3 file1 file2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


