Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Part 2 Answers: S1) {Borrow, Lend, Do Nothing} S2) {Buy, Sell, Do Nothing} S3) {Borrow, Lend, Do Nothing} S4) {Buy, Sell, Do Nothing} Problem 2

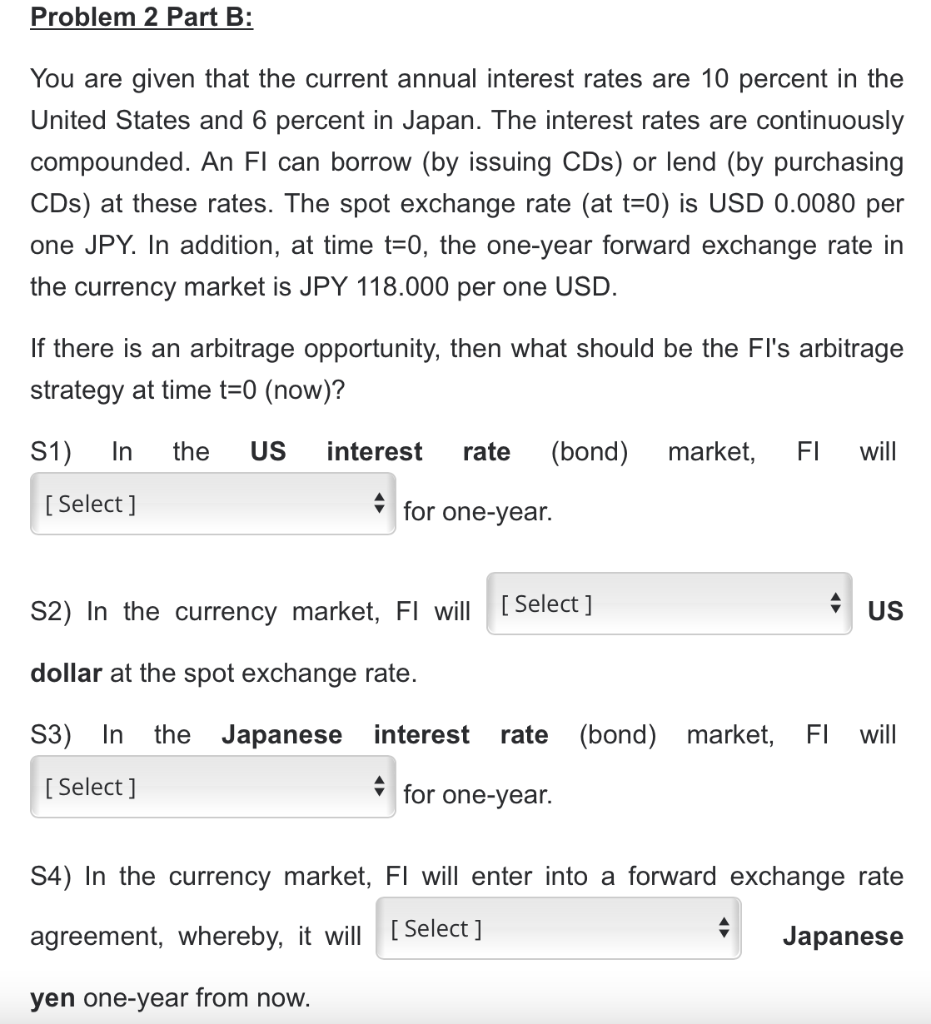

Part 2 Answers:
S1) {Borrow, Lend, Do Nothing}
S2) {Buy, Sell, Do Nothing}
S3) {Borrow, Lend, Do Nothing}
S4) {Buy, Sell, Do Nothing}
Problem 2 Part A: In the interest rate market, you are given annual interest rates of X percent in the United States and 6 percent in Japan. The interest rates are continuously compounded. An Fl can borrow (by issuing CDs) or lend (by purchasing CDs) at these rates. In the foreign currency market, at time t=0 (Now), the spot rate is USD 0.0080 per one JPY. And the one- year forward exchange rate is JPY 118.000 per one USD. Assuming the no-arbitrage principle holds, then as per the covered interest rate parity theorem, what should be the annual interest rate in the U.S. at time t=0 (now)? In other words, what is X? [REMEMBER, you need to find interest rate of US. Type Problem 2 Part B: You are given that the current annual interest rates are 10 percent in the United States and 6 percent in Japan. The interest rates are continuously compounded. An Fl can borrow (by issuing CDs) or lend (by purchasing CDs) at these rates. The spot exchange rate (at t=0) is USD 0.0080 per one JPY. In addition, at time t=0, the one-year forward exchange rate in the currency market is JPY 118.000 per one USD. If there is an arbitrage opportunity, then what should be the Fl's arbitrage strategy at time t=0 (now)? S1) In the US interest rate (bond) market, FI will [ Select ] 4 for one-year. A S2) In the currency market, Fl will [Select ] US dollar at the spot exchange rate. S3) In the Japanese interest rate (bond) market, FI will [ Select ] A for one-year. S4) In the currency market, Fl will enter into a forward exchange rate agreement, whereby, it will [ [ Select ] Japanese yen one-year from now. Problem 2 Part C: The current annual interest rates are 10.000 percent in the United States and 6.000 percent in Japan. The interest rates are continuously compounded. An Fl can borrow (by issuing CDs) or lend (by purchasing CDs) at these rates. In the foreign currency market, the spot rate is USD 0.0080 per one JPY. And the one-year forward exchange rate is JPY 118.000 per one USD. Assuming that at time t=0 (now), an arbitrager can borrow or lend exactly USD 1,000,000 in the US Interest rate (bond) market. Construct an arbitrage strategy whereby the arbitrager will have zero net cash flow at time t=0 (Now), but will have some positive net cash flow in USD at time one-year from now (t=12 months). What is the amount of that positive net cash flow in USD at time t=12 months from now? The abbreviation USD is for US Dollar, and JPY is for Japanese Yen. (Give your answer in USD. Round-off to at least 4 decimal places. DO Problem 2 Part A: In the interest rate market, you are given annual interest rates of X percent in the United States and 6 percent in Japan. The interest rates are continuously compounded. An Fl can borrow (by issuing CDs) or lend (by purchasing CDs) at these rates. In the foreign currency market, at time t=0 (Now), the spot rate is USD 0.0080 per one JPY. And the one- year forward exchange rate is JPY 118.000 per one USD. Assuming the no-arbitrage principle holds, then as per the covered interest rate parity theorem, what should be the annual interest rate in the U.S. at time t=0 (now)? In other words, what is X? [REMEMBER, you need to find interest rate of US. Type Problem 2 Part B: You are given that the current annual interest rates are 10 percent in the United States and 6 percent in Japan. The interest rates are continuously compounded. An Fl can borrow (by issuing CDs) or lend (by purchasing CDs) at these rates. The spot exchange rate (at t=0) is USD 0.0080 per one JPY. In addition, at time t=0, the one-year forward exchange rate in the currency market is JPY 118.000 per one USD. If there is an arbitrage opportunity, then what should be the Fl's arbitrage strategy at time t=0 (now)? S1) In the US interest rate (bond) market, FI will [ Select ] 4 for one-year. A S2) In the currency market, Fl will [Select ] US dollar at the spot exchange rate. S3) In the Japanese interest rate (bond) market, FI will [ Select ] A for one-year. S4) In the currency market, Fl will enter into a forward exchange rate agreement, whereby, it will [ [ Select ] Japanese yen one-year from now. Problem 2 Part C: The current annual interest rates are 10.000 percent in the United States and 6.000 percent in Japan. The interest rates are continuously compounded. An Fl can borrow (by issuing CDs) or lend (by purchasing CDs) at these rates. In the foreign currency market, the spot rate is USD 0.0080 per one JPY. And the one-year forward exchange rate is JPY 118.000 per one USD. Assuming that at time t=0 (now), an arbitrager can borrow or lend exactly USD 1,000,000 in the US Interest rate (bond) market. Construct an arbitrage strategy whereby the arbitrager will have zero net cash flow at time t=0 (Now), but will have some positive net cash flow in USD at time one-year from now (t=12 months). What is the amount of that positive net cash flow in USD at time t=12 months from now? The abbreviation USD is for US Dollar, and JPY is for Japanese Yen. (Give your answer in USD. Round-off to at least 4 decimal places. DOStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


