Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
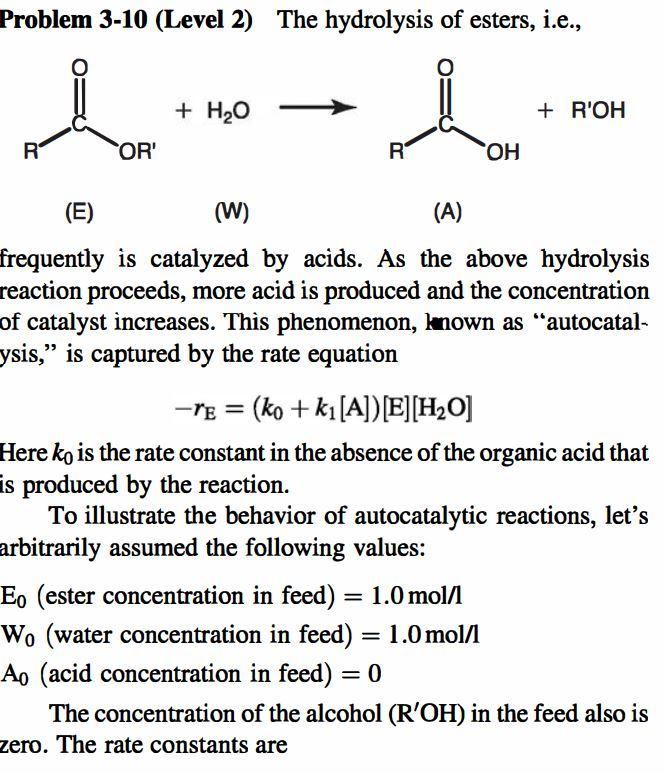
part c please! Problem 3-10 (Level 2) The hydrolysis of esters, i.e., + H2O io + R'OH R OR' RO R (E) (W) (A) frequently

part c please!
Problem 3-10 (Level 2) The hydrolysis of esters, i.e., + H2O io + R'OH R OR' RO R (E) (W) (A) frequently is catalyzed by acids. As the above hydrolysis reaction proceeds, more acid is produced and the concentration of catalyst increases. This phenomenon, known as "autocatal- ysis," is captured by the rate equation -re = (ko + ki[A])[E][H20] Here ko is the rate constant in the absence of the organic acid that is produced by the reaction. To illustrate the behavior of autocatalytic reactions, let's arbitrarily assumed the following values: Eo (ester concentration in feed) = 1.0 mol/l W. (water concentration in feed) = 1.0 mol/l Ao (acid concentration in feed) = 0 The concentration of the alcohol (R'OH) in the feed also is zero. The rate constants are = = = Wo (water concentration in feed) = 1.0 mol/l Ao (acid concentration in feed) = 0 The concentration of the alcohol (R'OH) in the feed also is zero. The rate constants are = = = ko = 0.01 1/mol-h k = 0.20 12/mol-h In answering the following questions, assume that the reaction takes place in the liquid phase. 1. Calculate values of -re at fractional conversions of ester (xE) = 0, 0.10, 0.20, 0.30, 0.40, 0.50, 0.60, and 0.70. = 2. Plot 1/-re versus x. 3. What kind of continuous reactor system would you use if a final ester conversion of 0.60 were desired, and if the reaction were to take place isothermally. Choose the reactor or combination of reactors that has the smallest volume. Justify your
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


