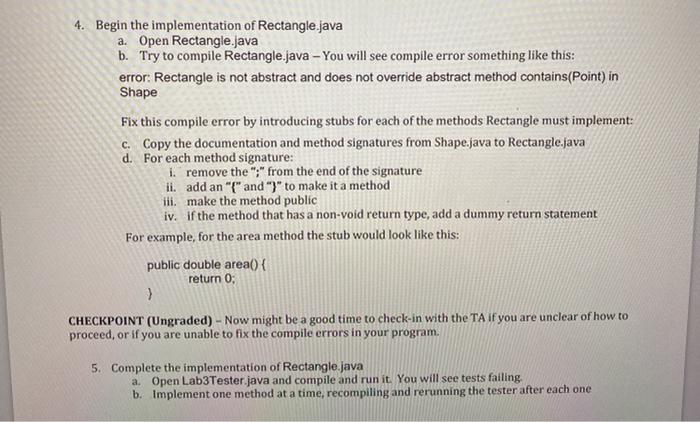
Part I - Interfaces 1. Download all of the provided lab files to your Lab3 working directory. We are going to use an interface to specify what a Shape class should look like. As depicted in the UML diagram below, a Shape should have methods for calculating area, calculating perimeter and determining whether a given Point lies with in a Shape. An interface does not include the implementation of these methods, only their signatures and documentation. The implementation details of these method is dependent on the type of Shape and therefore will be defined in the classes that implement the Shape interface (ie. Circle, Rectangle) 2. Start by opening Shape.java to familiarize yourself with the method documentation. The Circle and Rectangle classes implement the Shape interface (depicted by the dashed arrow between them in the UML diagram below) Circle and Rectangle both have an attribute of type Point (depicted by the solid line with no arrow between them in the UML diagram below). 3. Open Circle.java and you will see a full implementation of the Circle class. Notice, it contains implementations of all methods listed in Shape.java Shape
> + area double + perimeter(): double + contains (Point) : boolean + tostring(): String Point Rectangle X: int y! int + Point) + Point(int,int) + getX(): + set X (int): + getY(): + betyint): + tostring(): Crete int void int void string radiusi irit position Point + Curele) Circle(int) + Curele tint, Point) + area () double + perimeter() double + contains (Point) boolean + toString() 1 String length: int width: int position Point + Rectangle() + Rectangle (int, int) - Rectangle tint, int, Point) + area (11 double perimeter double contains (Point) boolean + tostring(): String 4. Begin the implementation of Rectangle.java a. Open Rectangle.java b. Try to compile Rectangle.java - You will see compile error something like this: error: Rectangle is not abstract and does not override abstract method contains(Point) in Shape Fix this compile error by introducing stubs for each of the methods Rectangle must implement: C. Copy the documentation and method signatures from Shape.java to Rectangle.java d. For each method signature: 1. remove the ";" from the end of the signature ii. add an "{" and "?" to make it a method ili. make the method public iv. if the method that has a non-void return type, add a dummy return statement For example, for the area method the stub would look like this: public double area() { return 0; > CHECKPOINT (Ungraded) - Now might be a good time to check-in with the TA if you are unclear of how to proceed, or if you are unable to fix the compile errors in your program. 5. Complete the implementation of Rectangle.java a. Open Lab3Tester.java and compile and run it. You will see tests failing b. Implement one method at a time, recompiling and rerunning the tester after each one Part 11 - Using classes to define a data structure We are now going to implement a class called ShapeList that will hold a collection of Shapes. The addition of this class is depicted in our UML diagram: Shape Ginterface Shapelit want shapes Ett int + dopol vot SEE int + og string veront word boble peritetit double + contains ont boolean tort Stri Point * The Vint pointtint, + X + CRI int vod YU Being + Boty + teking redint tine + Ctrleti Colent Circle at de + terit + portanto HY Hone length it wat in pation in tangle taglitt tangle mit Ni . die double contato 1. Start by opening Shapelist java Notice we have added the attributes, a blank constructor and method stubs for you a. Uncomment the call to testShapeList) in the main of Lab3Tester java and compile/runit b. Implement the constructor and each method one at a time 2. Add tests to testShopelist() to ensure your add method has the correct behaviour when more than 2 elements are added to the list a. It is up to you to decide how to handle the case when the underlying array is full. A new larger array should be allocated, and all elements should be copied into the new array 3. Write tests to testShapeliat) to ensure your removeFront method has the correct behaviour a. The first element should be removed, the size should go down one, and the order of all other elements should not change b. If there are no elements to remove, nothing should happen (thesive stays at 0 c. BONUS CHALLENGE: If the array is less than half full, allocate a smaller array and copy the elements over to it, so there is less wasted memory