
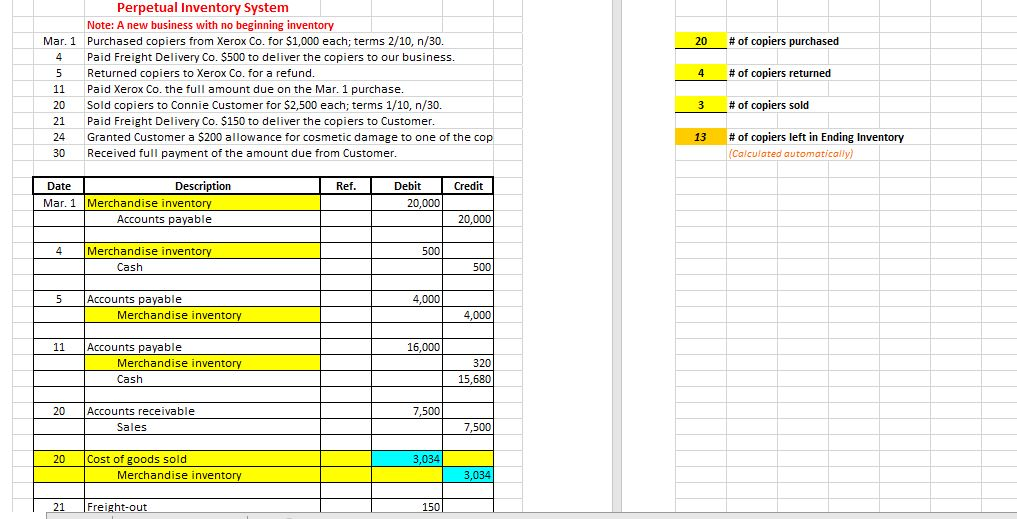
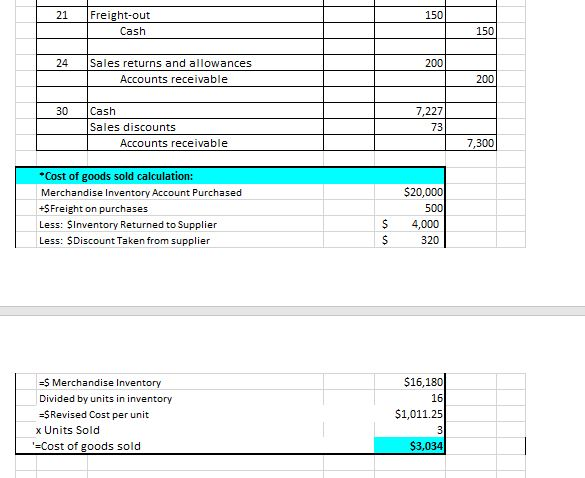
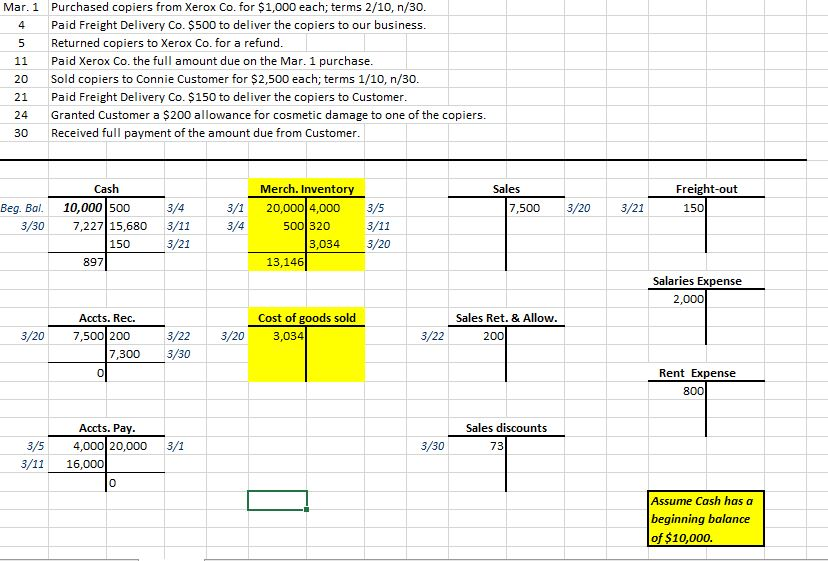
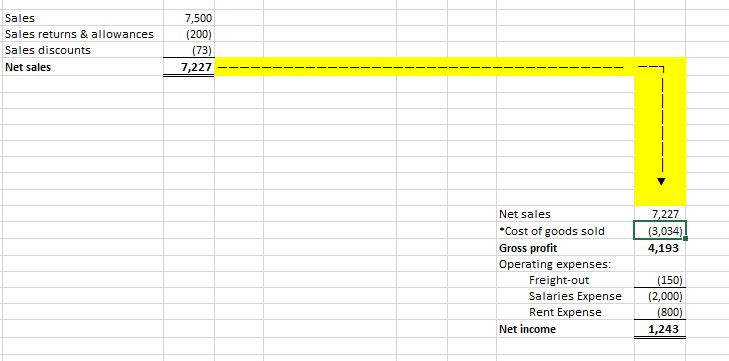
PART II: PERPETUAL INVENTORY SYSTEMS Perpetual Inventory Systems provide a hiqh level of control of inventories because the Merchandise Inventory account is constantly being updated. Debits are used to increase Merchandise Inventory because it is an asset. Likewise, Credits are used to decrease Merchandise Inventory. Some transactions of a merchandiser have NO EFFECT on this account. Open the EXCEL File "Perpetual Inventory Illustration Final" in the CONTENT Area of D2L-Module 8. Change the number of units purchased to 25, the number of units returned to 3, and the number of units sold to 18. Use the 3 TABS in this file (Journal, Ledger, and Statements) to answer the following questions: PERPETUAL INVENTORY SYSTEM 1. What account was debited when inventory was purchased on March 1? $amount 2. What account was debited when freight charges were paid on the purchase of inventory on March 4? 3. What account was credited when goods were returned to the suppler on March 5? $amount 4. What account was credited when a $Discount was taken when the merchandiser paid the supplier? $amount 5. Look at the Merchandise Inventory account in the Ledger. What 5 events affected this account? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Was Cost of Goods Sold determined when goods the period? were sold OR at the end of 7. What account was used to represent the cost of shipping goods to the customer? 8. What account represents the $ adjustment made when a customer determined that some goods were defective? 9, What account represents the $ reduction in the amount owed by the customer because they paid early? Perpetual Inventory System beginning inventory Purchased copiers from Xerox Co. for $1,000 each; terms 2/10, n/30. Note: A new business with #of copiers purchased Mar. 1 20 Paid Freight Delivery Co. $500 to deliver the copiers to our business. 4 #of copiers returned Returned copiers to Xerox Co. for a refund. Paid Xerox Co. the full amount due on the Mar. 1 purchase. Sold copiers to Connie Customer for $2,500 each; terms 1/10, n/30. Paid Freight Delivery Co. $150 to deliver the copiers to Customer. Granted Customer a $200 allowance for cosmetic damage to one of the cop) 11 #of copiers sold 20 21 #of copiers left in Ending Inventory 24 13 (Calculated automatically) 30 Received full payment of the amount due from Customer. Debit Description Ref Credit Date 20,000 Mar 1 Merchandise inventory Accounts payable 20,000 Merchandise inventory 500 Cash 500 Accounts payable 4,000 Merchandise inventory 4,000 11 Accounts payable 16,000 Merchandise inventory 320 Cash 15.680 20 Accounts receivable 7,500 7,500 Sales Cost of goods sold 3,034 20 Merchandise inventory 3.034 Freight-out 21 150 Freight-out 21 150 Cash 150 Sales returns and allowances 24 200 Accounts receivable 200 30 Cash 7,227 Sales discounts 73 Accounts receivable 7,300 Cost of goods sold calculation: $20,000 Merchandise Inventory Account Purchased +SFreight on purchases 500 S Less: SInventory Returned to Supplier 4,000 Less: SDiscount Taken from supplier 320 = S Merchandise Inventory $16,180 Divided by units in inventory 16 $1,011.25 -SRevised Cost per unit x Units Sold 3 $3,034 -Cost of goods sold Purchased copiers from Xerox Co. for $1,000 each; terms 2/10, n/30. Mar. 1 Paid Freight Delivery Co. $500 to deliver the copiers to our business. 4 Returned copiers to Xerox Co. for a refund. Paid Xerox Co. the full amount due on the Mar. 1 purchase. 11 Sold copiers to Connie Customer for $2,500 each; terms 1/10, n/30. 20 Paid Freight Delivery Co. $150 to deliver the copiers to Customer. 21 Granted Customer a $200 allowance for cosmetic damage to one of the copiers Received full payment of the amount due from Customer 24 30 Merch. Inventory Cash Sales Freight-out 10,000 500 Beg. Bal. 7,500 3/4 20,000 4,000 150 3/1 3/5 3/20 3/21 7,227 15,680 500 320 3/30 3/11 3/4 3/11 3/21 3/20 150 3,034 13,146 897 Salaries Expense 2,000 Cost of goods sold 3,034 Accts. Rec. Sales Ret. & Allow. 3/20 7,500 200 3/22 3/20 3/22 200 7,300 3/30 Rent Expense 0 800 Accts. Pay. Sales discounts 4,000 20,000 3/5 3/1 3/30 73 3/11 16,000 0 Assume Cash has a beginning balance of $10,000. Sales 7,500 Sales returns & allowances (200) Sales discounts (73) Net sales 7,227 Net sales 7,227 Cost of goods sold (3,034) Gross profit 4,193 Operating expenses: (150) Freight-out Salaries Expense (2,000) Rent Expense (800) Net income 1,243











