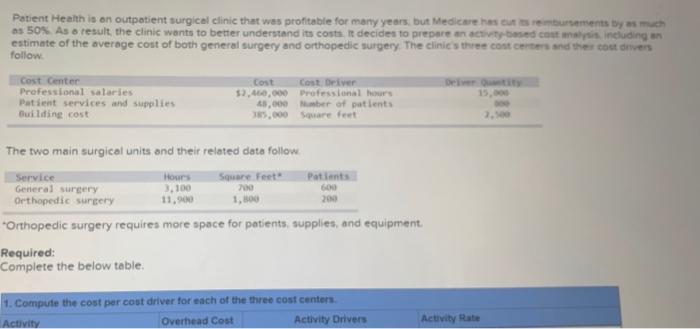
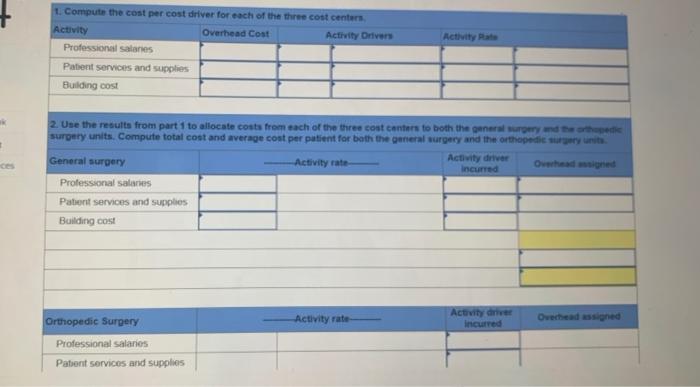
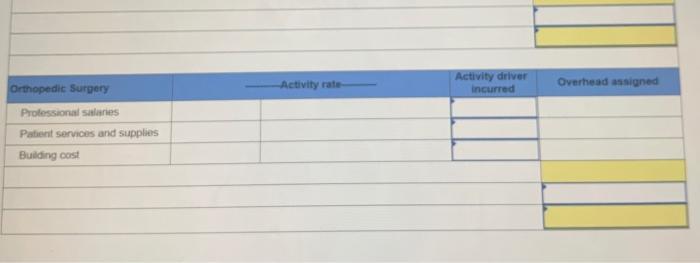
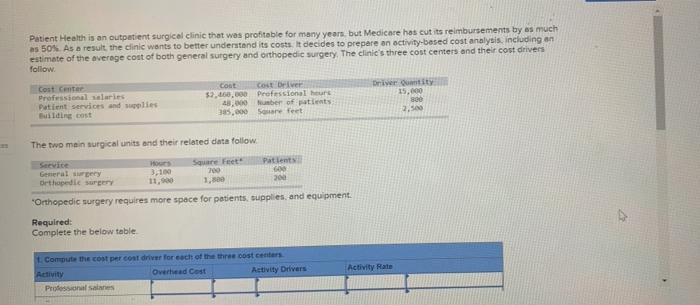
Patient Health is an outpatient surgical clinic that was profitable for many years, but Medicare has tremurenents tas much as 50% As a result, the clinic wants to better understand its costs. It decides to prepare an activity-based comes including an estimate of the average cost of both general surgery and orthopedic surgery. The clinic the concerns and the courses follow Cost Center Professional salaries Otis Patient services and supplies Cost Cost Driver 57,460,000 Professional hours 41,000 Number of patients 185.000 Sare feet Building cost 2.1 The two main surgical units and their related data follow Square Feet Service General Surgery Orthopedic surgery Hours 3.100 11,900 200 Patients 600 200 Orthopedic surgery requires more space for patients, supplies, and equipment Required: Complete the below table, 1. Compute the cost per cost driver for each of the three cost centers Overhead Cost Activity Drivers Activity Rate Activity 1. Compute the cost per cost driver for each of the three cost centers Activity Overhead Cost Activity Drivers Activity Rate Professional salaries Patient services and supplies Building cost 2. Use the results from part 1 to allocate costs from each of the three cost canters to both the general surgery and the othek surpery units. Compute total cost and average cost per patient for both the general surgery and the orthopedic surgery units Activity driver General surgery Activity rate Overhead and incurred Professional salaries Patient Services and supplies Building cost Orthopedic Surgery Activity rate Activity incurred Overhead assigned Professional salaries Patient services and supplies Orthopedic Surgery Activity rate Activity driver incurred Overhead assigned Professional Series Patient services and supplies Building cost Patient Health is an outpatient surgical clinic that was profitable for many years, but Medicare has cut its reimbursements by as much as 50%. As a result the clinic wants to better understand its costs. It decides to prepare an activity-based cost analysis including an estimate of the average cost of both general surgery and orthopedic surgery. The clinic's three cost centers and their cost drivers follow Driwity 15.000 Cost Center Professional salaries Patient services and supplies Building cost coot cost belver $2,400,000 Professional hours 43,000 ber of patients 385,000 Sore feet 2.500 The two main surgical units and their related data follow Patients Service General surgery Orthopedic surgery 3,100 11,90 Square Feet 200 1,500 20 "Orthopedic surgery requires more space for patients, supplies and equipment. Required: Complete the below table 1. Computer the cost per cont driver for each of the three cost centers Activity Overhead Cost Activity Drivers Activity Rate Professional Sales Patient Health is an outpatient surgical clinic that was profitable for many years, but Medicare has tremurenents tas much as 50% As a result, the clinic wants to better understand its costs. It decides to prepare an activity-based comes including an estimate of the average cost of both general surgery and orthopedic surgery. The clinic the concerns and the courses follow Cost Center Professional salaries Otis Patient services and supplies Cost Cost Driver 57,460,000 Professional hours 41,000 Number of patients 185.000 Sare feet Building cost 2.1 The two main surgical units and their related data follow Square Feet Service General Surgery Orthopedic surgery Hours 3.100 11,900 200 Patients 600 200 Orthopedic surgery requires more space for patients, supplies, and equipment Required: Complete the below table, 1. Compute the cost per cost driver for each of the three cost centers Overhead Cost Activity Drivers Activity Rate Activity 1. Compute the cost per cost driver for each of the three cost centers Activity Overhead Cost Activity Drivers Activity Rate Professional salaries Patient services and supplies Building cost 2. Use the results from part 1 to allocate costs from each of the three cost canters to both the general surgery and the othek surpery units. Compute total cost and average cost per patient for both the general surgery and the orthopedic surgery units Activity driver General surgery Activity rate Overhead and incurred Professional salaries Patient Services and supplies Building cost Orthopedic Surgery Activity rate Activity incurred Overhead assigned Professional salaries Patient services and supplies Orthopedic Surgery Activity rate Activity driver incurred Overhead assigned Professional Series Patient services and supplies Building cost Patient Health is an outpatient surgical clinic that was profitable for many years, but Medicare has cut its reimbursements by as much as 50%. As a result the clinic wants to better understand its costs. It decides to prepare an activity-based cost analysis including an estimate of the average cost of both general surgery and orthopedic surgery. The clinic's three cost centers and their cost drivers follow Driwity 15.000 Cost Center Professional salaries Patient services and supplies Building cost coot cost belver $2,400,000 Professional hours 43,000 ber of patients 385,000 Sore feet 2.500 The two main surgical units and their related data follow Patients Service General surgery Orthopedic surgery 3,100 11,90 Square Feet 200 1,500 20 "Orthopedic surgery requires more space for patients, supplies and equipment. Required: Complete the below table 1. Computer the cost per cont driver for each of the three cost centers Activity Overhead Cost Activity Drivers Activity Rate Professional Sales