Question
Pelzer Printing Inc. has bonds outstanding with 10 years left to maturity. The bonds have a 9% annual coupon rate and were issued 1 year
Pelzer Printing Inc. has bonds outstanding with 10 years left to maturity. The bonds have a 9% annual coupon rate and were issued 1 year ago at their par value of $1,000. However, due to changes in interest rates, the bond's market price has fallen to $950.70. The capital gains yield last year was -4.93%.
a. What is the yield to maturity? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places.
b. For the coming year, what is the expected current yield? (Hint: Refer to Footnote 6 for the definition of the current yield and to Table 7.1.) Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places.
c. For the coming year, what is the expected capital gains yield? (Hint: Refer to Footnote 6 for the definition of the current yield and to Table 7.1.) Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places.
d.
Will the actual realized yields be equal to the expected yields if interest rates change? If not, how will they differ?
- As long as promised coupon payments are made, the current yield will not change as a result of changing interest rates. However, changing rates will cause the price to change and as a result, the realized return to investors should equal the YTM.
- As long as promised coupon payments are made, the current yield will change as a result of changing interest rates. However, changing rates will cause the price to change and as a result, the realized return to investors should equal the YTM.
- As long as promised coupon payments are made, the current yield will change as a result of changing interest rates. However, changing rates will not cause the price to change and as a result, the realized return to investors should equal the YTM.
- As rates change they will cause the end-of-year price to change and thus the realized capital gains yield to change. As a result, the realized return to investors will differ from the YTM.
- As long as promised coupon payments are made, the current yield will change as a result of changing interest rates. However, changing rates will cause the price to change and as a result, the realized return to investors will differ from the YTM.

footnote 6
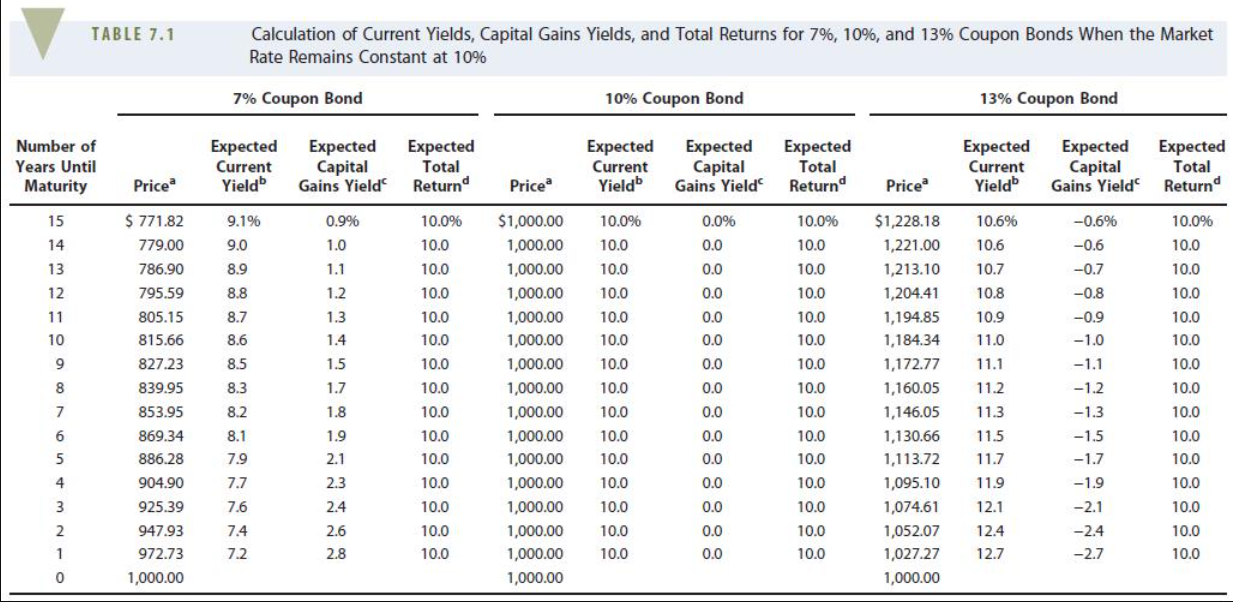
table 7.1
"Brokerage houses occasionally report a bond's current yield, defined as the annual interest payment divided by the current price. For example, if Allied's 10% coupon bonds were sell- ing for $985, the current yield would be $100/$985 = 10.15%. Unlike the YTM or YTC, the cur- rent yield does not represent the actual return that investors should expect because it does not account for the capital gain or loss that will be realized if the bond is held until it matures or is called. The current yield was popular before calculators and computers came along because it was easy to calculate. However, it can be misleading, and now it's easy enough to calculate the YTM and YTC. TABLE 7.1 Calculation of Current Yields, Capital Gains Yields, and Total Returns for 7%, 10%, and 13% Coupon Bonds When the Market Rate Remains Constant at 10% 7% Coupon Bond 10% Coupon Bond 13% Coupon Bond Number of Years Until Maturity Expected Current Yield" Expected Capital Gains Yield" Expected Total Return Expected Current Yield" Expected Capital Gains Yield Expected Total Return Expected Current Yield" Expected Capital Gains Yield Expected Total Return Price Price Price 15 0.9% 10.0% 10.0% $ 771.82 779.00 9.1% 9.0 0.0% 0.0 14 1.0 10.0 10.0 10.6% 10.6 10.7 10.8 10.0 10.0 8.9 0.0 1.1 1.2 0.0 13 12 11 10 8.8 8.7 10.0% 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 0.0 786.90 795.59 805.15 815.66 827.23 839.95 10.9 1.3 1.4 8.6 0.0 11.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0% 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 9 8.5 0.0 11.1 11.2 10.0 10.0 8 8.3 0.0 $1,000.00 1,000.00 1,000.00 1,000.00 1,000.00 1,000.00 1,000.00 1,000.00 1,000.00 1,000.00 1,000.00 1,000.00 1,000.00 1,000.00 1,000.00 1,000.00 10.0 10.0 $1,228.18 1,221.00 1,213.10 1,204.41 1,194.85 1,184.34 1,172.77 1,160.05 1,146.05 1,130.66 1,113.72 1,095.10 1,074.61 1,052.07 1,027.27 1,000.00 -0.6% -0.6 -0.7 -0.8 -0.9 -1.0 -1.1 -1.2 -1.3 -1.5 -1.7 -1.9 -2.1 -2.4 -2.7 7 853.95 8.2 10.0 1.5 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.1 2.3 0.0 11.3 10.0 6 8.1 0.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 5 7.9 11.5 11.7 11.9 0.0 4 7.7 0.0 10.0 869.34 886.28 904.90 925.39 947.93 972.73 10.0 10.0 3 0.0 10.0 10.0 7.6 7.4 7.2 2 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 2.4 2.6 2.8 0.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 12.1 12.4 12.7 10.0 10.0 1 0.0 0 1,000.00Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


