






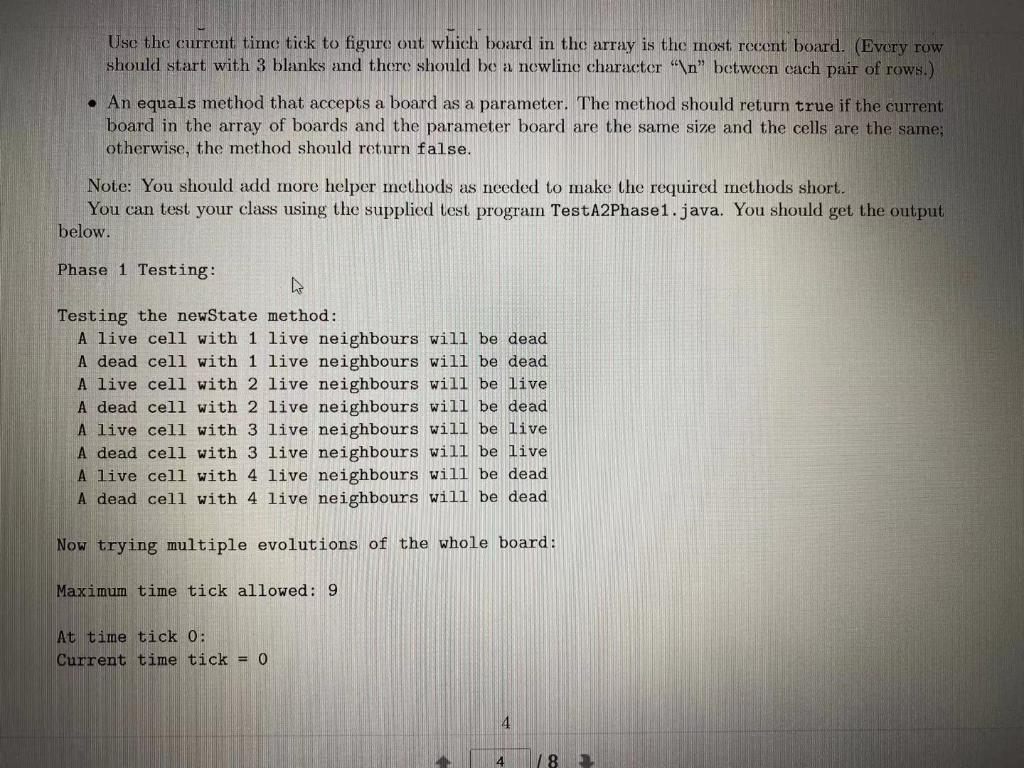

Phase 1: We are going to implement the Game of Life using two-dimensional arrays of ints (called "boards"). Each int in a board is a cell - if the cell is alive, then the corresponding int is 1, and if the cell is dead, then the corresponding int is 0. At each time tick, all the cells evolve simultaneously we get a new board. We are going to store all the different boards, starting at time tick 0, in an array of boards we're really going to be working with a three dimensional array of ints. The extra dimension in the array represents time. In this phase, implement a simple class GameOfLife, which should have: . Two instance variables: the three dimensional array of ints representing the boards over time, and another variable (an int) that contains the current time tick that is, the variable tells you how many times the starting board at time tick () has been evolved so far. A class (static method cloneOneBoard that accepts a board (a 2D array of ints) as a parameter and returns a clone (deep copy) of it. Use the following header: public static int[] [] cloneOneBoard( int[[] board) A constructor that accepts a starting board (a 2D array of ints) and a number, n, of time ticks (an int). The constructor should initialize the 3D array instance variable so that it can hold boards for n time ticks (including the starting board at time tick 0). (You should initialize the instance variable but only allocate the time dimension (the first dimension). We will add the boards for various time ticks later.) The current time tick instance variable should be set to 0. Finally, the constructor should also create a clone of the starting board and make the clone be the board at time tick 0 in the 3D array instance variable. 3 18 - (The darker cells are the neighbours of c in this diagram.) . Each cell that is on an edge of the 2D array (except corner cells) has five neighbours, like cells ct, Cr, c), and c in the following diagram: CE CL Each corner cell of the 2D array has only three neighbours: Ci CA Here are the rules for computing the next state of a cell: If the cell is currently alive and has exactly two or three live neighbours, it is alive after the transition. . If the cell is currently alive, but does NOT have exactly two or three live neighbours, it is dead after the transition. If the cell is currently dead and has exactly three live neighbours, then it is alive after the transition If the cell is currently dead, but does not have exactly three live neighbours, then it stays dead after the transition Here's a sample sequence of transitions from a starting board to show you how the rules work (the dark cells are alive and the white cells are dead. If the cell is currently dead and has exactly three live neighbours, then it is alive after the transition. If the cell is currently dead, but does not have exactly three live neighbours, then it stays dead after the transition. Here's a sample sequence of transitions from a starting board to show you how the rules work (the dark cells are alive and the white cells are dead): At time tick 0: At time tick 1: At time tick 2: At time tick 3: Testing Your Code We have provided sample test files for each phase to help you verify that your code is working to the assignment specifications (e.g., correct method headers). These files are only starting points for testing your code. Part of developing your skills as a programmer is to think through additional important test cases and to write your own code to test these cases. The test files should give you a sense what this additional code could consist of. 2 Phase 1: We are going to implement the Game of Life using two-dimensional arrays of ints (called "boards"). Each int in a board is a cell - if the cell is alive, then the corresponding int is 1, and if the cell is dead, then the corresponding int is 0. At each time tick, all the cells evolve simultaneously we get a new board. We are going to store all the different boards, starting at time tick 0, in an array of boards we're really going to be working with a three dimensional array of ints. The extra dimension in the array represents time. In this phase, implement a simple class GameOfLife, which should have: . Two instance variables: the three dimensional array of ints representing the boards over time, and another variable (an int) that contains the current time tick that is, the variable tells you how many times the starting board at time tick () has been evolved so far. A class (static method cloneOneBoard that accepts a board (a 2D array of ints) as a parameter and returns a clone (deep copy) of it. Use the following header: public static int[] [] cloneOneBoard( int[[] board) A constructor that accepts a starting board (a 2D array of ints) and a number, n, of time ticks (an int). The constructor should initialize the 3D array instance variable so that it can hold boards for n time ticks (including the starting board at time tick 0). (You should initialize the instance variable but only allocate the time dimension (the first dimension). We will add the boards for various time ticks later.) The current time tick instance variable should be set to 0. Finally, the constructor should also create a clone of the starting board and make the clone be the board at time tick 0 in the 3D array instance variable. 3 18 - Use the current time tick to figure out which board in the array is the most recent board. (Every row should start with 3 blanks and there should be a newline character " " between cach pair of rows.) An equals method that accepts a board as a parameter. The method should return true if the current board in the array of boards and the parameter board are the same size and the cells are the same; otherwise, the method should return false. Note: You should add more helper methods as needed to make the required methods short. You can test your class using the supplied test program TestA2Phase1.java. You should get the output below. Phase 1 Testing: Testing the newState method: A live cell with 1 live neighbours will be dead A dead cell with 1 live neighbours will be dead A live cell with 2 live neighbours will be live A dead cell with 2 live neighbours will be dead A live cell with 3 live neighbours will be live A dead cell with 3 live neighbours will be live A live cell with 4 live neighbours will be dead A dead cell with 4 live neighbours will be dead Now trying multiple evolutions of the whole board: Maximum time tick allowed: 9 At time tick 0: Current time tick = 0 4 18 Two accessor methods: getCurrentTick, which returns the current time tick that is, it returns the time tick of the most recently created board stored in the 3D array instance variable. getMaxTick, which returns the time tick that would be associated with the last position in the 3D array instance variable that is, if we filled up the 3D array instance variable completely, what would be the time tick associated with the last board created? (Remember: Time tick 0 is the time tick of the starting board.) An instance method newState that accepts a cell's current state and the number of live neighbours it currently has. The method should return the new state of the cell after the next time tick, using the rules above. Use the following header: public int newState( int cellCurrentState, int numLiveNeighbours ) An instance method evolveOnce that first checks if the current time tick is less that the length of the time dimension (the first dimension) of the array of boards this check ensures that we have room for one more board in the array of boards. If there is room for one more board in the array, then it creates a new board (the same size as the starting board), puts it into the 3D array as the board at the next time tick, transitions all cells (puts their new states into the new board), and increments the current time tick to the new time tick. (If there is no room for one more board in the array of boards, then this method should do nothing.) Use the following header: public void evolveOnce() Two accessor methods: getCurrentTick, which returns the current time tick that is, it returns the time tick of the most recently created board stored in the 3D array instance variable. getMaxTick, which returns the time tick that would be associated with the last position in the 3D array instance variable that is, if we filled up the 3D array instance variable completely, what would be the time tick associated with the last board created? (Remember: Time tick 0 is the time tick of the starting board.) An instance method newState that accepts a cell's current state and the number of live neighbours it currently has. The method should return the new state of the cell after the next time tick, using the rules above. Use the following header: public int newState( int cellCurrentState, int numLiveNeighbours ) An instance method evolveOnce that first checks if the current time tick is less that the length of the time dimension (the first dimension) of the array of boards this check ensures that we have room for one more board in the array of boards. If there is room for one more board in the array, then it creates a new board (the same size as the starting board), puts it into the 3D array as the board at the next time tick, transitions all cells (puts their new states into the new board), and increments the current time tick to the new time tick. (If there is no room for one more board in the array of boards, then this method should do nothing.) Use the following header: public void evolveOnce() Use the current time tick to figure out which board in the array is the most recent board. (Every row should start with 3 blanks and there should be a newline character " " between cach pair of rows.) An equals method that accepts a board as a parameter. The method should return true if the current board in the array of boards and the parameter board are the same size and the cells are the same; otherwise, the method should return false. Note: You should add more helper methods as needed to make the required methods short. You can test your class using the supplied test program TestA2Phase1.java. You should get the output below. Phase 1 Testing: Testing the newState method: A live cell with 1 live neighbours will be dead A dead cell with 1 live neighbours will be dead A live cell with 2 live neighbours will be live A dead cell with 2 live neighbours will be dead A live cell with 3 live neighbours will be live A dead cell with 3 live neighbours will be live A live cell with 4 live neighbours will be dead A dead cell with 4 live neighbours will be dead Now trying multiple evolutions of the whole board: Maximum time tick allowed: 9 At time tick 0: Current time tick = 0 4 18 001 111 010 At time tick 1: Current time tick = 1 001 101 111 At time tick 2: Current time tick = 2 010 101 101 At time tick 3: Current time tick = 3 010 101 000 Current time tick at very end: 3 Phase 2: In this phase, we're going to read in a starting board from a file. Each line of the file contains exactly one int, except the first line, which contains exactly two ints. A starting board is stored in a file as follows















