Question
Pinto.com has developed a powerful new server that would be used for corporations' Internet activities. It would cost $25 million at Year 0 to buy
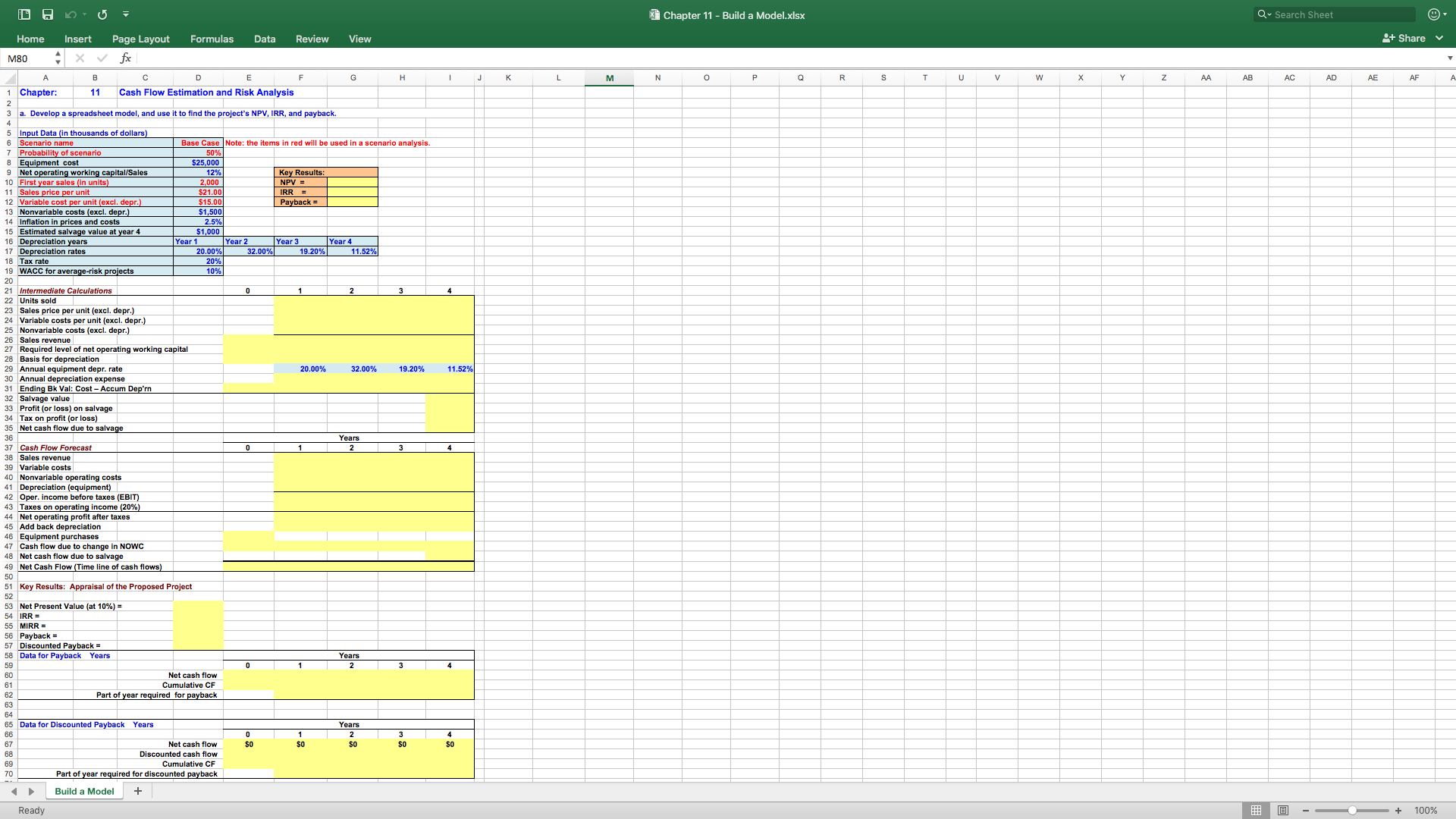
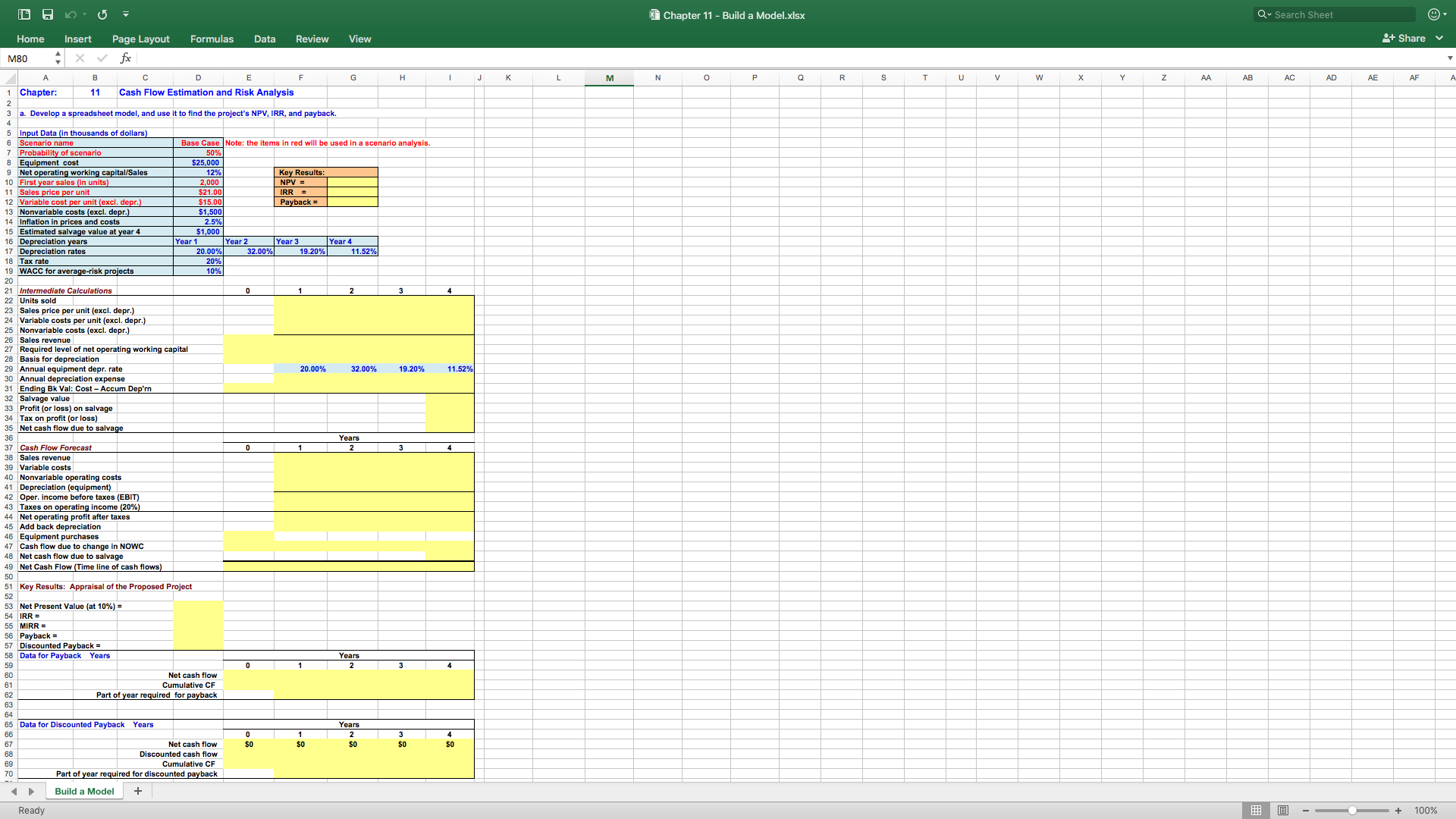
Pinto.com has developed a powerful new server that would be used for corporations' Internet activities. It would cost $25 million at Year 0 to buy the equipment necessary to manufacture the server. The project would require net working capital at the beginning of each year in an amount equal to 12% of the year's projected sales; for example, NWC0= 12%(Sales1). The servers would sell for $21,000 per unit, and Pinto believes that variable costs would amount to $15,000 per unit. After Year 1, the sales price and variable costs will increase at the inflation rate of 2.5%. The company's nonvariable costs would be $1.5 million at Year 1 and would increase with inflation. The server project would have a life of 4 years. If the project is undertaken, it must be continued for the entire 4 years. Also, the project's returns are expected to be highly correlated with returns on the firm's other assets. The firm believes it could sell 2,000 units per year. The equipment would be depreciated over a 5-year period, using MACRS rates. The estimated market value of the equipment at the end of the project's 4-year life is $1 million. Pinto.com's federal-plus-state tax rate is 20%. Its cost of capital is 10% for average-risk projects, defined as projects with a coefficient of variation of NPV between 0.8 and 1.2. Low-risk projects are evaluated with an 8% project cost of capital and high-risk projects at 13%.
- Develop a spreadsheet model, and use it to find the project's NPV, IRR, and payback.
- Now conduct a sensitivity analysis to determine the sensitivity of NPV to changes in the sales price, variable costs per unit, and number of units sold. Set these variables' values at 10% and 20% above and below their base-case values.
- Now conduct a scenario analysis. Assume that there is a 25% probability that best-case conditions, with each of the variables discussed in Part b being 20% better than its base-case value, will occur. There is a 25% probability of worst-case conditions, with the variables 20% worse than base, and a 50% probability of base-case conditions.
- If the project appears to be more or less risky than an average project, find its risk-adjusted NPV, IRR, and payback.
- On the basis of information in the problem, would you recommend the project should be accepted?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


