Question
Plan production for a four-month period: February through May. For February and March, you should produce to exact demand forecast. For April and May, you
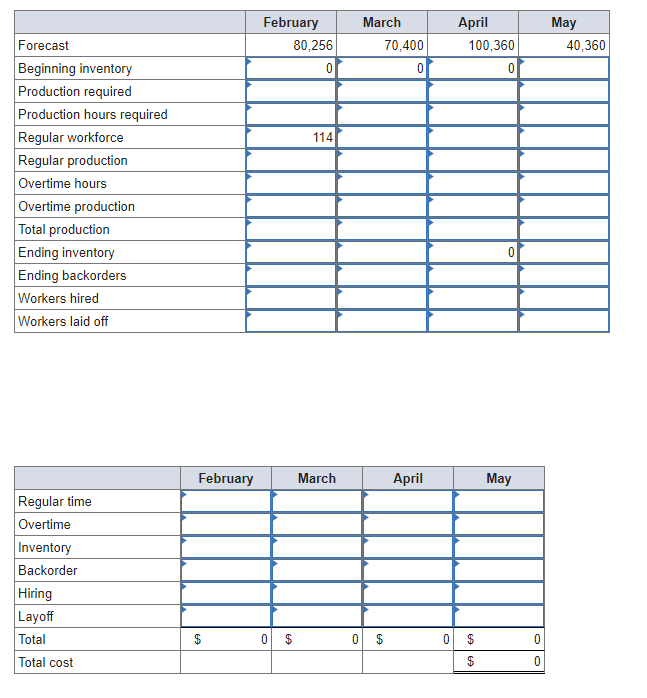
Plan production for a four-month period: February through May. For February and March, you should produce to exact demand forecast. For April and May, you should use overtime and inventory with a stable workforce; stable means that the number of workers needed for March will be held constant through May. However, government constraints put a maximum of 5,000 hours of overtime labor per month in April and May (zero overtime in February and March). If demand exceeds supply, then backorders occur. There are 100 workers on January 31. You are given the following demand forecast: February, 80,256; March, 70,400; April, 100,360; May, 40,360. Productivity is four units per worker hour, eight hours per day, 22 days per month. Assume zero inventory on February 1. Costs are: hiring, $45 per new worker; layoff, $65 per worker laid off; inventory holding, $10 per unit-month; regular time labor, $10 per hour; overtime, $15 per hour; backorder, $20 per unit. Develop a production plan and calculate the total cost of this plan. Note: Assume any layoffs occur at beginning of next month. (Leave the cells blank, whenever zero (0) is required. Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round your answers to the nearest whole number.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


