Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
LAB 10: THIN LENSES PURPOSE You will observe the location of images produced by thin lenses, and verify the thin lens equation for several

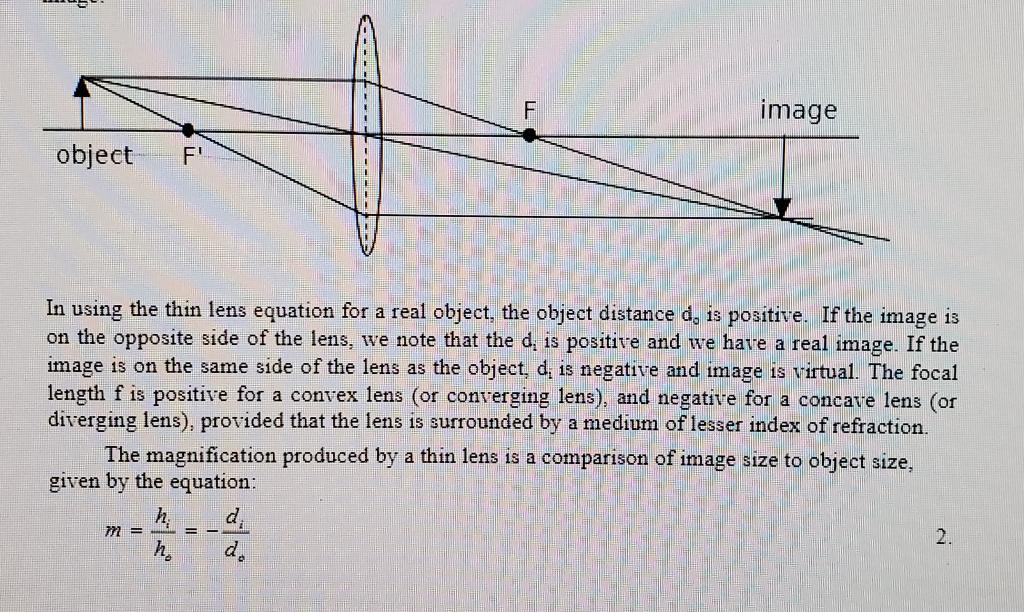


LAB 10: THIN LENSES PURPOSE You will observe the location of images produced by thin lenses, and verify the thin lens equation for several different object positions. APPARATUS Optical bench, source light, screen, converging lens, object arrows. INTRODUCTION The image produced by a thin lens may be real or virtual. A real image can be projected on a screen, a virtual one cannot. In addition, the image may be upright or inverted, it may be larger or smaller than the object, and it may located either side of the lens. The image location and its other properties can be deduced from a knowledge of the object position and focal length of the lens, using the thin lens equation: 1 1 1 do d; + = 1. where do = object distance, di image distance and f = focal length. The image can also be located using a ray diagram as shown below for a convex lens. F is the focal point of the lens. One ray is chosen to run parallel to the optical axis, and is refracted thru F. A second ray is drawn through the focal point F' and emerges from the lens parallel to the optical axis. The other ray goes straight through the center of the lens. Together they define the arrow point of the image. object F' m = F In using the thin lens equation for a real object, the object distance d, is positive. If the image is on the opposite side of the lens, we note that the d, is positive and we have a real image. If the image is on the same side of the lens as the object, d, is negative and image is virtual. The focal length f is positive for a convex lens (or converging lens), and negative for a concave lens (or diverging lens), provided that the lens is surrounded by a medium of lesser index of refraction. The magnification produced by a thin lens is a comparison of image size to object size, given by the equation: h d h == image 2. 1. 2. 3. Lab 10: Thin Lenses PROCEDURE: Determine the focal length, f, of a converging lens in air using a distant object or light source (Distant means at least 10 meters away, the farther the better). f = 19.8 cm Measure the length of the arrow that is the object for the lenses. Using the optical bench, the converging lens, the light source and the hooded screen measure the image size and location for the three cases below. 1) d. = 3f 2) d = 2f 3) d = 1.5f Also determine whether the images in these three cases are real or virtual; upright or inverted. Present your results in a table of the form illustrated below. 2 Case 1. d. = 3f 2. d = 2f 3. d. = 1.5f 4. d. d real? virtual? upright? inverted? Draw a quantitatively accurate ray diagram for case 1 (do-3f) in part 3. (Use graph paper. Make the vertical scale larger than the horizontal scale, e.g. you might make the object height 4cm on the vertical scale and the focal length 4cm on the horizontal scale.)
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.46 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
i for do 3 f RP Given f 198com from lens formula sin...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


