Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
please answer all. Liquid extraction is an operation used to separate the components of a liquid mixture of two or more species. In the simplest

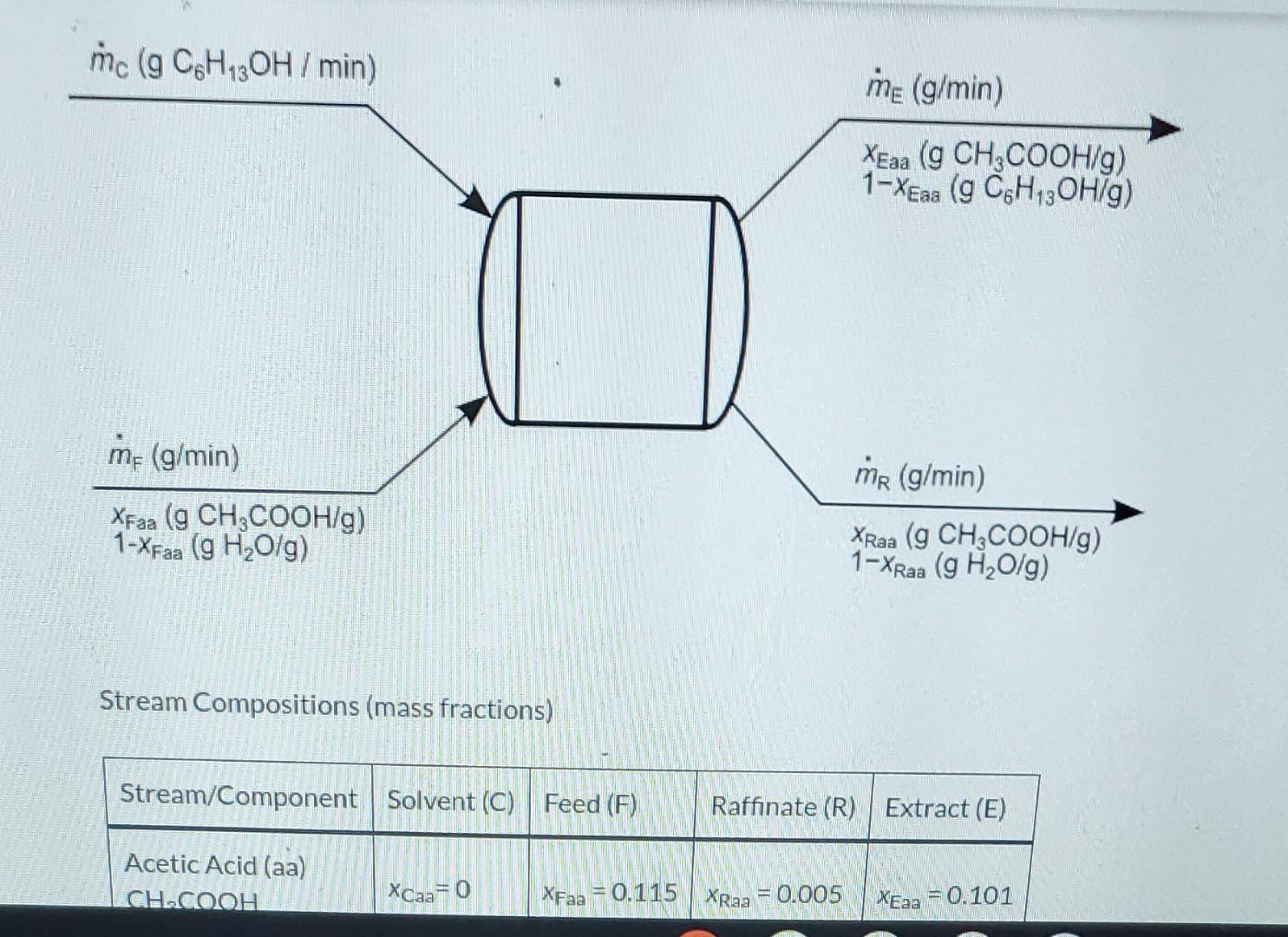
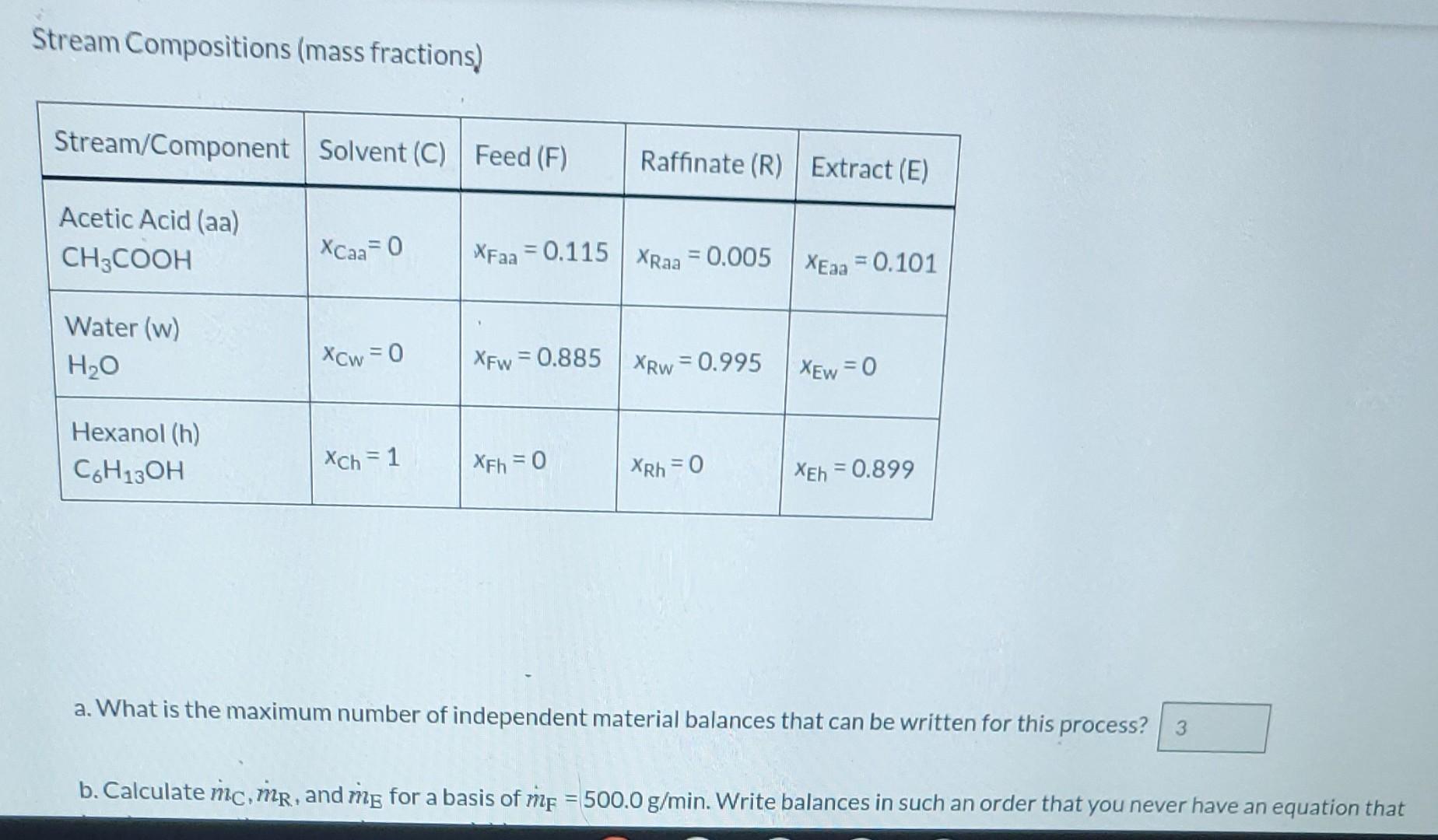

please answer all.
Liquid extraction is an operation used to separate the components of a liquid mixture of two or more species. In the simplest case, the mixture contains two components: a solute (A) and a liquid solvent (B). The mixture is contacted in an agitated vessle with a second liquid solvent (C) that has two key properties: A dissolves in it, and B is immiscible or nearly immiscible with it. (For example, B may be water, C a hydrocarbon oil, and A a species that has significant solubility in both water and oil.) Some of the A transfers from B to C, and then the B-rich phase (the raffinate) and the C-rich phase (the extract) separate from each other in a settling tank. If the raffinate is then contacted with fresh C in another stage, more A will be transferred from it. This process can be repeated until essentially all of the A has been extracted from the B. Shown below is a flowchart of a process in which acetic acid (aa) is extracted from a mixture of acetic acid and water (w) into 1-hexanol (h), a liquid immiscible with water. mc (g C6H12OH / min) me (g/min) XEaa (g CH2COOH/g) 1-X..lad.HOHla mc (g C6H12OH / min) me (g/min) XEaa (g CH3COOH/g) 1 - XEaa (g CH3OH/g) mi (g/min) me (g/min) XFaa (g CH3COOH/g) 1-XFaa (g H2O/g) XRaa (g CH,COOH/g) 1-XRaa (g H2O/g) Stream Compositions (mass fractions) Stream/Component Solvent (C) Feed (F) Raffinate (R) Extract (E) Acetic Acid (aa) CHOCOOH XCaa=0 XFaa = 0.115 XRaa = 0.005 XEag = 0.101 Stream Compositions (mass fractions) Stream/Component Solvent (C) Feed (F) Raffinate (R) Extract (E) Acetic Acid (aa) CH3COOH Xcaa=0 XFaa = 0.115 XRaa = 0.005 XEaa =0.101 Water (w) HO Xow=0 XFw = 0.885 XRw = 0.995 XEw=0 Hexanol (h) C6H130H Xch=1 XEh =0 XRh = 0 XEh = 0.899 a. What is the maximum number of independent material balances that can be written for this process? 3 b. Calculate mc, mr, and mig for a basis of me = 500.0 g/min. Write balances in such an order that you never have an equation that a. What is the maximum number of independent material balances that can be written for this process? 3 b. Calculate mic, mr, and mg for a basis of mp = 500.0 g/min. Write balances in such an order that you never have an equation that involves more than one unknown variable. nic g/min mr 11 g/min 11 g/min c. Calculate the mass flow rates of acetic acid in the feed stream, the extract stream, and the raffinate stream Acetic acid entering system: i g/min Acetic acid leaving in extract: i g/min Acetic acid leaving in raffinate: i g/minStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


