Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
please answer all parts options for blanks (in order from first to last): Bond valuations and yields: What do they mean, and how do you
please answer all parts
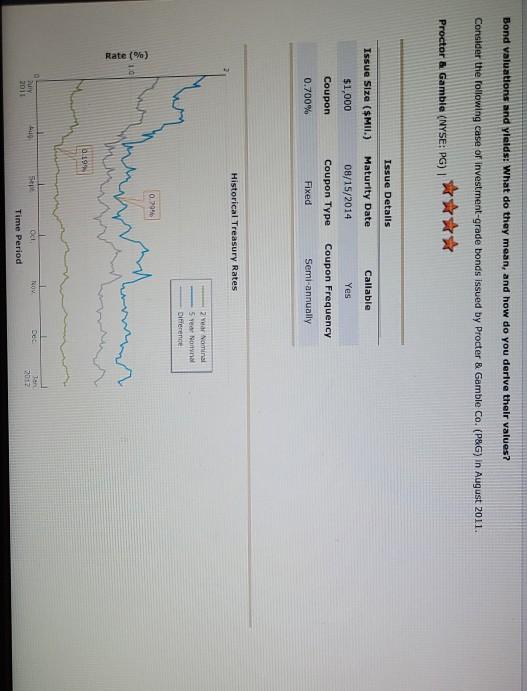
options for blanks (in order from first to last):
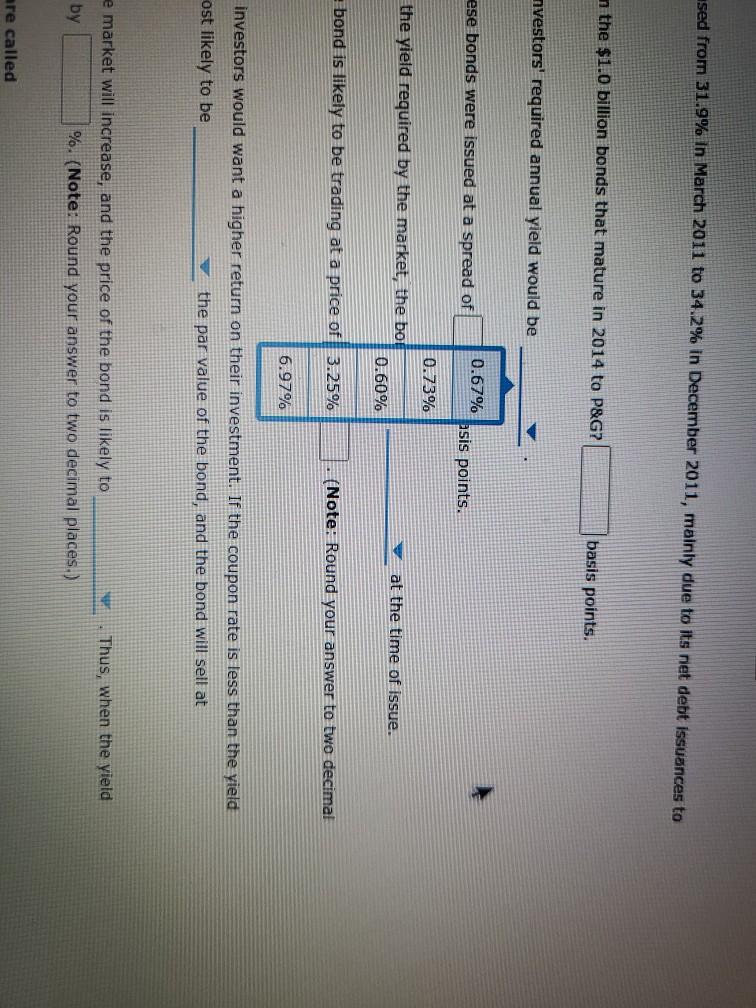
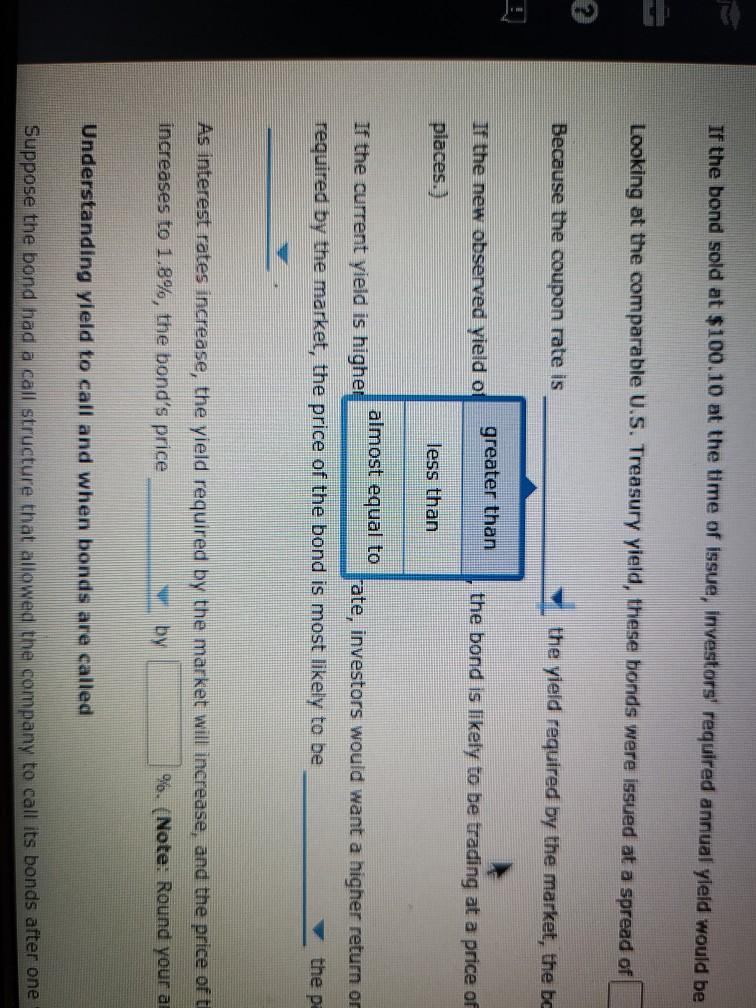
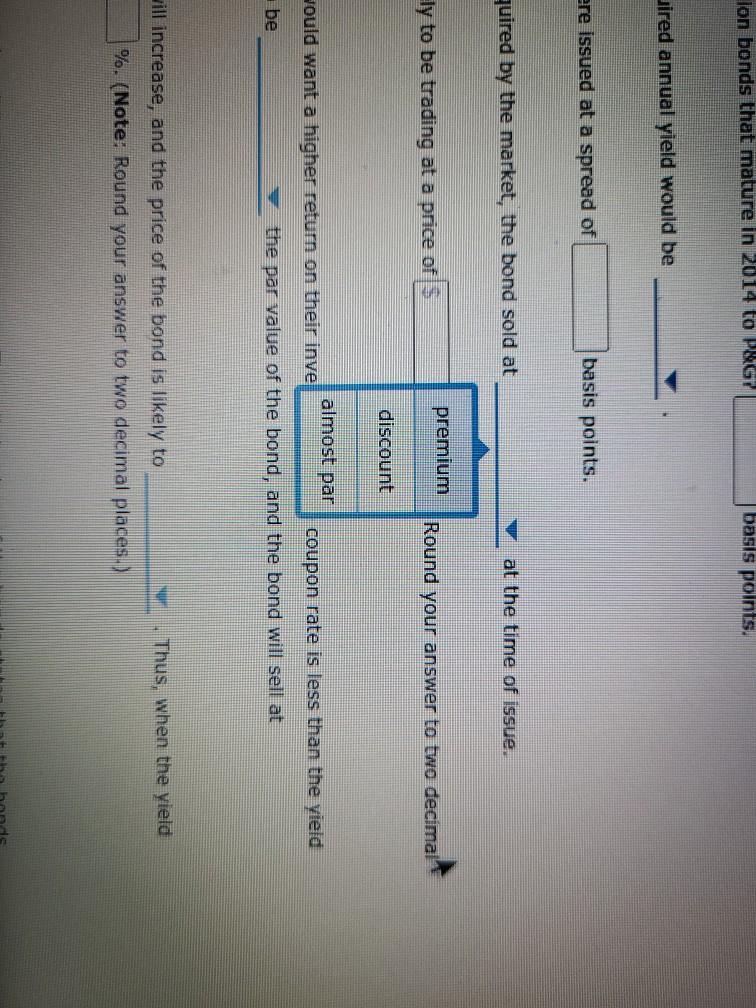
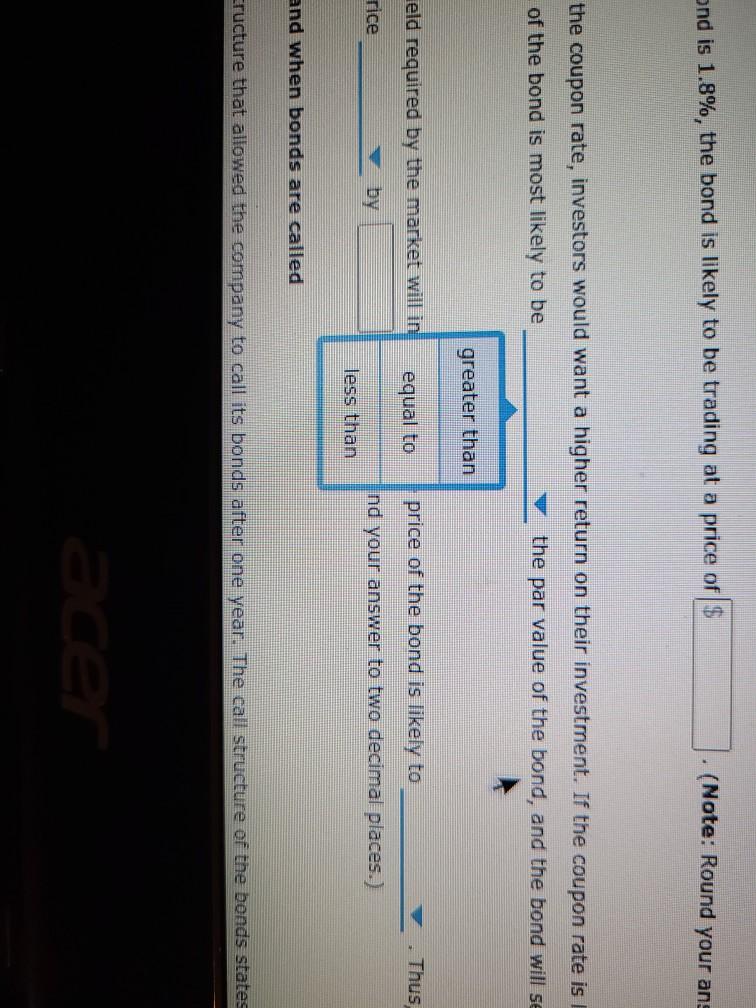
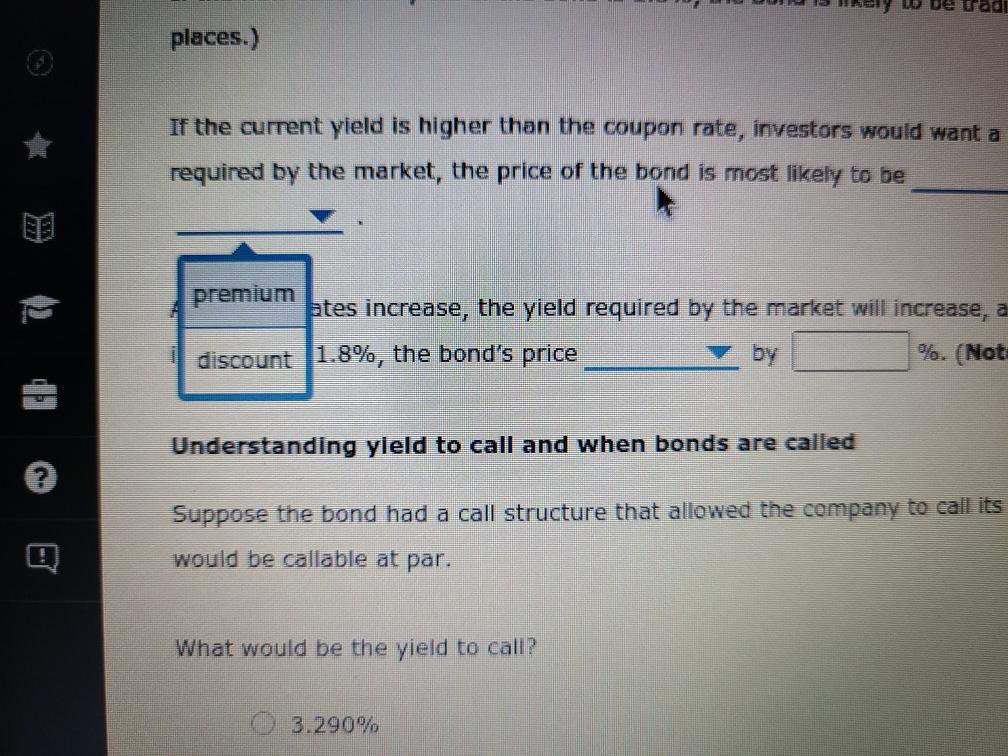
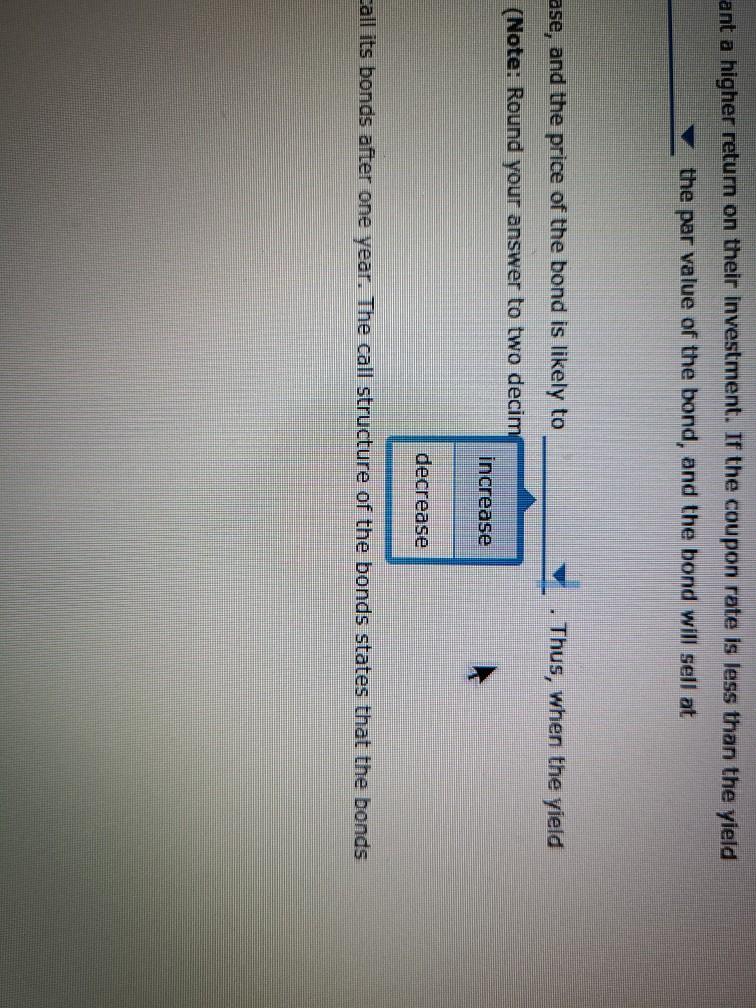
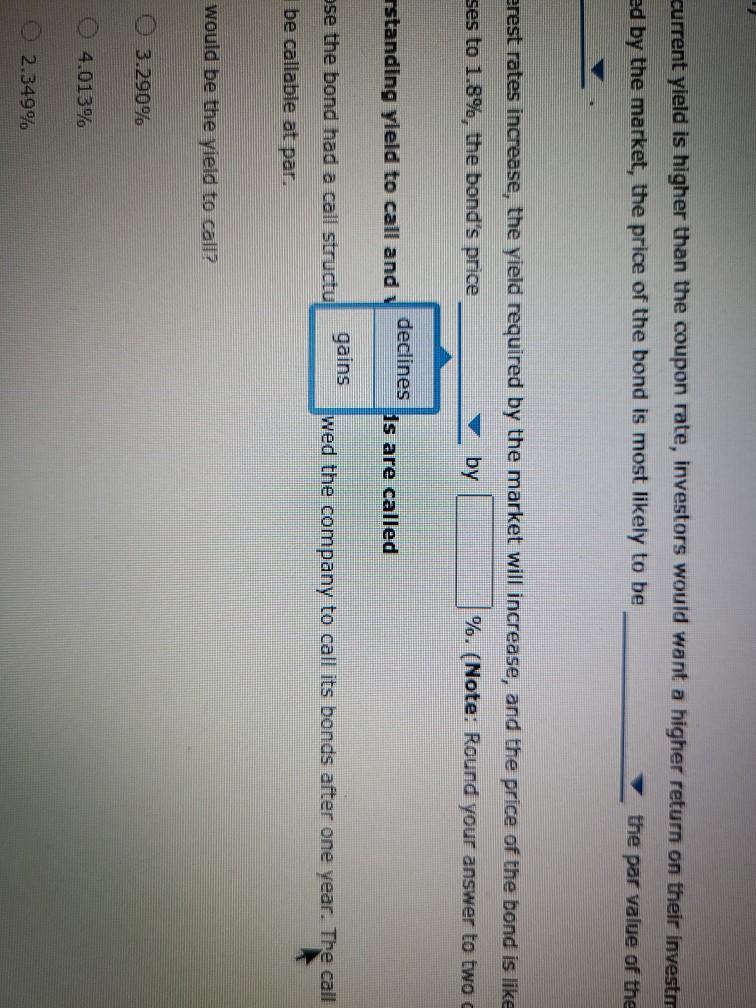
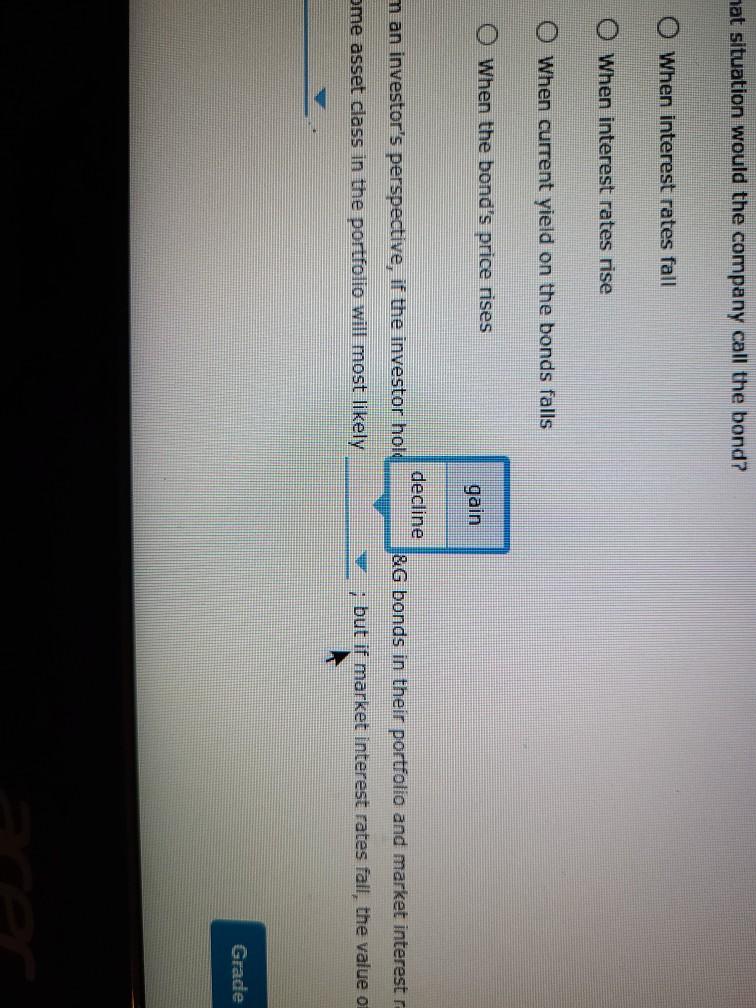
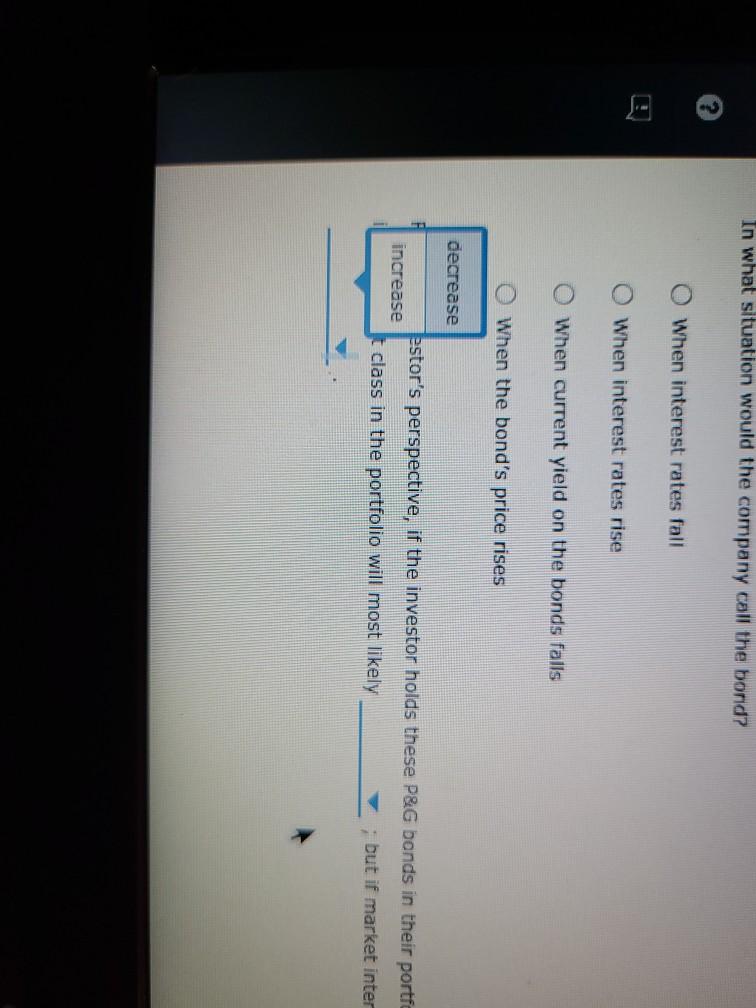
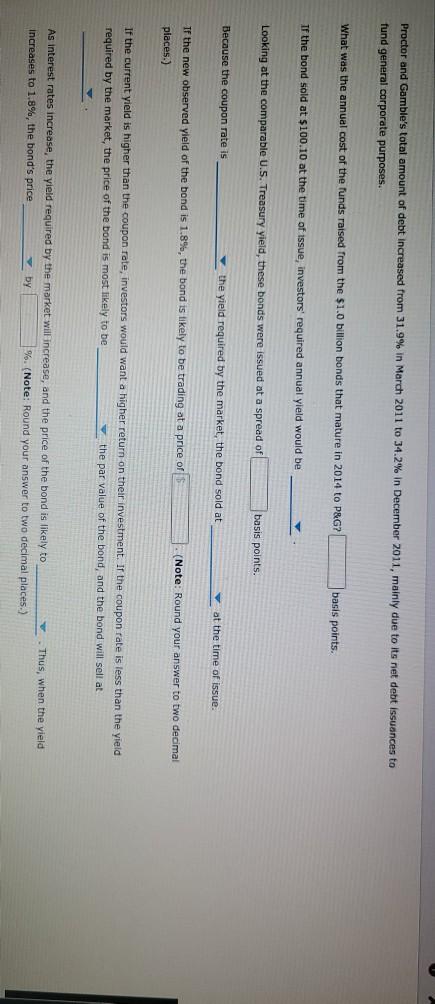
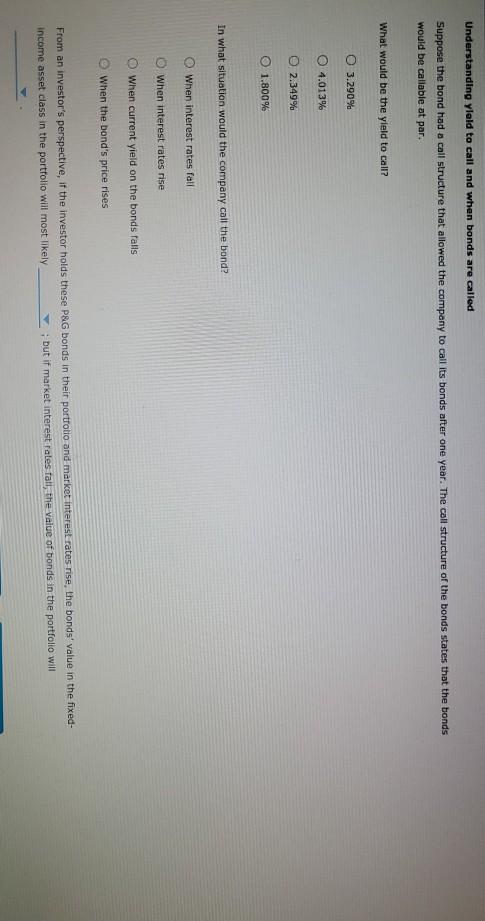
Bond valuations and yields: What do they mean, and how do you derive their values? Consider the following case or investment-grade bonds issued by Procter & Gamble Co. (P&G) in August 2011. Proctor & Gamble (NYSE: PG) Issue Details Issue Size ($MII.) Maturity Date Callable $1,000 08/15/2014 Yes Coupon Coupon Type Coupon Frequency 0.700% Fixed Semi-annually Historical Treasury Rates 2 Year Namini 5 Year Nonna Difference 0.79 Rate(%) 0:19 Quy 5 Aug Dec 10V OCH Time Period 2017 Proctor and Gamble's total amount of debt increased from 31.9% in March 2011 to 34.2% in December 2011, mainly due to its net debt issuances to fund general corporate purposes. What was the annual cost of the funds raised from the $1.0 billion bonds that mature in 2014 to P&G? basis points. If the bond sold at $100.10 at the time of issue, investors' required annual yield would be Looking at the comparable U.S. Treasury yield, these bonds were issued at a spread of basis points. Because the coupon rate is the yield required by the market, the bond sold at at the time of issue. If the new observed yield of the bond is 1.8%, the bond is likely to be trading at a price of 5 places.) (Note: Round your answer to two decimal If the current yield is higher than the coupon rate, investors would want a higher return on their investment. If the coupon rate is less than the yield required by the market, the price of the bond most likely to be the par value of the bond, and the bond will sell at As interest rates increase, the yield required by the market will increase, and the price of the bond likely to increases to 1.8%, the bond's price by %. (Note: Round your answer to two decimal places.) Thus, when the yield Understanding yield to call and when bonds are called Suppose the bond had a call structure that allowed the company to call its bonds after one year. The call structure of the bonds states that the bonds would be callable at par What would be the yield to call? 0 3.290% 4.013% 2.349% O 1.800% In what situation would the company call the bond? When interest rates fall When interest rates rise When current yield on the bonds falls When the bond's price rises From an investor's perspective, if the investor holds these P&G bonds in their portfolio and market interest rates-rise, the bonds' value in the fixed- Income asset class in the portfolio will most likely ; but if market interest rates fall, the value of bonds in the portfolio will ased from 31.9% In March 2011 to 34.2% in December 2011, mainly due to its net debt issuances to n the $1.0 billion bonds that mature in 2014 to P&G? basis points. nvestors' required annual yield would be ese bonds were issued at a spread of 0.67% asis points. 0.73% the yield required by the market, the bol 0.60% at the time of issue. bond is likely to be trading at a price of 3.25% (Note: Round your answer to two decimal 6.97% investors would want a higher return on their investment. If the coupon rate is less than the yield ost likely to be the par value of the bond, and the bond will sell at Thus, when the yield e market will increase, and the price of the bond is likely to by %. (Note: Round your answer to two decimal places.) are called If the bond sold at $100.10 at the time of issue, investors' required annual yleid would be Looking at the comparable U.S. Treasury yield, these bonds were issued at a spread of Because the coupon rate is the yield required by the market, the bo If the new observed vield of greater than the bond is likely to be trading at a price of places.) less than almost equal to If the current yield is higher fate, investors would want a higher return on required by the market, the price of the bond is most likely to be the pa As interest rates increase, the yield required by the market will increase, and the price of t increases to 1.8%, the bond's price by 9. (Note: Round your a Understanding yield to call and when bonds are called Suppose the bond had a call structure that allowed the company to call its bonds after one Jon bonds that mature in 2014 to P&G basis points. uired annual yield would be ere issued at a spread of basis points. quired by the market, the bond sold at at the time of issue. premium ly to be trading at a price of Round your answer to two decimal discount almost par would want a higher return on their inve coupon rate is less than the vield be the par value of the bond, and the bond will sell at Thus, when the yield will increase, and the price of the bond is likely to %. (Note: Round your answer to two decimal places.) and is 1.8%, the bond is likely to be trading at a price of $ (Note: Round your ans the coupon rate, investors would want a higher return on their investment. If the coupon rate is of the bond is most likely to be the par value of the bond, and the bond will se greater than eld required by the market will in equal to Thus price of the bond is likely to nd your answer to two decimal places.) rice by less than and when bonds are called Eructure that allowed the company to call its bonds after one year. The call structure of the bends states be a places.) If the current yield is higher than the coupon rate, investors would want a required by the market, the price of the bond is most likely to be premium ates increase, the yield required by the market will increase, a discount 1.8%, the bond's price %. (Not Understanding yield to call and when bonds are called Suppose the bond had a call structure that allowed the company to call its would be callable at par. What would be the yield to call? 3.290% ant a higher return on their investment. If the coupon rate is less than the yield the par value of the bond, and the bond will sell at Thus, when the yield ase, and the price of the bond is likely to (Note: Round your answer to two decim increase decrease call its bonds after one year. The call structure of the bonds states that the bonds current yield is higher than the coupon rate, investors would want a higher return on their investor ed by the market, the price of the bond is most likely to be the par value of the erest rates increase, the yield required by the market will increase, and the price of the bond is like ses to 1.8%, the bond's price by %. (Note: Round your answer to two declines rstanding yield to call and y Is are called gains ose the bond had a call structu wed the company to call its bonds after one year. The call be callable at par. would be the yield to call? 3.2907 4.013% 2.349% hat situation would the company call the bond? O When interest rates fall O When interest rates rise When current yield on the bonds falls When the bond's price rises gain decline man investor's perspective, if the investor hold &G bonds in their portfolio and market interest ome asset class in the portfolio will most likely ; but if market interest rates fall, the value of Grade In what situation would the company call the bond? When interest rates fall When interest rates rise When current yield on the bonds falls When the bond's price rises decrease estor's perspective, if the investor holds these P&G bands in their portfe increase t class in the portfolio will most likely but if market inter
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


