Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
please answer as soon as possible for thumbs up Question 3 (13 marks) You are recording from a neuromuscular junction. You have a stimulating electrode
please answer as soon as possible for thumbs up 
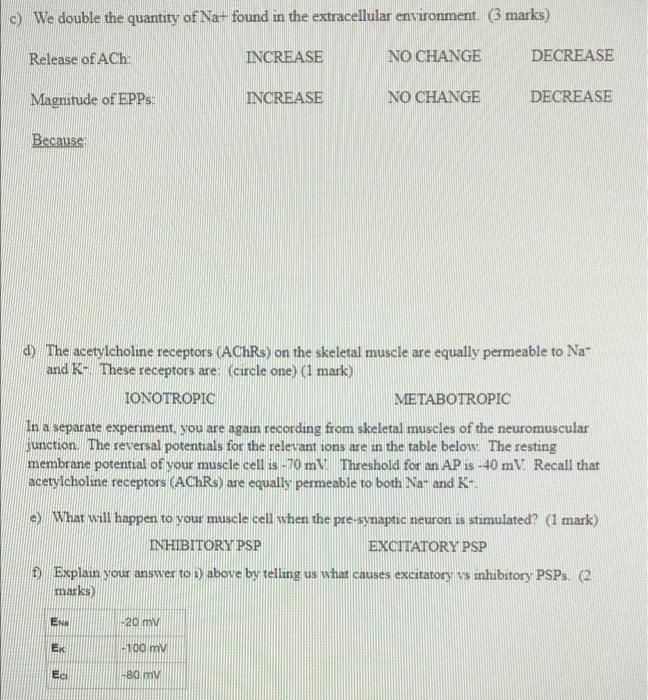
Question 3 (13 marks) You are recording from a neuromuscular junction. You have a stimulating electrode in the axon terminal of the pre-synaptic neuron and are recording from the muscle cell. Stimulation from the electrode is able to directly activate all voltage-gated Cap- channels. Under control conditions, stimulating your pre-synaptic neuron leads to a post-synaptic potential (called EPP in muscles) in the muscle. You perform a series of experiments outlined below. For each experiment, tell us 1) what will happen to the release of ACh from the presynaptic terminal, and 2) what will happen to the magnitude of postsynaptic EPPs, compared to controls when you stimulate the neuron once with the stimulating electrode. For each explain WHY Consider each experiment separately. a) A chemical called BAPTA - which instantly removes all Ca.- - is included in the intracellular solution of the pre-synaptic neuron. (3 marks) Release of ACH INCREASE NO CHANGE DECREASE Magnitude of EPP INCREASE NO CHANGE DECREASE Because b) We block all voltage-gated K-channels in the neuron and muscle cell. (3 marks) Release of ACH: INCREASE NO CHANGE DECREASE Magnitude of EPP INCREASE NO CHANGE DECREASE Because c) We double the quantity of Nat found in the extracellular environment. 3 marks) Release of Ach INCREASE NO CHANGE DECREASE Magnitude of EPPs: INCREASE NO CHANGE DECREASE Because d) The acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) on the skeletal muscle are equally permeable to Na and These receptors are: (circle one) (1 mark) IONOTROPIC METABOTROPIC In a separate experiment, you are again recording from skeletal muscles of the neuromuscular junction. The reversal potentials for the relevant ions are in the table below. The resting membrane potential of your muscle cell is -70 m Threshold for an AP is -40 mV. Recall that acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) are equally permeable to both Na- and K- e What will happen to your muscle cell when the pre-synaptic neuron is stimulated? (1 mark) INHIBITORY PSP EXCITATORY PSP Explain your answer to ) above by telling us what causes excitatory s inhibitory PSPS. (2 marks) ENN -20 my EK 1100 mv Ee 80 mm 

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


