Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
please answer both questions and parts thanks Harold McWilliams owns and manages a general merchandise store in a rural area of Virginia. Harold sells appliances,
please answer both questions and parts thanks 
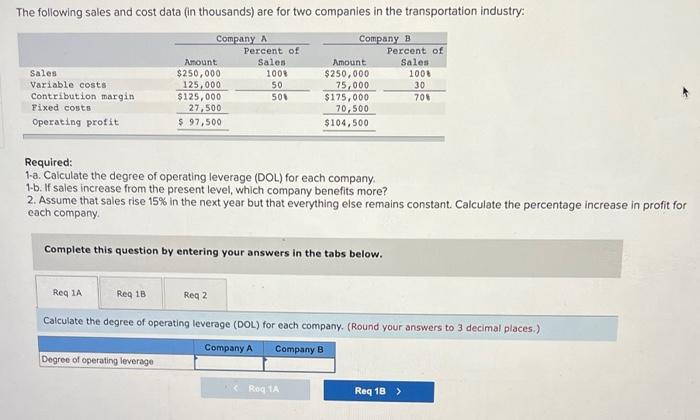
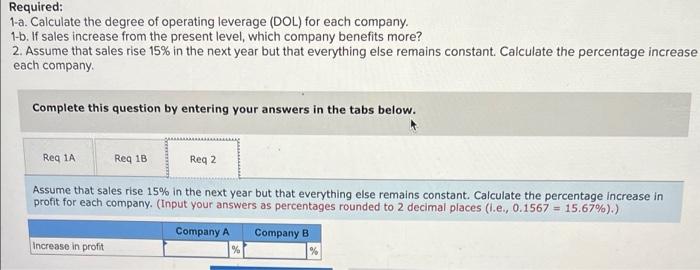
Harold McWilliams owns and manages a general merchandise store in a rural area of Virginia. Harold sells appliances, clothing, auto parts, and farming equipment, among a wide variety of other types of merchandise. Because of normal seasonal and cyclical fluctuations in the local economy, he knows that his business will also have these fluctuations, and he is planning to use CVP analysis to help him understand how he can expect his profits to change with these fluctuations. Harold has the following information for his most recent year. Cost of goods sold represents the cost paid for the merchandise he sells, while operating costs represent rent, insurance, and salaries, which are entirely fixed Sales Cost of merchandise sold Contribution margin Operating costs Operating profit $600,000 384.000 216,000 95,400 $120.600 Required: 1-a. What is Harold's margin of safety (MOS) in dollars? (Do not round intermediate calculations.) 1.b. What is the margin of safety (MOS) ratio? (Input your answer as a percentage rounded to 2 decimal places (ie., 0.1567= 15.67%).) 3. What is Harold's margin of safety in dollars) and operating profit if sales should fall to $525,000? (Do not round intermediate calculations.) 1-a. Margin of safety (MOS) 1.5. MOS ratio 3 Margin of safety Operating profit % The following sales and cost data (in thousands) are for two companies in the transportation industry: Sales Variable costs Contribution margin Fixed costs Operating profit Company A Percent of Amount Sales $250,000 1008 125,000 50 $125,000 500 27,500 $ 97,500 Company 3 Percent of Amount Sales $250,000 1001 75,000 30 $175,000 705 70,500 $104,500 Required: 1-a. Calculate the degree of operating leverage (DOL) for each company, 1-b. If sales increase from the present level, which company benefits more? 2. Assume that sales rise 15% in the next year but that everything else remains constant. Calculate the percentage increase in profit for each company Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req 1A Reg 1B Reg 2 Calculate the degree of operating leverage (DOL) for each company. (Round your answers to 3 decimal places.) Company A Company B Degree of operating leverage ROQ 1A Req 18> Required: 1-a. Calculate the degree of operating leverage (DOL) for each company. 1-b. If sales increase from the present level, which company benefits more? 2. Assume that sales rise 15% in the next year but that everything else remains constant. Calculate the percentage increase each company Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Reg 1A Req 1B Reg 2 Assume that sales rise 15% in the next year but that everything else remains constant. Calculate the percentage Increase in profit for each company. (Input your answers as percentages rounded to 2 decimal places (.e., 0.1567 = 15.67%).) Company A Company B Increase in profit % 


Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


