Please answer E, F & G with clear explanations
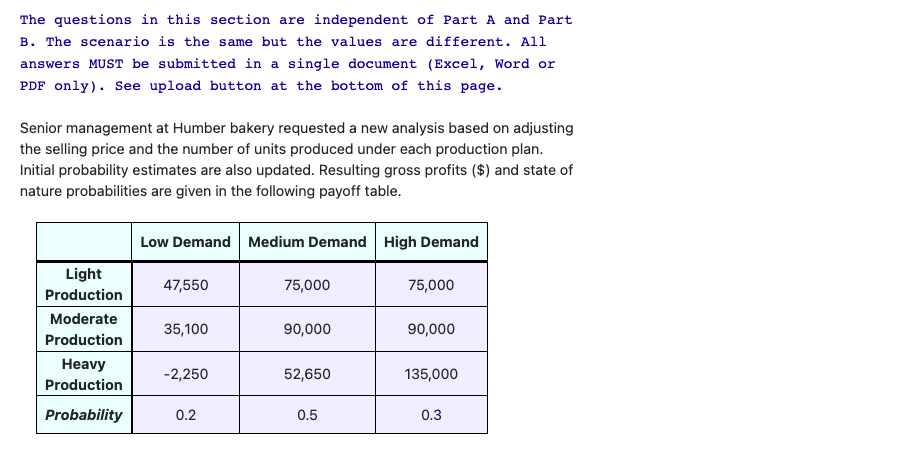

The questions in this section are independent of Part A and Part B. The scenario is the same but the values are different. All answers MUST be submitted in a single document (Excel, Word or PDF only). See upload button at the bottom of this page. Senior management at Humber bakery requested a new analysis based on adjusting the selling price and the number of units produced under each production plan. Initial probability estimates are also updated. Resulting gross profits ($) and state of nature probabilities are given in the following payoff table. Low Demand Medium Demand High Demand Light Production 47,550 75,000 75,000 Moderate 35,100 90,000 90,000 Production Heavy -2,250 52,650 135,000 Production Probability 0.2 0.5 0.3 The new analysis also necessitated updating the offer made to Bramptinos under the heavy production plan. The probability that Bramptinos will accept the new offer is 26% and the associated gross profit is determined to be $121,500. Again here, if Bramptinos declines the offer, the loaves will still sell based on current demand conditions (low, medium, or high). b) [8 marks] Using the decision tree you selected from Part B along with the payoffs and probabilities provided in this section, construct a decision tree for the problem. (You can draw manually or use software. Marks will be given for presentation). What is the optimal decision in this case? Why? Before making a final decision on the production plan to adopt, the bakery's manager decides to contact Professor Leung in the Math Department to conduct a market research survey. The results of the survey will indicate either favourable or unfavourable market conditions for premium breads. In the past, when there was Low Demand, Professor Leung's predictions were unfavorable 80% of the time. The professor's predictions have also been favourable given Medium Demand 88% of the time, and unfavourable given High Demand 10% of the time. c) [12 marks] Calculate posterior (revised) probabilities (Round to 3 decimal places; do not round intermediate results). Show calculations or tables. d) [25 marks] Construct a multistage decision tree (based on part b) with the additional information from Professor Leung. e) [2 marks] What is the value of the sample information (EVSI) provided by Professor Leung? f) [3 marks] State the optimal decision strategy if Professor Leung's consulting fees were $500. g) [2 marks] Does the strategy change if Professor Leung's consulting fees were $1,500? If yes, state the new optimal strategy? If no, explain. The questions in this section are independent of Part A and Part B. The scenario is the same but the values are different. All answers MUST be submitted in a single document (Excel, Word or PDF only). See upload button at the bottom of this page. Senior management at Humber bakery requested a new analysis based on adjusting the selling price and the number of units produced under each production plan. Initial probability estimates are also updated. Resulting gross profits ($) and state of nature probabilities are given in the following payoff table. Low Demand Medium Demand High Demand Light Production 47,550 75,000 75,000 Moderate 35,100 90,000 90,000 Production Heavy -2,250 52,650 135,000 Production Probability 0.2 0.5 0.3 The new analysis also necessitated updating the offer made to Bramptinos under the heavy production plan. The probability that Bramptinos will accept the new offer is 26% and the associated gross profit is determined to be $121,500. Again here, if Bramptinos declines the offer, the loaves will still sell based on current demand conditions (low, medium, or high). b) [8 marks] Using the decision tree you selected from Part B along with the payoffs and probabilities provided in this section, construct a decision tree for the problem. (You can draw manually or use software. Marks will be given for presentation). What is the optimal decision in this case? Why? Before making a final decision on the production plan to adopt, the bakery's manager decides to contact Professor Leung in the Math Department to conduct a market research survey. The results of the survey will indicate either favourable or unfavourable market conditions for premium breads. In the past, when there was Low Demand, Professor Leung's predictions were unfavorable 80% of the time. The professor's predictions have also been favourable given Medium Demand 88% of the time, and unfavourable given High Demand 10% of the time. c) [12 marks] Calculate posterior (revised) probabilities (Round to 3 decimal places; do not round intermediate results). Show calculations or tables. d) [25 marks] Construct a multistage decision tree (based on part b) with the additional information from Professor Leung. e) [2 marks] What is the value of the sample information (EVSI) provided by Professor Leung? f) [3 marks] State the optimal decision strategy if Professor Leung's consulting fees were $500. g) [2 marks] Does the strategy change if Professor Leung's consulting fees were $1,500? If yes, state the new optimal strategy? If no, explain








