Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Today is the first day of your summer internship at a cryptocurrency startup. Before you join,the marketing team decided that they want to differentiate
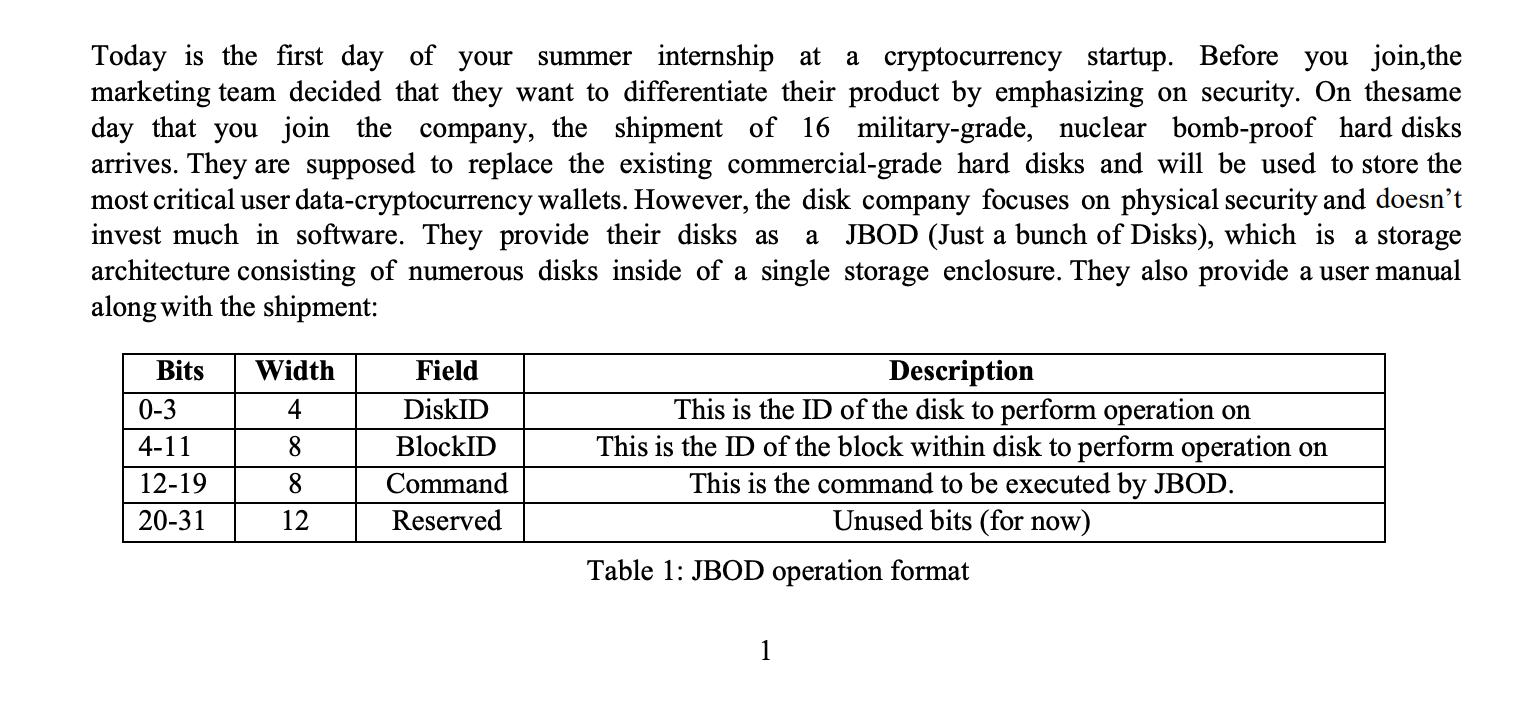




Today is the first day of your summer internship at a cryptocurrency startup. Before you join,the marketing team decided that they want to differentiate their product by emphasizing on security. On thesame day that you join the company, the shipment of 16 military-grade, nuclear bomb-proof hard disks arrives. They are supposed to replace the existing commercial-grade hard disks and will be used to store the most critical user data-cryptocurrency wallets. However, the disk company focuses on physical security and doesn't invest much in software. They provide their disks as a JBOD (Just a bunch of Disks), which is a storage architecture consisting of numerous disks inside of a single storage enclosure. They also provide a user manual along with the shipment: Bits 0-3 4-11 12-19 20-31 Width 4 8 8 12 Field DiskID BlockID Command Reserved Description This is the ID of the disk to perform operation on This is the ID of the block within disk to perform operation on This is the command to be executed by JBOD. Unused bits (for now) Table 1: JBOD operation format 1 Thank you for purchasing our military-grade, nuclear bomb-proof hard disks, built with patented NASA technologies. Each of the disks in front of you consists of i blocks, and each block has 256 bytes. Since you bought j disks, the combined capacity is ixjx 256= 1,048,576 bytes = 1 MB. We provide you with a device driver with a single function that you can use to control the disks. i and j are unknown and integers. int jbod_operation (uint32_t op, uint8_t *block); This function returns 0 on success and -1 on failure. It accepts an operation through the op parameter, the format of which is described in Table 1, and a pointer to a buffer. The command field can be one of the following commands, which are declared as a C enum type in the header that we have provide to you: 1. JBOD_MOUNT: mount all disks in the JBOD and make them ready to serve commands. This is the first command that should be called on the JBOD before issuing any other commands; all commands before JBOD_MOUNT will fail. When the command field of op is set to this command, all other fields in op are ignored bythe JBOD driver. Similarly, the block argument passed to jbod_operation can be NULL. 2. JBOD UNMOUNT: unmount all disks in the JBOD. This is the last command that should be called on the JBOD; all commands after it will fail. When the command field of op is set to this command, all other fields in op are ignored by the JBOD driver. Similarly, the block argument passed to jbod_operation can be NULL. 3. JBOD_SEEK_TO_DISK: seeks to a specific disk. JBOD internally maintains an I/O position, a tuple consisting of {CurrentDiskID, Current BlockID} which determines where the next I/O operation will happen. This command seeks to the beginning of disk specified by DiskID field in op. In other words, it modifies I/O position: it sets CurrentDiskID to DiskID specified in op and it sets CurrentBlockID to 0. When the command field of op is set to this command, the BlockID field in op is ignored by the JBOD driver. Similarly, the block argument passed to jbod_operation can be NULL. 4. JBOD_SEEK_TO_BLOCK: seeks to a specific block in current disk. This command sets the Current- BlockID in I/O position to the block specified in BlockID field in op. When the command field of op is set to this command, the DiskID field in op is ignored by the JBOD driver. Similarly, the block argument passed to jbod_operation can be NULL. 5. JBOD_READ_BLOCK: reads the block in current I/O position into the buffer specified by the block argument to j bod_operation. The buffer pointed by block must be of block size, that is 256 bytes. More importantly, after this operation completes, the CurrentBlockID in I/O position is incre- mented by 1; that is, the next I/O operation will happen on the next block of the current disk. When the command field of op is set to this command, all other fields in op are ignored by the JBODdriver. After you finished I your onboarding session with HR and enjoyed the free lunch with your new colleagues, you received the following email from the manager of the team. 2 Welcome, to the team! Here's your task for the next two weeks. You will be working on integrating JBOD into our existing storage system. Specifically, you will implement one of the functionalities of the mdadm utility in Linux. Mdadm stands for multiple disk and device administration, and it is a tool for doing cool tricks with multiple disks. You will implement one of such tricks supported by mdadm, called linear device. A linear device makes multiple disks appear as a one large disk to the operating system. In our case, we will use your program to configure j disks of size k KB as a single 1 MB disk. Below are the functions you need to implement. Before implementing the functions, fill out correct values for JBOD_NUM_DISKS, JBOD_DISK_SIZE, JBOD_BLOCK_SIZE, JBOD_NUM_BLOCKS_PER_DISK in jbod.h file. It is required for implementing below functions. The right values are regarding the unknown i, j and k. int mdadm mount (void): Mount the linear device; now mdadm user can run read and operations on the linear address space that combines all disks. It should return 1 on success and -1 on failure. Calling this function, the second time without calling mdadm_unmount in between, should fail. int mdadm_mount (void): Mount the linear device; now mdadm user can run read and operations on the linear address space that combines all disks. It should return 1 on success and -1 on failure. Calling this function, the second time without calling mdadm_unmount in between, should fail. int mdadm unmount (void): Unmount the linear device; now all commands to the linear device should fail. It should return 1 on success and -1 on failure. Calling this function the second time without calling mdadm_mount in between, should fail. int mdadm read (uint32_t start_addr, uint32 t read len, uint8 t *read_buf): Read read_len bytes into read_buf starting at start_addr. Read from an out-of -bound linear address should fail. A read larger than 1024 bytes should fail; in other words, read_len can be 1,024 at most. There are a few more restrictions that you will findout as you try to pass the tests. Good luck with your task! Now you are all pumped up and ready to make an impact in the new company. You spend the afternoon with your mentor, who goes through the directory structure and the development procedure with you: 1. jbod.h: The interface of JBOD. You will use the constants defined here in your implementation. (NOTE: you have to edit the right values in this file) 2. jbod. o: The object file containing the JBOD driver. 3. mdadm.h: A header file that lists the functions you should implement. 4. mdadm.c: Your implementation of mdadm functions. (NOTE: You will edit this file with all your implementations) 5. tester.h: Tester header file. 6. tester.c: Unit tests for the functions that you will implement. This file will compile into an executa- ble, tester, which you will run to see if you pass the unit tests. 7. util.h: Utility functions used by JBOD implementation and the tester. 8. util.c: Implementation of utility functions. 9. Makefile: instructions for compiling and building tester used by the make utility. Your workflow will consist of (1) Editing with right values in jbod.h (2) Implementing functions by modifying mdadm.c (3) Run make clean to remove object files (4) Run make command to build the tester (5) Run./tester to see if you pass the unit tests Repeating these steps until you pass all the tests. Although you only need to edit jbod.h and mdadm.c for successfully completing the assignment, you can modify any file you want if it helps you in some way. When testing your submission, however, we will use the original forms of all files except jbod.h, mdadm.c and mdadm.h. Remember that you are free to create helper functions if that helps you in mdadm.c (e.g., if you want to have a helper function to determine which block and disk correspond to a specific linear address).
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.23 Rating (141 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The code and task you provided belong to the field of Computer Science and more specifically it falls under the domain of System Programming and Operating Systems Heres a breakdown of the relevant sub...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


