please answer questions 1-9 with the data above and show all work
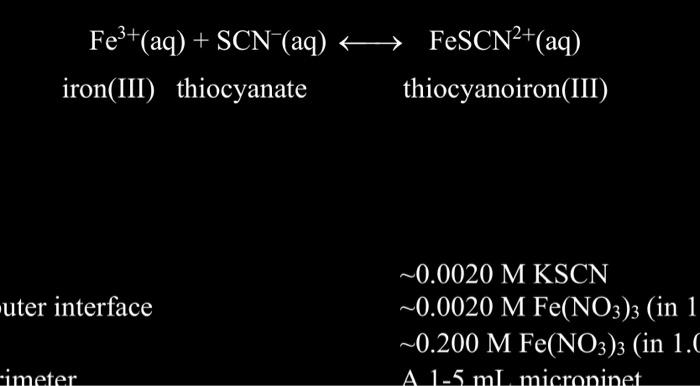
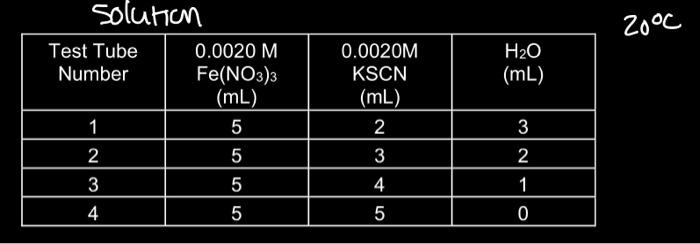
Fe3+(aq)+SCN(aq)iron(III)thiocyanateFeSCN2+(aq)thiocyanoiron(III)0.0020MKSCN10.0020MFe(NO3)3(in10.200MFe(NO3)3(in1.0 solution \begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|} \hline TestTubeNumber & 0.0020MFe(NO3)3(mL) & 0.0020MKSCN(mL) & H2O(mL) \\ \hline 1 & 5 & 2 & 3 \\ \hline 2 & 5 & 3 & 2 \\ \hline 3 & 5 & 4 & 1 \\ \hline 4 & 5 & 5 & 0 \\ \hline \end{tabular} This is an example of some of the information that should be handwritten with integrity in ink in your lab notebook. Other information is also required according to the instructions: PROCESSING THE DATA 1. Write the Kc expression for the reaction in the Data and Calculation table. 2. Calculate the initial concentration of Fe3+, based on the dilution that results from adding KSCN solution and water to the original 0.0020MFe(NO3)3 solution. See Step 2 of the procedure for the volume of each substance used in Test Tubes 1-4. Calculate [Fe3+]i using the equation (will be the same for all four test tubes): [Fe3+]i=totalmLFe(NO3)3mL(0.0020M) This is essentially the same as filling out part of the " F " row in an ICE table. 3. Calculate the initial concentration of SCN, based on its dilution by Fe(NO3)3 and water: [SCN]i=totalmLKSCNmL(0.0020MKSCN) In Test Tube 1, [SCN]i=(2mL/10mL)(0.0020MKSCN)=0.00040MKSCN. Calculate this for the other three test tubes. 204 Chemistry with Vernier Chemical Equilibrium: Finding a Constant, Kf This is essentially the same as filling out part of the "I" row in an ICE table. 4. [FeSCN 2+]eq is calculated using the formula: [FeSCN2+]eq=AsddAeeq[FeSCN2+]stdEquation(1) where Ary and Astd are the absorbance values for the equilibrium and standard test tubes, respectively, and [FeSCN2+]std=[SCN]istd=(2mL/20mL)(0,0020MKSCN)(1mol FeSCN2/1molKSCN)=0.00020MFeSCN2+ ns. Calculate [FeSCN2+]eq for each of the four test tubes: 5. [Fe3+]eq : Calculate the concentration of Fe3+ at equilibrium for Test tubes 14 using: [Fe3+]eq=[Fe3+]i[FeSCN2+]eq 6. [SCN ]cq; : Calculate the concentration of SCN at equilibrium for Test tubes 14 using: [SCN]eq=[SCN]i[FeSCN2+]eq 7. Calculate Kc for Test tubes 1-4. Be sure to show the Kc expression and the values substituted in for each of these ealculations. 8. Using your four calculated Ke values, determine an average value for Ke. How constant were your Kc values? 9. For preparing the standard solution, what is the purpose of using LeChatlier's Principle to be able to assume that the [FeSCN2+]sdd is equal to [SCN] isad? Fe3+(aq)+SCN(aq)iron(III)thiocyanateFeSCN2+(aq)thiocyanoiron(III)0.0020MKSCN10.0020MFe(NO3)3(in10.200MFe(NO3)3(in1.0 solution \begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|} \hline TestTubeNumber & 0.0020MFe(NO3)3(mL) & 0.0020MKSCN(mL) & H2O(mL) \\ \hline 1 & 5 & 2 & 3 \\ \hline 2 & 5 & 3 & 2 \\ \hline 3 & 5 & 4 & 1 \\ \hline 4 & 5 & 5 & 0 \\ \hline \end{tabular} This is an example of some of the information that should be handwritten with integrity in ink in your lab notebook. Other information is also required according to the instructions: PROCESSING THE DATA 1. Write the Kc expression for the reaction in the Data and Calculation table. 2. Calculate the initial concentration of Fe3+, based on the dilution that results from adding KSCN solution and water to the original 0.0020MFe(NO3)3 solution. See Step 2 of the procedure for the volume of each substance used in Test Tubes 1-4. Calculate [Fe3+]i using the equation (will be the same for all four test tubes): [Fe3+]i=totalmLFe(NO3)3mL(0.0020M) This is essentially the same as filling out part of the " F " row in an ICE table. 3. Calculate the initial concentration of SCN, based on its dilution by Fe(NO3)3 and water: [SCN]i=totalmLKSCNmL(0.0020MKSCN) In Test Tube 1, [SCN]i=(2mL/10mL)(0.0020MKSCN)=0.00040MKSCN. Calculate this for the other three test tubes. 204 Chemistry with Vernier Chemical Equilibrium: Finding a Constant, Kf This is essentially the same as filling out part of the "I" row in an ICE table. 4. [FeSCN 2+]eq is calculated using the formula: [FeSCN2+]eq=AsddAeeq[FeSCN2+]stdEquation(1) where Ary and Astd are the absorbance values for the equilibrium and standard test tubes, respectively, and [FeSCN2+]std=[SCN]istd=(2mL/20mL)(0,0020MKSCN)(1mol FeSCN2/1molKSCN)=0.00020MFeSCN2+ ns. Calculate [FeSCN2+]eq for each of the four test tubes: 5. [Fe3+]eq : Calculate the concentration of Fe3+ at equilibrium for Test tubes 14 using: [Fe3+]eq=[Fe3+]i[FeSCN2+]eq 6. [SCN ]cq; : Calculate the concentration of SCN at equilibrium for Test tubes 14 using: [SCN]eq=[SCN]i[FeSCN2+]eq 7. Calculate Kc for Test tubes 1-4. Be sure to show the Kc expression and the values substituted in for each of these ealculations. 8. Using your four calculated Ke values, determine an average value for Ke. How constant were your Kc values? 9. For preparing the standard solution, what is the purpose of using LeChatlier's Principle to be able to assume that the [FeSCN2+]sdd is equal to [SCN] isad