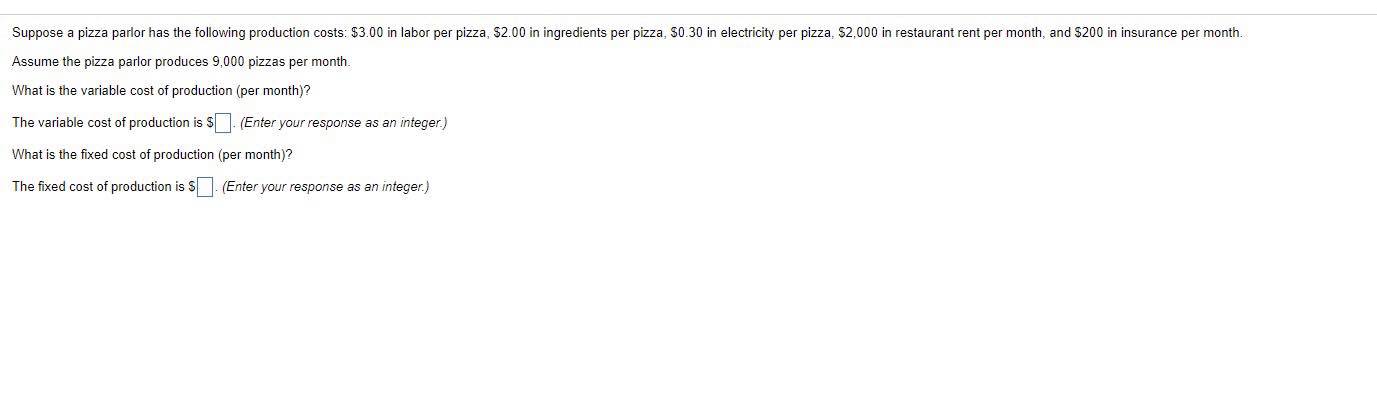Please answer the following
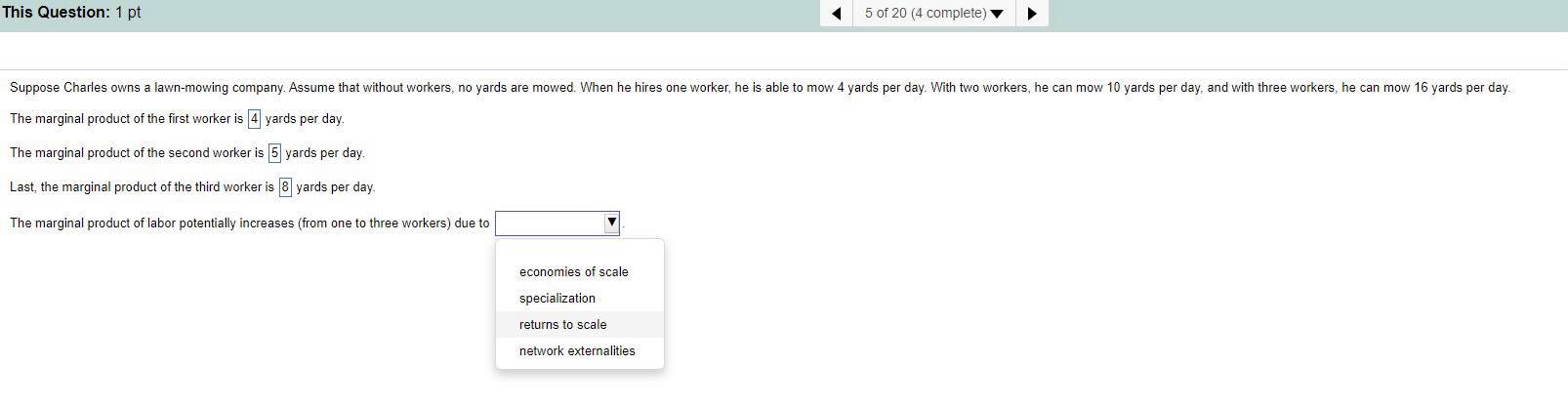
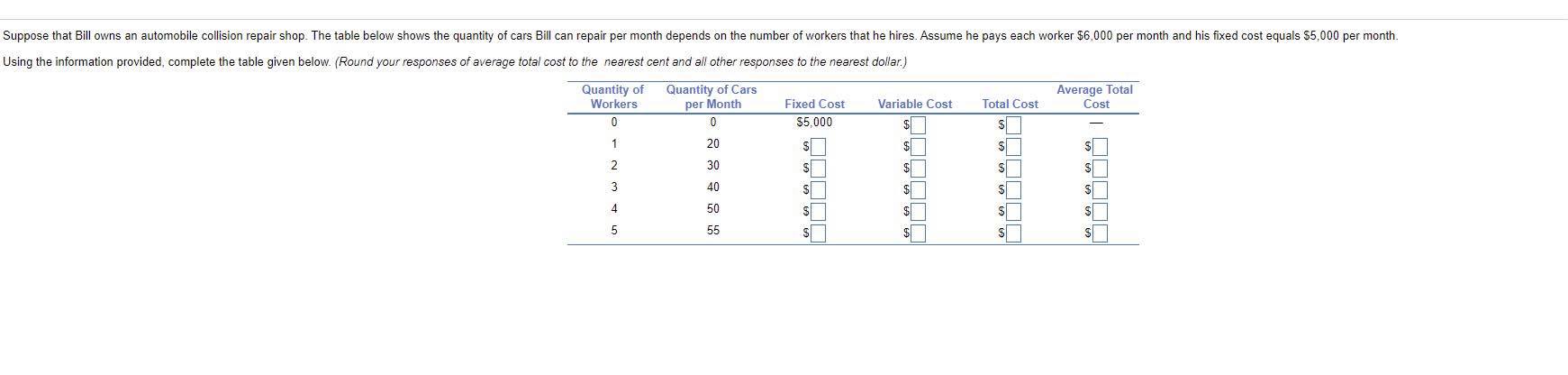
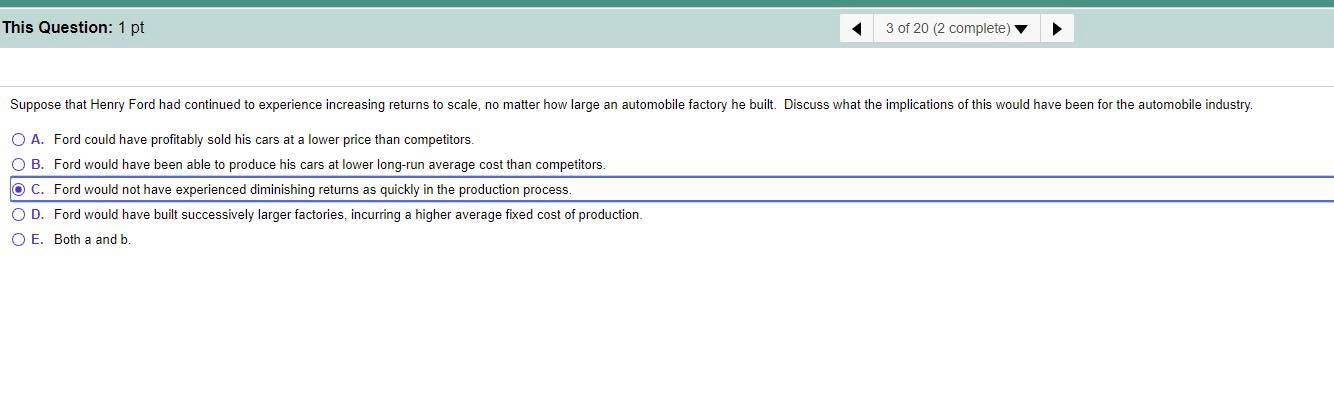
Suppose a pizza parlor has the following production costs: $3.00 in labor per pizza, $2.00 in ingredients per pizza, $0.30 in electricity per pizza, $2,000 in restaurant rent per month, and $200 in insurance per month. Assume the pizza parlor produces 9,000 pizzas per month. What is the variable cost of production (per month)? The variable cost of production is $ ]. (Enter your response as an integer.) What is the fixed cost of production (per month)? The fixed cost of production is $. (Enter your response as an integer.)This Question: 1 pt 5 of 20 (4 complete) Suppose Charles owns a lawn-mowing company. Assume that without workers, no yards are mowed. When he hires one worker, he is able to mow 4 yards per day. With two workers, he can mow 10 yards per day, and with three workers, he can mow 16 yards per day. The marginal product of the first worker is 4 yards per day. The marginal product of the second worker is 5 yards per day. Last, the marginal product of the third worker is 8 yards per day. The marginal product of labor potentially increases (from one to three workers) due to economies of scale specialization returns to scale network externalitiesSuppose that Bill owns an automobile collision repair shop. The table below shows the quantity of cars Bill can repair per month depends on the number of workers that he hires. Assume he pays each worker $6,000 per month and his fixed cost equals $5,000 per month. Using the information provided, complete the table given below. (Round your responses of average total cost to the nearest cent and all other responses to the nearest dollar.) Quantity of Quantity of Cars Average Total Workers per Month Fixed Cost Variable Cost Total Cost Cost 0 $5,000 AWN- $ S 20 S 30 S 40 S 50 S 55This Question: 1 pt 3 of 20 (2 complete) Suppose that Henry Ford had continued to experience increasing returns to scale, no matter how large an automobile factory he built. Discuss what the implications of this would have been for the automobile industry. O A. Ford could have profitably sold his cars at a lower price than competitors. O B. Ford would have been able to produce his cars at lower long-run average cost than competitors. O C. Ford would not have experienced diminishing returns as quickly in the production process O D. Ford would have built successively larger factories, incurring a higher average fixed cost of production. O E. Both a and b.What is minimum efficient scale? Minimum efficient scale is O A. the level of output at which the long-run average cost of production begins to decline. O B. the level of output at which all economies of scale are exhausted. O C. the level of output at which all diseconomies of scale are exhausted. O D. the level of output at which a firm begins to experience economies of scale. O E. the level of output at which the marginal cost of production reaches a minimum. What is likely to happen in the long run to firms that do not reach minimum efficient scale? A firm that does not reach its minimum efficient scale O A. will lose money if it remains in business. O B. will be experiencing constant returns to scale. O C. will become a natural monopoly. O D. will earn positive profits if it remains in business. O E. both a and b