Please can someone help me out with these exercices, i completed the missing portion
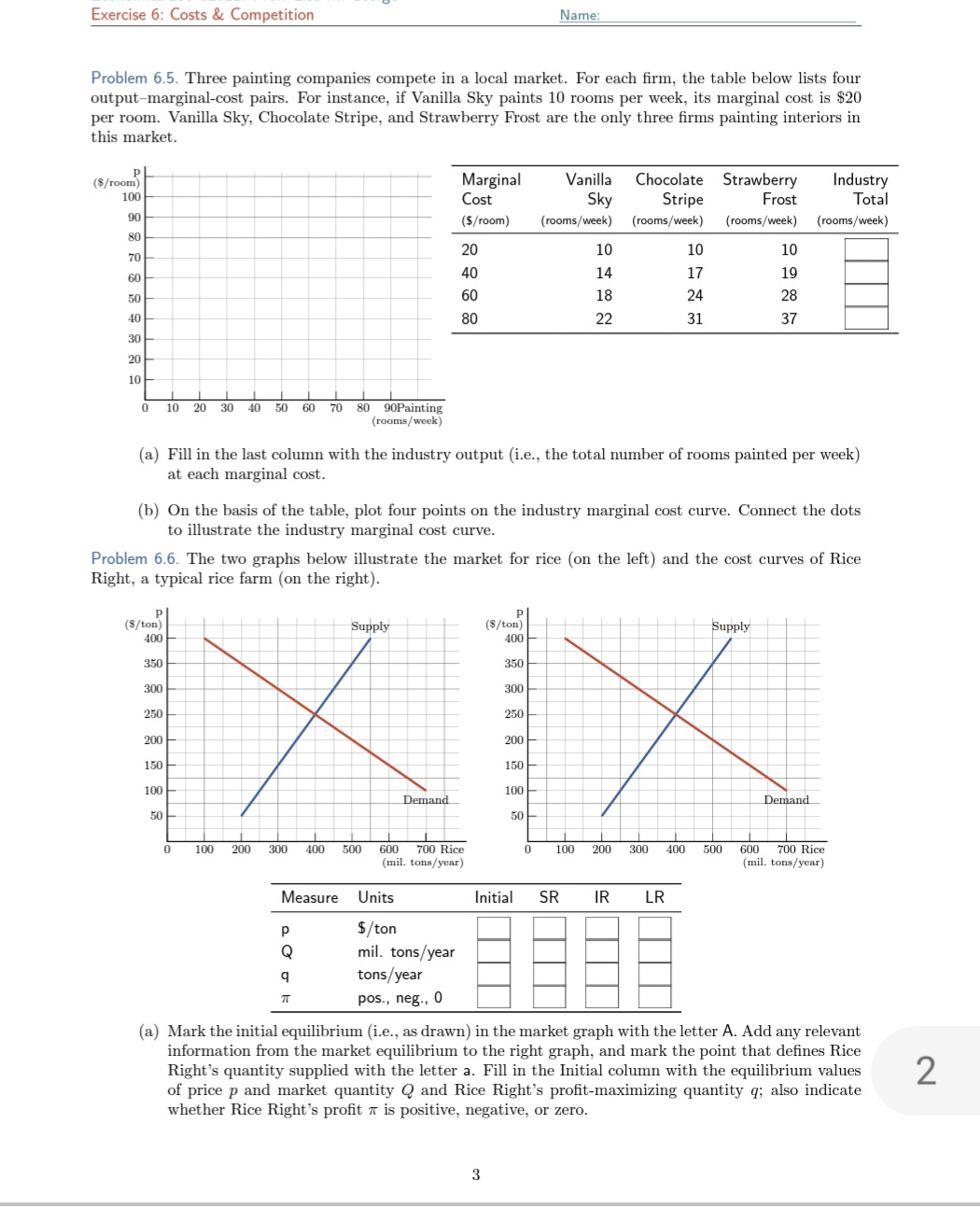
Exercise 6: Costs & Competition Name: Problem 6.5. Three painting companies compete in a local market. For each firm, the table below lists four output-marginal-cost pairs. For instance, if Vanilla Sky paints 10 rooms per week, its marginal cost is $20 per room. Vanilla Sky, Chocolate Stripe, and Strawberry Frost are the only three firms painting interiors in this market. ($/room) Marginal Vanilla Chocolate Strawberry Industry 100 Cost Sky Stripe Frost Total 90 ($/room) (rooms/week (rooms/week) (rooms/week) (rooms/week) 80 70 20 10 10 60 40 14 17 19 50 60 18 24 28 40 80 22 31 37 30 20 10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90Painting (rooms/week) (a) Fill in the last column with the industry output (i.e., the total number of rooms painted per week) at each marginal cost. (b) On the basis of the table, plot four points on the industry marginal cost curve. Connect the dots to illustrate the industry marginal cost curve. Problem 6.6. The two graphs below illustrate the market for rice (on the left) and the cost curves of Rice Right, a typical rice farm (on the right). ($/ton) ($/ton) 400 400 350 350 300 300 250 250 200 200 150 150 100 X 100 Demand 50 50 200 300 4 600 700 Rice 100 600 700 Rice (mil. tons/year) (mil. tons/year) Measure Units Initial SR IR LR $/ton mil. tons/year tons/ year pos., neg., 0 (a) Mark the initial equilibrium (i.e., as drawn) in the market graph with the letter A. Add any relevant information from the market equilibrium to the right graph, and mark the point that defines Rice Right's quantity supplied with the letter a. Fill in the Initial column with the equilibrium values 2 of price p and market quantity Q and Rice Right's profit-maximizing quantity q; also indicate whether Rice Right's profit a is positive, negative, or zero.(a) Mark the initial equilibrium (i.e., as drawn) in the market graph with the letter A. Add any relevant information from the market equilibrium to the right graph1 and mark the point that denes Rice Right's quantity supplied with the letter 3. Fill in the Initial column with the equilibrium values of price p and market quantity Q and Rice Right's pmtmaidmizing quantity 9; also indicate whether Rice Right's prot 11' is positive, negative, or zero. Economics 200 52021: Prof. Lisa M. George Exercise 6: Costs 84 Competition Name: (1:!) The government starts subsidizing ethanol fuel, a rice-based substitute for gasoline. The program increases rice demand by 300 million tons per year. In the market graph, illustrate the new demand curve, and mark the new equilibrium point with the letter B. Also, illustrate Rice Right's prot-maximizing point with the letter b. Fill in the table's short run (SR) column. (a) .. ., we . . rm .. farming. (d) In the intermediate run, entry or exit changes supply by 150 million tons per year. (You decide whether the change is an increase or a decrease.) Plot the new short-run supply curve in the intermediate run. Mark the intermediate-run equilibrium point with the letter C, carry the relevant equilibrium information over to Rice Right's graph, and mark Rice Right's protmaximizing point in the intermediate run with the letter c. Fill in the table's intermediate run (IR) column. (e) The long-run equilibrium price is per ton. In the long-run equilibrium, enough rms enter rice farming to increase rice supply by tons per year (at each price). Draw the short-run supply curve in the long-run equilibrium. ar the long-run equilibrium with the letter D, carry the relevant information over to Rice Right's graph, and mark Rice Right's prot maximising point in the long run with the letter d. Fill in the table's long run (LR) column. (1') The government subsidy El increases El decreases El doesn't affect the prot of rice farm- ers in the long run. Problem 6.7. The graph below replicates the market graph from Problem 6.6. {a} Add your points A, B, C, and D to this graph. (b) The graph includes the initial short-run supply curve. Draw and label the intermediate-run and long-run supply curves. (c) The intermediate-run supply of corn is elastic than the short-run SUPP 3'. an t ' ong-run supply of corn is \":1 perfectly inelastic E] perfectly elastic E] unit elasticl. I] III] 200 sec too too can 7130 Rice (mil. tom/year)