Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please complete all parts Marc Goudreau, administrator of Clearwater Hospital, was puzzled by the prior month's reports. Every month, it's anyone's guess whether the lab
Please complete all parts
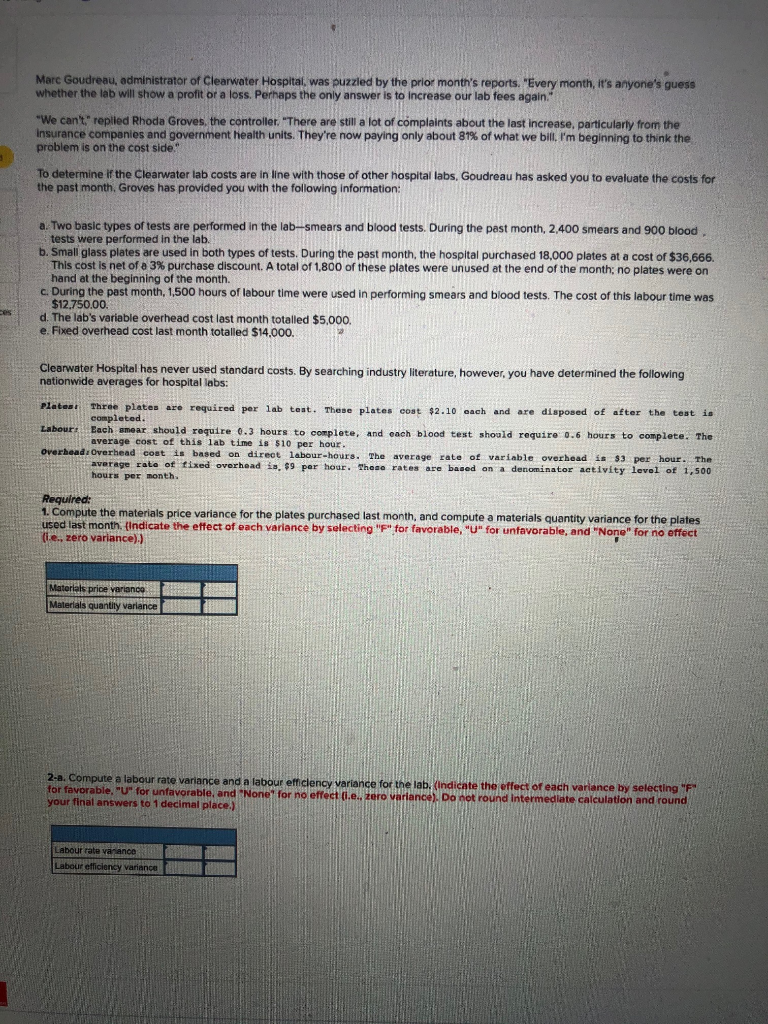
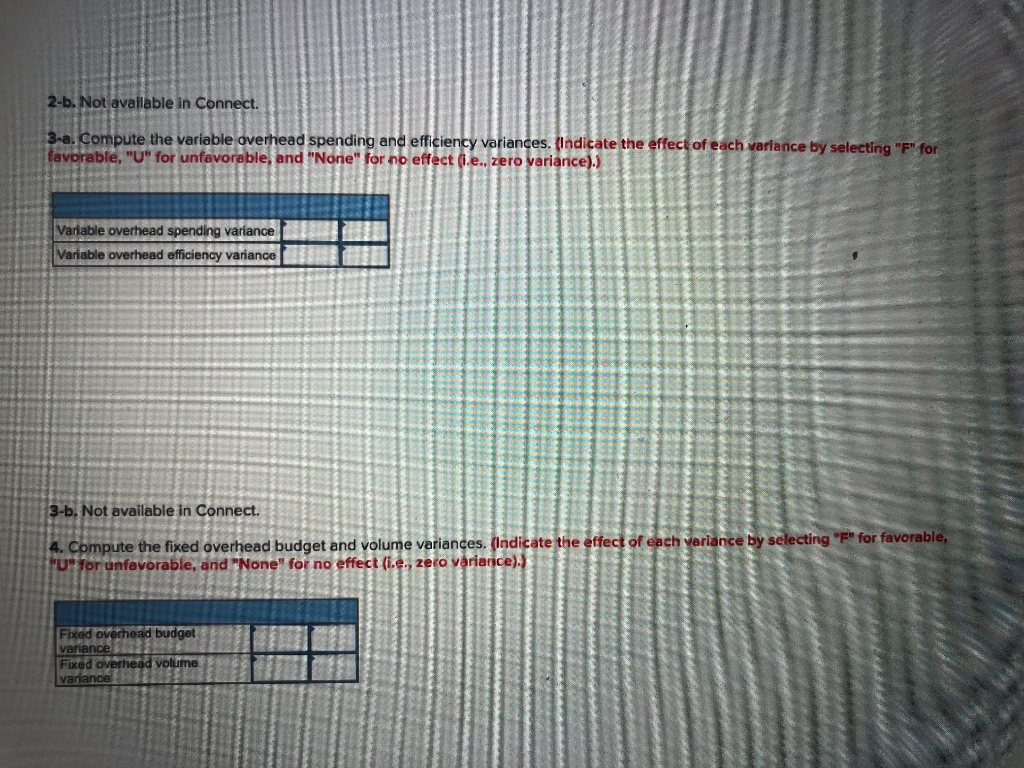
Marc Goudreau, administrator of Clearwater Hospital, was puzzled by the prior month's reports. "Every month, it's anyone's guess whether the lab will show a profit or a loss. Perhaps the only answer is to increase our lab fees again." "We can't." replied Rhoda Groves, the controller. "There are still a lot of complaints about the last increase, particularly from the Insurance companies and government health units. They're now paying only about 81% of what we bill, I'm beginning to think the problem is on the cost side." To determine if the Clearwater lab costs are in line with those of other hospital labs, Goudreau has asked you to evaluate the costs for the past month. Groves has provided you with the following information: a. Two basic types of tests are performed in the lab-smears and blood tests. During the past month, 2.400 smears and 900 blood tests were performed in the lab. b. Small glass plates are used in both types of tests. During the past month, the hospital purchased 18,000 plates at a cost of $36,666. This cost is net of a 3% purchase discount. A total of 1,800 of these plates were unused at the end of the month: no plates were on hand at the beginning of the month. c. During the past month, 1,500 hours of labour time were used in performing smears and blood tests. The cost of this labour time was $12.750.00 d. The lab's variable overhead cost last month totalled $5,000. e. Fixed overhead cost last month totalled $14,000. Clearwater Hospital has never used standard costs. By searching industry literature, however, you have determined the following nationwide averages for hospital labs: Platest Three plates are required per lab teat. These plates cost $2.10 each and are disposed of after the test is completed. Labours Each smear should require 0.3 hours to complete, and each blood test should require 0.6 hours to complete. The average cost of this lab time is $10 per hour. overhead.Overhead coat is based on direct labour-hours. The average rate of variable overhead is $3 per hour. The average rate of tixed overhead is. $9 per hour. These rates are based on a denominator activity level of 1,500 hours per month. Required: 1. Compute the materials price variance for the plates purchased last month, and compute a materials quantity variance for the plates used last month. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (ie, zero variance).) Materials price variance Materials quantity variance 2-a. Compute a labour rate variance and a labour efficiency variance for the lab. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable. "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect i.e.. zero variance). Do not round Intermediate calculation and round your final answers to 1 decimal place.) Labour rate vanance Labour efficiency variance 2-b. Not available in Connect. 3-a. Compute the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (.e., zero variance).) Variable overhead spending variance Variable overhead efficiency variance 3-b. Not available in Connect. 14. Compute the fixed overhead budget and volume variances. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variarice).) Fixed overhead budget variance Fixed overhead volume variance Marc Goudreau, administrator of Clearwater Hospital, was puzzled by the prior month's reports. "Every month, it's anyone's guess whether the lab will show a profit or a loss. Perhaps the only answer is to increase our lab fees again." "We can't." replied Rhoda Groves, the controller. "There are still a lot of complaints about the last increase, particularly from the Insurance companies and government health units. They're now paying only about 81% of what we bill, I'm beginning to think the problem is on the cost side." To determine if the Clearwater lab costs are in line with those of other hospital labs, Goudreau has asked you to evaluate the costs for the past month. Groves has provided you with the following information: a. Two basic types of tests are performed in the lab-smears and blood tests. During the past month, 2.400 smears and 900 blood tests were performed in the lab. b. Small glass plates are used in both types of tests. During the past month, the hospital purchased 18,000 plates at a cost of $36,666. This cost is net of a 3% purchase discount. A total of 1,800 of these plates were unused at the end of the month: no plates were on hand at the beginning of the month. c. During the past month, 1,500 hours of labour time were used in performing smears and blood tests. The cost of this labour time was $12.750.00 d. The lab's variable overhead cost last month totalled $5,000. e. Fixed overhead cost last month totalled $14,000. Clearwater Hospital has never used standard costs. By searching industry literature, however, you have determined the following nationwide averages for hospital labs: Platest Three plates are required per lab teat. These plates cost $2.10 each and are disposed of after the test is completed. Labours Each smear should require 0.3 hours to complete, and each blood test should require 0.6 hours to complete. The average cost of this lab time is $10 per hour. overhead.Overhead coat is based on direct labour-hours. The average rate of variable overhead is $3 per hour. The average rate of tixed overhead is. $9 per hour. These rates are based on a denominator activity level of 1,500 hours per month. Required: 1. Compute the materials price variance for the plates purchased last month, and compute a materials quantity variance for the plates used last month. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (ie, zero variance).) Materials price variance Materials quantity variance 2-a. Compute a labour rate variance and a labour efficiency variance for the lab. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable. "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect i.e.. zero variance). Do not round Intermediate calculation and round your final answers to 1 decimal place.) Labour rate vanance Labour efficiency variance 2-b. Not available in Connect. 3-a. Compute the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (.e., zero variance).) Variable overhead spending variance Variable overhead efficiency variance 3-b. Not available in Connect. 14. Compute the fixed overhead budget and volume variances. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variarice).) Fixed overhead budget variance Fixed overhead volume varianceStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


