Question
Please create a MatLab code for the following: 1. Create two separate function files that compute f() and g() based on input. 2. Create a
Please create a MatLab code for the following:
1. Create two separate function files that compute f() and g() based on input.
2. Create a function file that calculates position, linear velocity and linear acceleration of the piston based on the revolution of the crank n.
3. Calculate the position, linear velocity and linear acceleration of the piston for one revolution of the crank. Take a minimum of 200 equally spaced elements. 4.
Write an output file as Piston_rod_crank.dat that has title as Piston Rod Crank Mechanism with four vertical columns with headers over each columns as angle(degree) Position(x, m) Velocity (u, m/s) acceleration(a, m/s2 ).
5. Plot the position, linear velocity and linear acceleration of the piston in three different graphs. Make sure that all the curves are properly labeled.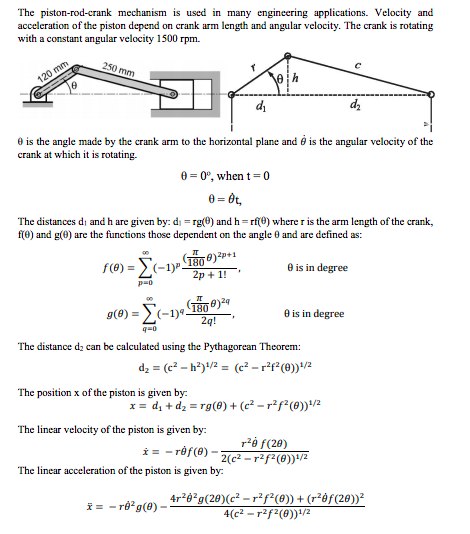
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


