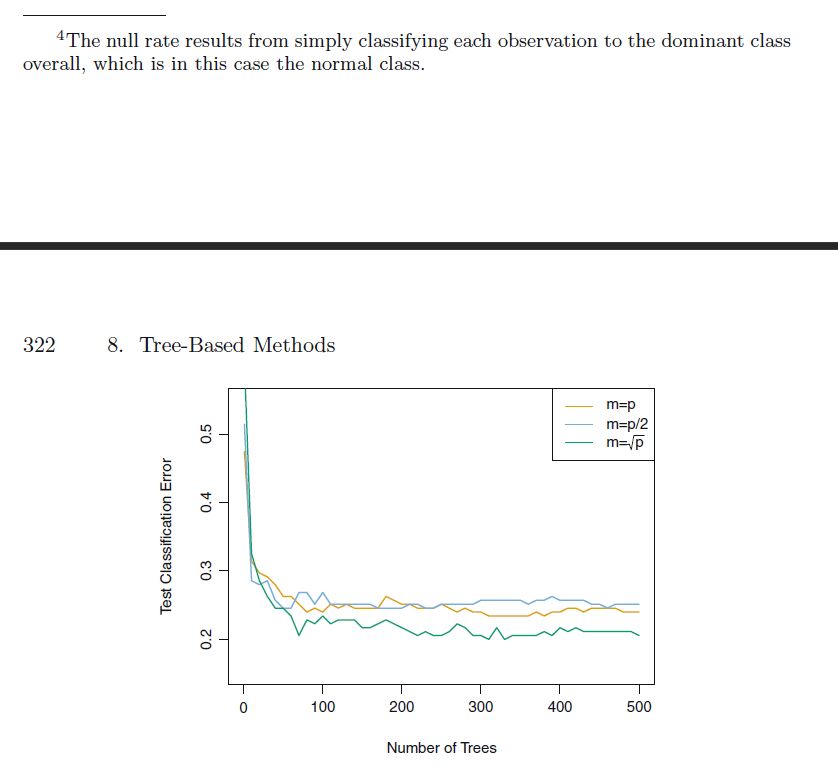
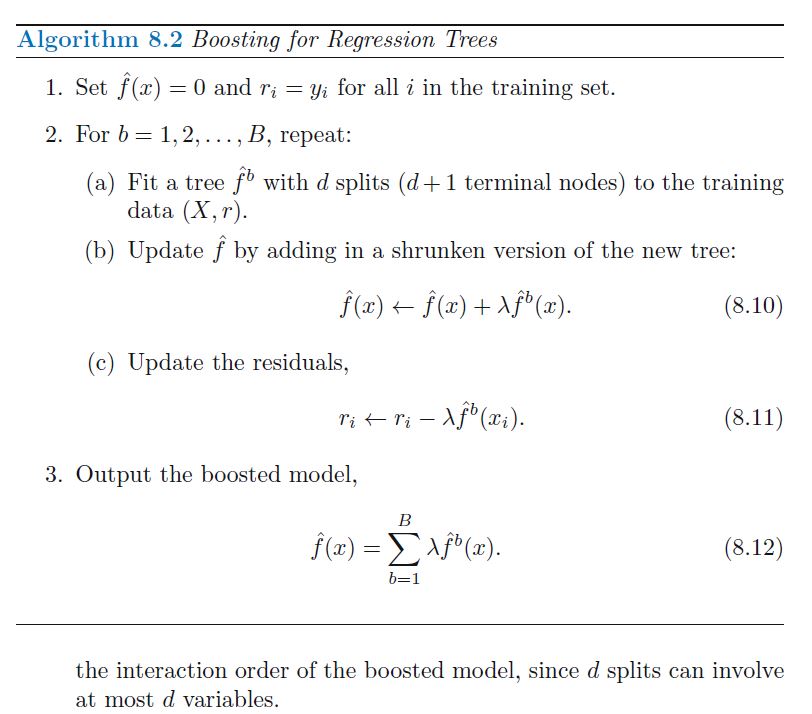
PLEASE DO NOT COPY ANSWER FROM OTHER WEBSITE
2. It is mentioned in Section 8.2.3 that boosting using depthone trees (or stamps) leads to an additive model: that is, a model of the form f(X) = ijlle- 3:1 Explain why this is the case. You can begin with (8.12) in Algorithm 8.2. 3. Consider the Gini index, classication error, and entropy in a simple classication setting with two classes. Create a single plot that displays each of these quantities as a function of ml. The :1:- axis should display pml, ranging from O to 1, and the yaxis should display the value of the Gini index, classication error, and entropy. Hint: In a setting with two classes, p'ml : 1 + pm. You could make this plot by hand, but it will be much easier to make in R. 8. 2. 3 Boosting We now discuss boosting, yet another approach for improving the predic- tions resulting from a decision tree. Like bagging, boosting is a general approach that can be applied to many statistical learning methods for re- gression or classication. Here we restrict our discussion of boosting to the context of decision trees. Recall that bagging involves creating multiple copies of the original train- ing data set using the bootstrap, tting a separate decision tree to each copy, and then combining all of the trees in order to create a single predic- tive model. Notably, each tree is built on a bootstrap data set, independent of the other trees. Boosting works in a similar way, except that the trees are grown sequentially: each tree is grown using information from previously grown trees. Boosting does not involve bootstrap sampling; instead each tree is t on a modied version of the original data set. Consider rst the regression setting. Like bagging, boosting involves com- bining a large number of decision trees, f1, . . . , f3. Boosting is described in Algorithm 8.2. What is the idea behind this procedure? Unlike tting a single large deci- sion tree to the data, which amounts to tting the data. herd and potentially overtting, the boosting approach instead teams slowly. Given the current model, we t a decision tree to the residuals from the model. That is, we t a tree using the current residuals, rather than the outcome Y, as the re- sponse. We then add this new decision tree into the tted function in order to update the residuals. Each of these trees can be rather small, with just a few terminal nodes, determined by the parameter d in the algorithm. By boosting The null rate results from simply classifying each observation to the dominant class overall, which is in this case the normal class. 322 8. Tree-Based Methods m=p m=p/2 0.5 m=/p 0.4 Test Classification Error 0.3 0 100 200 300 400 500 Number of TreesAlgorithm 8.2 Boosting for Regression flees 1. Set at) : 0 and in; : ya: for all i in the training set. 2. For I? : 1,2j . . . . B, repeat: (a) Fit a tree fb with d splits {d + 1 terminal nodes) to the training data (X, r). (b) Update f by adding in a shrunken version of the new tree: e\")