please explain and compte part a and b
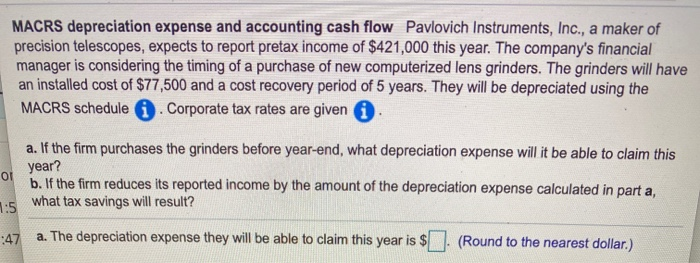
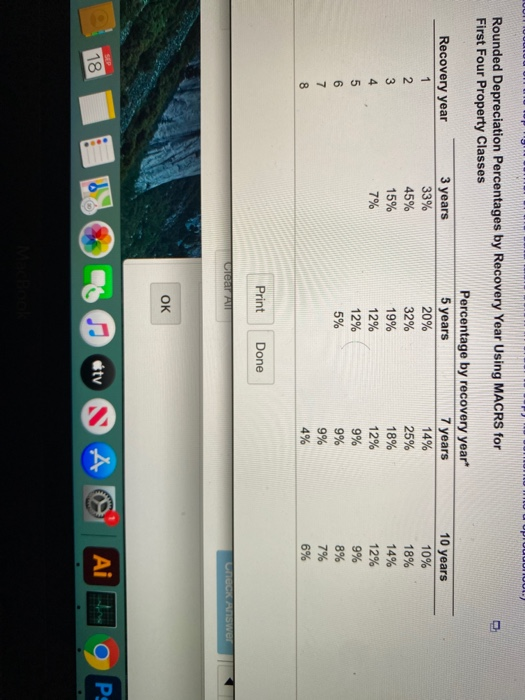
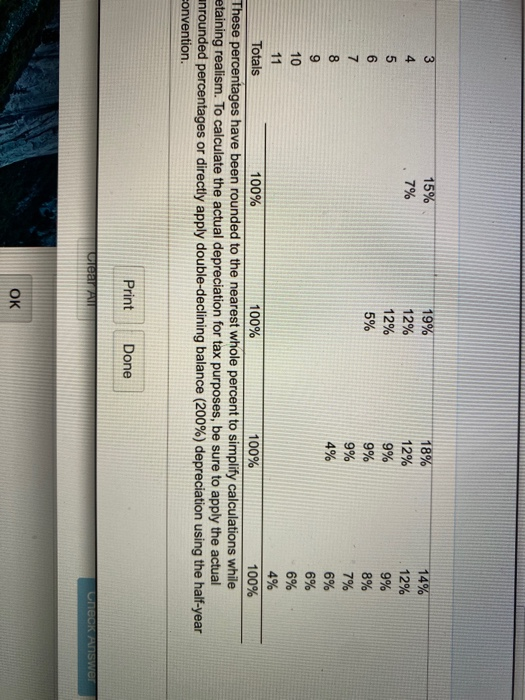
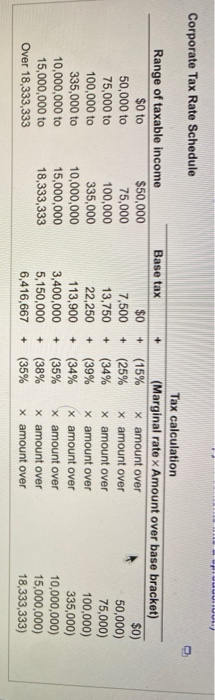
MACRS depreciation expense and accounting cash flow Pavlovich Instruments, Inc., a maker of precision telescopes, expects to report pretax income of $421,000 this year. The company's financial manager is considering the timing of a purchase of new computerized lens grinders. The grinders will have an installed cost of $77,500 and a cost recovery period of 5 years. They will be depreciated using the MACRS schedule Corporate tax rates are given OI a. If the firm purchases the grinders before year-end, what depreciation expense will it be able to claim this year? b. If the firm reduces its reported income by the amount of the depreciation expense calculated in part a, what tax savings will result? 1:5 :47 a. The depreciation expense they will be able to claim this year is $ (Round to the nearest dollar.) D 10 years Rounded Depreciation Percentages by Recovery Year Using MACRS for First Four Property Classes Percentage by recovery year Recovery year 3 years 5 years 7 years 1 33% 20% 14% 2 45% 32% 25% 3 15% 19% 18% 4 7% 12% 5 12% 9% 6 5% 9% 7 9% 8 4% 12% 10% 18% 14% 12% 9% 8% 7% 6% Print Done Clear A COCK Answer OK SEP Aitors 6 D v A P: 18 3 15% 19% 18% 14% 4 7% 12% 12% 12% 5 12% 9% 9% 6 5% 9% 8% 7 9% 7% 8 4% 6% 9 6% 10 6% 11 4% Totals 100% 100% 100% 100% These percentages have been rounded to the nearest whole percent to simplify calculations while etaining realism. To calculate the actual depreciation for tax purposes, be sure to apply the actual unrounded percentages or directly apply double-declining balance (200%) depreciation using the half-year convention. Print Done Check Answer OK wuuuiiu Corporate Tax Rate Schedule + $0) + Range of taxable income $0 to $50,000 50,000 to 75,000 75,000 to 100,000 100,000 to 335,000 335,000 to 10,000,000 10,000,000 to 15,000,000 15,000,000 to 18,333,333 Over 18,333,333 Base tax $0 7,500 13,750 22,250 113,900 3,400,000 5,150,000 6,416,667 Tax calculation + (Marginal rate x Amount over base bracket) (15% x amount over + (25% x amount over 50,000) (34% x amount over 75,000) (39% x amount over 100,000) (34% x amount over 335,000) (35% x amount over 10,000,000) (38% x amount over 15,000,000) + (35% x amount over 18,333,333) + + + +