Please fill in highlighted cells according to the requirements listed.
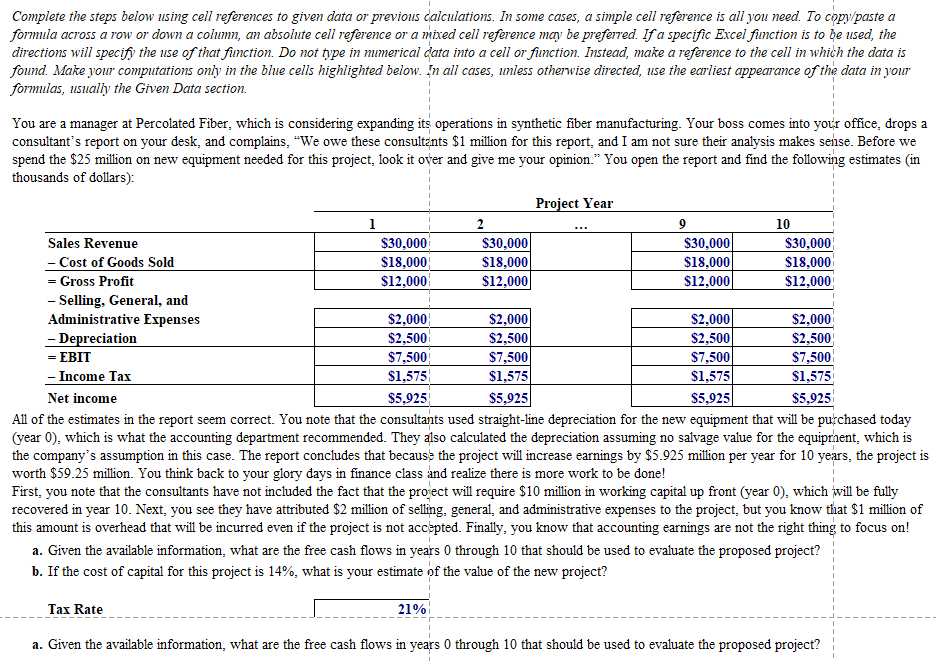
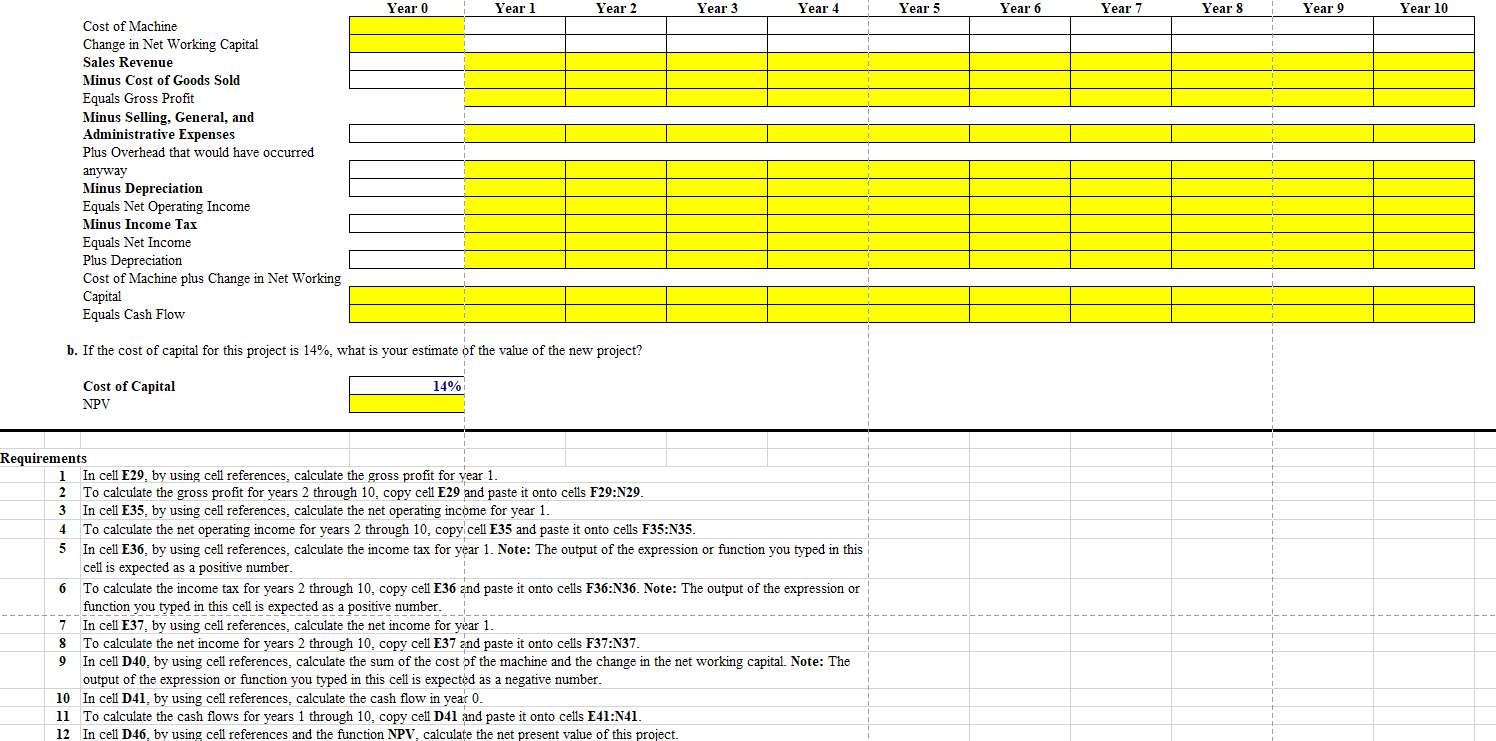
Complete the steps below using cell references to given data or previous calculations. In some cases, a simple cell reference is all you need. To copy/paste a formula across a row or down a column, an absolute cell reference or a mixed cell reference may be preferred. If a specific Excel function is to be used, the directions will specify the use of that function. Do not type in numerical data into a cell or function. Instead, make a reference to the cell in which the data is found. Make your computations only in the blue cells highlighted below. In all cases, unless otherwise directed, use the earliest appearance of the data in your formulas, usually the Given Data section. You are a manager at Percolated Fiber, which is considering expanding its operations in synthetic fiber manufacturing. Your boss comes into your office, drops a consultant's report on your desk, and complains, We owe these consultents $1 million for this report, and I am not sure their analysis makes sense. Before we spend the $25 million on new equipment needed for this project, look it over and give me your opinion." You open the report and find the following estimates (in thousands of dollars): Project Year 1 2 9 10 Sales Revenue $30,000 $30,000 $30,000 $30,000 - Cost of Goods Sold $18,000 $18,000 $18,000 $18,000 = Gross Profit $12,000 $12,000 $12,000 $12,000 - Selling, General, and Administrative Expenses $2,000 $2,000 $2,000 $2,000 - Depreciation $2,500 $2,500 $2,500 $2,500 = EBIT $7,500 $7,500 $7,500 $7,500 - Income Tax $1,575 $1,575 $1,575 $1,575 Net income $5,925 $5,925 $5,925 $5,925 All of the estimates in the report seem correct. You note that the consultants used straight-line depreciation for the new equipment that will be purchased today (year 0), which is what the accounting department recommended. They also calculated the depreciation assuming no salvage value for the equipment, which is the company's assumption in this case. The report concludes that because the project will increase earnings by $5.925 million per year for 10 years, the project is worth $59.25 million. You think back to your glory days in finance class and realize there is more work to be done! First, you note that the consultants have not included the fact that the pro ect will require $10 million in working capital up front (year 0), which will be fully recovered in year 10. Next, you see they have attributed $2 million of selling general, and administrative expenses to the project, but you know that $1 million of this amount is overhead that will be incurred even if the project is not accepted. Finally, you know that accounting earnings are not the right thing to focus on! a. Given the available information, what are the free cash flows in years 0 through 10 that should be used to evaluate the proposed project? b. If the cost of capital for this project is 14%, what is your estimate of the value of the new project? Tax Rate 21% a. a. Given the available information, what are the free cash flows in years 0 through 10 that should be used to evaluate the proposed project? Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Year 7 Year 8 Year 9 Year 10 Cost of Machine Change in Net Working Capital Sales Revenue Minus Cost of Goods Sold Equals Gross Profit Minus Selling, General, and Administrative Expenses Plus Overhead that would have occurred anyway Minus Depreciation Equals Net Operating Income Minus Income Tax Equals Net Income Plus Depreciation Cost of Machine plus Change in Net Working Capital Equals Cash Flow b. If the cost of capital for this project is 14%, what is your estimate of the value of the new project? 14% Cost of Capital NPV 4 6 Requirements 1 In cell E29, by using cell references, calculate the gross profit for year 1. 2 To calculate the gross profit for years 2 through 10, copy cell E29 and paste it onto cells F29:N29. 3 In cell E35, by using cell references, calculate the net operating income for year 1. To calculate the net operating income for years 2 through 10, copy cell E35 and paste it onto cells F35:N35. 5 In cell E36, by using cell references, calculate the income tax for year 1. Note: The output of the expression or function you typed in this cell is expected as a positive number. To calculate the income tax for years 2 through 10, copy cell E36 and paste it onto cells F36:N36. Note: The output of the expression or function you typed in this cell is expected as a positive number. 7 In cell E37, by using cell references, calculate the net income for year 1. 8 To calculate the net income for years 2 through 10, copy cell E37 and paste it onto cells F37:N37. 9 In cell D40, by using cell references, calculate the sum of the cost of the machine and the change in the net working capital. Note: The output of the expression or function you typed in this cell is expected as a negative number. 10 In cell D41, by using cell references, calculate the cash flow in year 0. 11 To calculate the cash flows for years 1 through 10, copy cell D41 and paste it onto cells E41:N41. 12 In cell 046, by using cell references and the function NPV, calculate the net present value of this project. Complete the steps below using cell references to given data or previous calculations. In some cases, a simple cell reference is all you need. To copy/paste a formula across a row or down a column, an absolute cell reference or a mixed cell reference may be preferred. If a specific Excel function is to be used, the directions will specify the use of that function. Do not type in numerical data into a cell or function. Instead, make a reference to the cell in which the data is found. Make your computations only in the blue cells highlighted below. In all cases, unless otherwise directed, use the earliest appearance of the data in your formulas, usually the Given Data section. You are a manager at Percolated Fiber, which is considering expanding its operations in synthetic fiber manufacturing. Your boss comes into your office, drops a consultant's report on your desk, and complains, We owe these consultents $1 million for this report, and I am not sure their analysis makes sense. Before we spend the $25 million on new equipment needed for this project, look it over and give me your opinion." You open the report and find the following estimates (in thousands of dollars): Project Year 1 2 9 10 Sales Revenue $30,000 $30,000 $30,000 $30,000 - Cost of Goods Sold $18,000 $18,000 $18,000 $18,000 = Gross Profit $12,000 $12,000 $12,000 $12,000 - Selling, General, and Administrative Expenses $2,000 $2,000 $2,000 $2,000 - Depreciation $2,500 $2,500 $2,500 $2,500 = EBIT $7,500 $7,500 $7,500 $7,500 - Income Tax $1,575 $1,575 $1,575 $1,575 Net income $5,925 $5,925 $5,925 $5,925 All of the estimates in the report seem correct. You note that the consultants used straight-line depreciation for the new equipment that will be purchased today (year 0), which is what the accounting department recommended. They also calculated the depreciation assuming no salvage value for the equipment, which is the company's assumption in this case. The report concludes that because the project will increase earnings by $5.925 million per year for 10 years, the project is worth $59.25 million. You think back to your glory days in finance class and realize there is more work to be done! First, you note that the consultants have not included the fact that the pro ect will require $10 million in working capital up front (year 0), which will be fully recovered in year 10. Next, you see they have attributed $2 million of selling general, and administrative expenses to the project, but you know that $1 million of this amount is overhead that will be incurred even if the project is not accepted. Finally, you know that accounting earnings are not the right thing to focus on! a. Given the available information, what are the free cash flows in years 0 through 10 that should be used to evaluate the proposed project? b. If the cost of capital for this project is 14%, what is your estimate of the value of the new project? Tax Rate 21% a. a. Given the available information, what are the free cash flows in years 0 through 10 that should be used to evaluate the proposed project? Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Year 7 Year 8 Year 9 Year 10 Cost of Machine Change in Net Working Capital Sales Revenue Minus Cost of Goods Sold Equals Gross Profit Minus Selling, General, and Administrative Expenses Plus Overhead that would have occurred anyway Minus Depreciation Equals Net Operating Income Minus Income Tax Equals Net Income Plus Depreciation Cost of Machine plus Change in Net Working Capital Equals Cash Flow b. If the cost of capital for this project is 14%, what is your estimate of the value of the new project? 14% Cost of Capital NPV 4 6 Requirements 1 In cell E29, by using cell references, calculate the gross profit for year 1. 2 To calculate the gross profit for years 2 through 10, copy cell E29 and paste it onto cells F29:N29. 3 In cell E35, by using cell references, calculate the net operating income for year 1. To calculate the net operating income for years 2 through 10, copy cell E35 and paste it onto cells F35:N35. 5 In cell E36, by using cell references, calculate the income tax for year 1. Note: The output of the expression or function you typed in this cell is expected as a positive number. To calculate the income tax for years 2 through 10, copy cell E36 and paste it onto cells F36:N36. Note: The output of the expression or function you typed in this cell is expected as a positive number. 7 In cell E37, by using cell references, calculate the net income for year 1. 8 To calculate the net income for years 2 through 10, copy cell E37 and paste it onto cells F37:N37. 9 In cell D40, by using cell references, calculate the sum of the cost of the machine and the change in the net working capital. Note: The output of the expression or function you typed in this cell is expected as a negative number. 10 In cell D41, by using cell references, calculate the cash flow in year 0. 11 To calculate the cash flows for years 1 through 10, copy cell D41 and paste it onto cells E41:N41. 12 In cell 046, by using cell references and the function NPV, calculate the net present value of this project








