 please full detail
please full detail
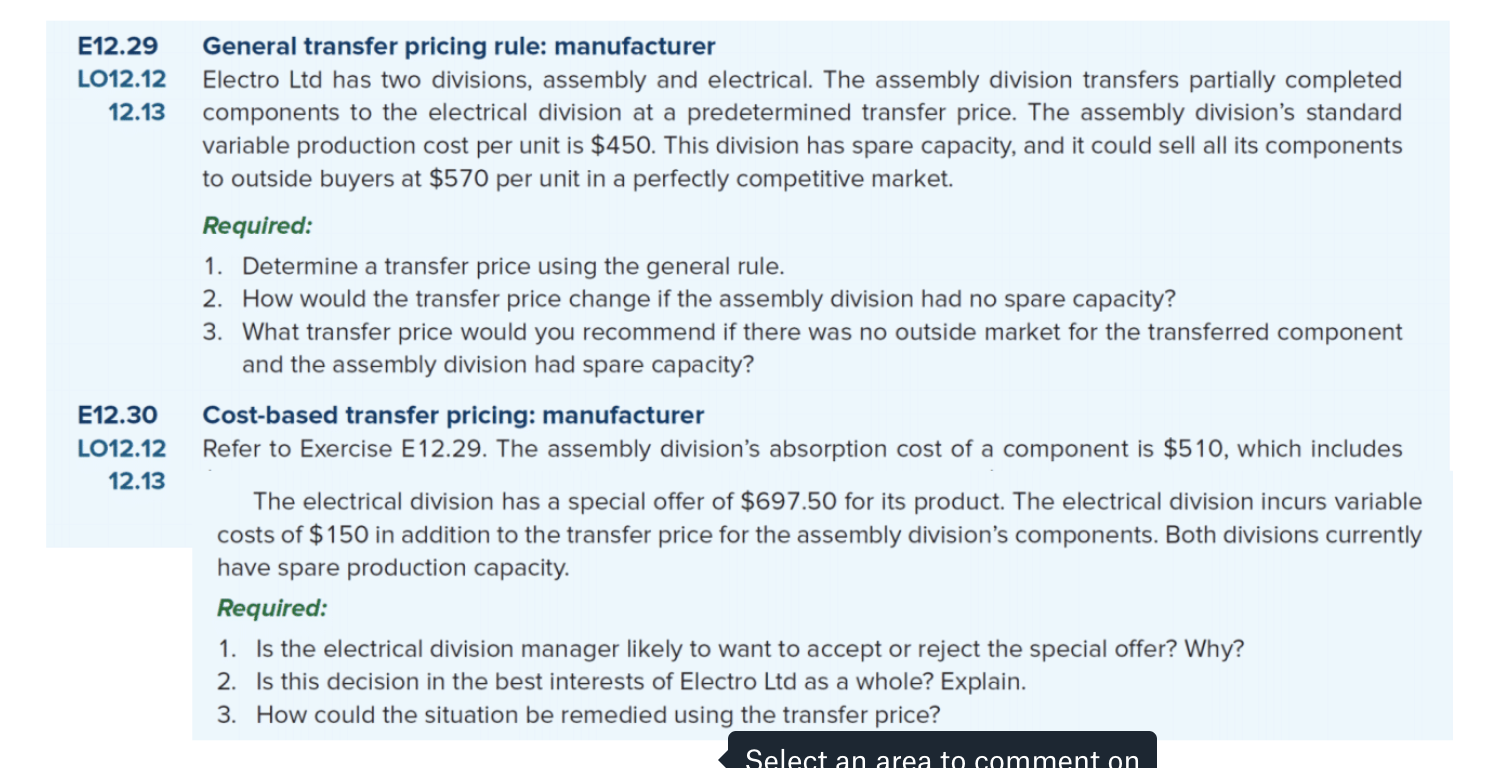
E12.29 LO12.12 12.13 General transfer pricing rule: manufacturer Electro Ltd has two divisions, assembly and electrical. The assembly division transfers partially completed components to the electrical division at a predetermined transfer price. The assembly division's standard variable production cost per unit is $450. This division has spare capacity, and it could sell all its components to outside buyers at $570 per unit in a perfectly competitive market. Required: 1. Determine a transfer price using the general rule. 2. How would the transfer price change if the assembly division had no spare capacity? 3. What transfer price would you recommend if there was no outside market for the transferred component and the assembly division had spare capacity? Cost-based transfer pricing: manufacturer Refer to Exercise E12.29. The assembly division's absorption cost of a component is $510, which includes The electrical division has a special offer of $697.50 for its product. The electrical division incurs variable costs of $150 in addition to the transfer price for the assembly division's components. Both divisions currently have spare production capacity. Required: 1. Is the electrical division manager likely to want to accept or reject the special offer? Why? 2. Is this decision in the best interests of Electro Ltd as a whole? Explain. 3. How could the situation be remedied using the transfer price? Select an area to comment on E12.30 LO12.12 12.13 E12.29 LO12.12 12.13 General transfer pricing rule: manufacturer Electro Ltd has two divisions, assembly and electrical. The assembly division transfers partially completed components to the electrical division at a predetermined transfer price. The assembly division's standard variable production cost per unit is $450. This division has spare capacity, and it could sell all its components to outside buyers at $570 per unit in a perfectly competitive market. Required: 1. Determine a transfer price using the general rule. 2. How would the transfer price change if the assembly division had no spare capacity? 3. What transfer price would you recommend if there was no outside market for the transferred component and the assembly division had spare capacity? Cost-based transfer pricing: manufacturer Refer to Exercise E12.29. The assembly division's absorption cost of a component is $510, which includes The electrical division has a special offer of $697.50 for its product. The electrical division incurs variable costs of $150 in addition to the transfer price for the assembly division's components. Both divisions currently have spare production capacity. Required: 1. Is the electrical division manager likely to want to accept or reject the special offer? Why? 2. Is this decision in the best interests of Electro Ltd as a whole? Explain. 3. How could the situation be remedied using the transfer price? Select an area to comment on E12.30 LO12.12 12.13
 please full detail
please full detail





