Question: please give description too Set-UID. Do your attacks in Step I still work? Please describe and explain your observations 2.9 Task 9: Capability Leaking To
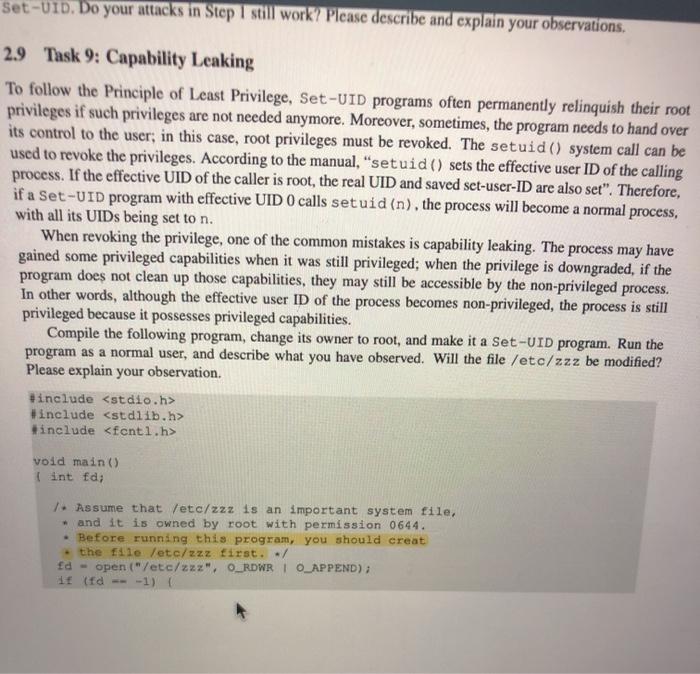
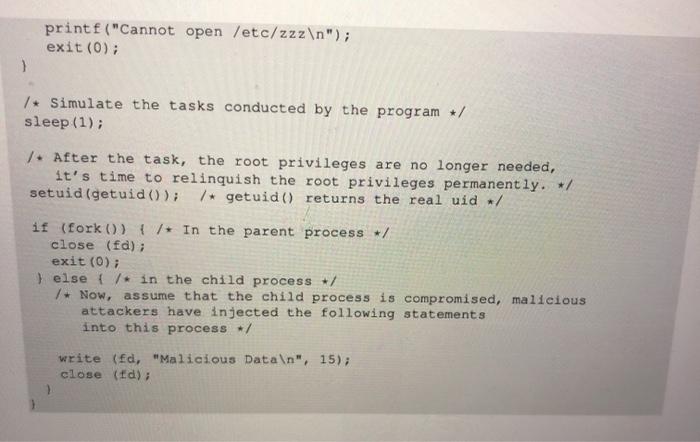
Set-UID. Do your attacks in Step I still work? Please describe and explain your observations 2.9 Task 9: Capability Leaking To follow the Principle of Least Privilege, Set-UID programs often permanently relinquish their root privileges if such privileges are not needed anymore. Moreover, sometimes, the program needs to hand over its control to the user, in this case, root privileges must be revoked. The setuid() system call can be used to revoke the privileges. According to the manual, "setuid() sets the effective user ID of the calling process. If the effective UID of the caller is root, the real UID and saved set-user-ID are also set". Therefore, if a Set-UID program with effective UID O calls setuid (n), the process will become a normal process, with all its UIDs being set to n. When revoking the privilege, one of the common mistakes is capability leaking. The process may have gained some privileged capabilities when it was still privileged; when the privilege is downgraded, if the program does not clean up those capabilities, they may still be accessible by the non-privileged process. In other words, although the effective user ID of the process becomes non-privileged, the process is still privileged because it possesses privileged capabilities. Compile the following program, change its owner to root, and make it a Set-UID program. Run the program as a normal user, and describe what you have observed. Will the file /etc/zzz be modified? Please explain your observation. #include
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


