Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please give me reason for each answer. Thanks. Tim Petrovich is the portfolio manager of fixed income securities at Gamma Bank. Petrovich is concerned about



Please give me reason for each answer. Thanks.
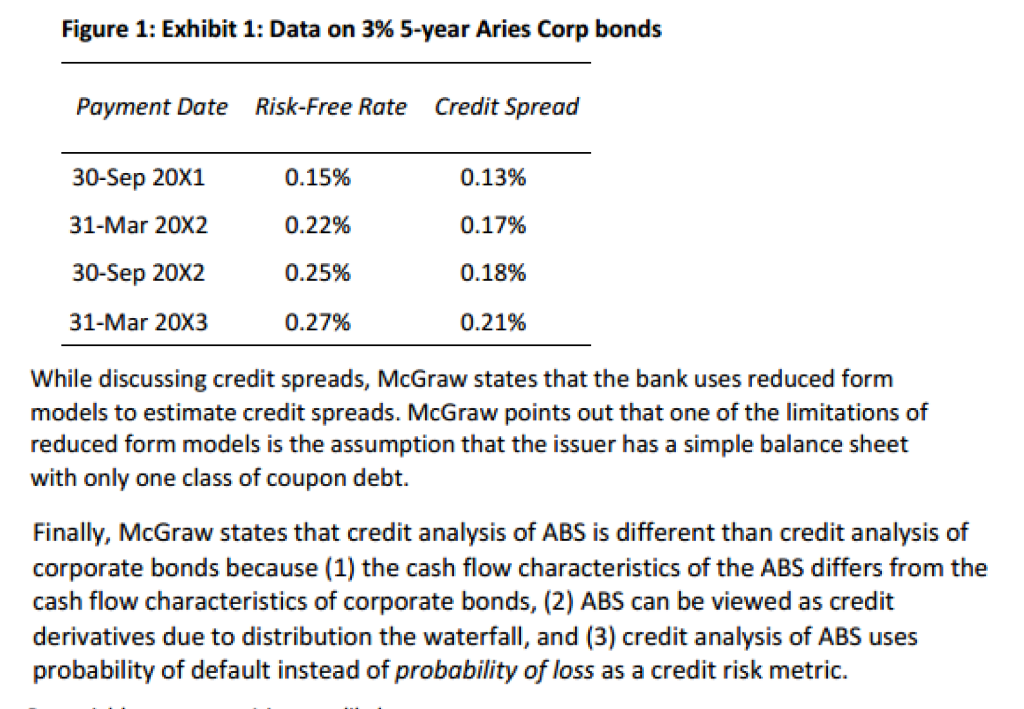
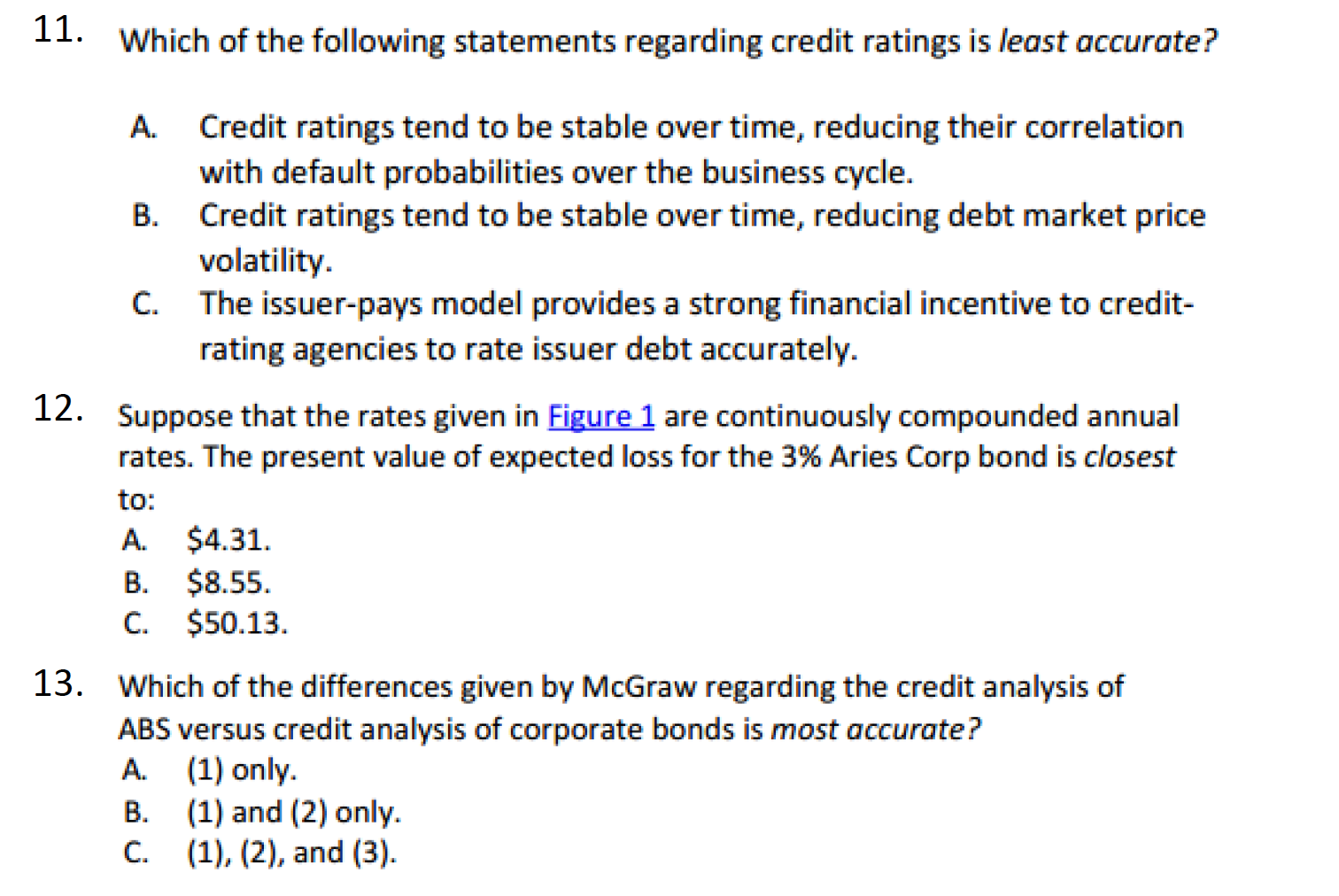
Tim Petrovich is the portfolio manager of fixed income securities at Gamma Bank. Petrovich is concerned about the performance of the bank's corporate bond portfolio over the past four years. He feels that the bank's credit analysis models have been inadequate in evaluating the impact of changing market conditions on the bank's investments. Petrovich evaluates some of the metrics currently being generated by the credit analysis department of the bank. While comparing the metrics, Petrovich makes the following statement: Statement 1: The expected loss metric and present value of expected loss metric differ only in terms of time value of money and discounting of expected future losses. Petrovich discusses credit ratings with Steve McGraw, the bank's senior credit analyst. McGraw states that the bank uses S&P's credit ratings, and these ratings divide the credit-risky bond universe into 21 categories with an equal number of issues in each category. The ratings themselves tend to be stable even though default probabilities fluctuate with the business cycle. Petrovich examines the term structure of credit spreads for one of the bank's holdings. He obtains the data on Aries Corp's 5-year, 3% senior unsecured bonds issued three years ago. Figure 1 shows the relevant data. Figure 1: Exhibit 1: Data on 3% 5-year Aries Corp bonds Payment Date Risk-Free Rate Credit Spread Figure 1: Exhibit 1: Data on 3% 5-year Aries Corp bonds Payment Date Risk-Free Rate Credit Spread 30-Sep 20X1 0.15% 0.13% 31-Mar 20X2 0.22% 0.17% 30-Sep 20X2 0.25% 0.18% 31-Mar 20X3 0.27% 0.21% While discussing credit spreads, McGraw states that the bank uses reduced form models to estimate credit spreads. McGraw points out that one of the limitations of reduced form models is the assumption that the issuer has a simple balance sheet with only one class of coupon debt. Finally, McGraw states that credit analysis of ABS is different than credit analysis of corporate bonds because (1) the cash flow characteristics of the ABS differs from the cash flow characteristics of corporate bonds, (2) ABS can be viewed as credit derivatives due to distribution the waterfall, and (3) credit analysis of ABS uses probability of default instead of probability of loss as a credit risk metric. 5. Petrovich's statement 1 is most likely: A. correct. B. incorrect, because the expected loss computation uses risk-neutral probabilities. C. incorrect, because the present value of expected loss also adjusts default probabilities to capture the riskiness of the cash flows (i.e., the risk premium) 6. correct. B. 7. B. 8. B. McGraw's statement about credit ratings is most likely: A. incorrect in regards to the stability of credit ratings. C. incorrect in regards to the number of issues in each rating category. McGraw's statement about limitation of reduced form model is most likely: A. correct. incorrect, as the reduced form model assumes one class of zero- coupon debt. C. incorrect, as structural models assume a simple balance sheet. Which of the following least accurately describes an assumption of the structural model of credit analysis? A. The issuer's assets are traded in frictionless markets. The issuer's debt is traded in frictionless markets. The value of the issuer's assets at the time of the maturity of debt has a lognormal distribution. The credit spread in Figure 1 most likely includes a premium for: credit risk only. credit risk and liquidity risk only. C. credit risk, liquidity risk, and interest rate risk. Under the structural model, a long position in a debt security can be viewed as equivalent to a long position in: A. a risk-free asset and a short position in a European put option on the stock of the issuer. the assets of the issuer and short position on a risk-free asset. a risk-free asset and a short position in a European put option on the assets of the issuer. C. 9. A B. 10. B. C. 11. Which of the following statements regarding credit ratings is least accurate? A. B. Credit ratings tend to be stable over time, reducing their correlation with default probabilities over the business cycle. Credit ratings tend to be stable over time, reducing debt market price volatility. The issuer-pays model provides a strong financial incentive to credit- rating agencies to rate issuer debt accurately. 12. Suppose that the rates given in Figure 1 are continuously compounded annual rates. The present value of expected loss for the 3% Aries Corp bond is closest to: A. $4.31. B. $8.55. C. $50.13. 13. Which of the differences given by McGraw regarding the credit analysis of ABS versus credit analysis of corporate bonds is most accurate? A. (1) only. B. (1) and (2) only. C. (1), (2), and (3). Tim Petrovich is the portfolio manager of fixed income securities at Gamma Bank. Petrovich is concerned about the performance of the bank's corporate bond portfolio over the past four years. He feels that the bank's credit analysis models have been inadequate in evaluating the impact of changing market conditions on the bank's investments. Petrovich evaluates some of the metrics currently being generated by the credit analysis department of the bank. While comparing the metrics, Petrovich makes the following statement: Statement 1: The expected loss metric and present value of expected loss metric differ only in terms of time value of money and discounting of expected future losses. Petrovich discusses credit ratings with Steve McGraw, the bank's senior credit analyst. McGraw states that the bank uses S&P's credit ratings, and these ratings divide the credit-risky bond universe into 21 categories with an equal number of issues in each category. The ratings themselves tend to be stable even though default probabilities fluctuate with the business cycle. Petrovich examines the term structure of credit spreads for one of the bank's holdings. He obtains the data on Aries Corp's 5-year, 3% senior unsecured bonds issued three years ago. Figure 1 shows the relevant data. Figure 1: Exhibit 1: Data on 3% 5-year Aries Corp bonds Payment Date Risk-Free Rate Credit Spread Figure 1: Exhibit 1: Data on 3% 5-year Aries Corp bonds Payment Date Risk-Free Rate Credit Spread 30-Sep 20X1 0.15% 0.13% 31-Mar 20X2 0.22% 0.17% 30-Sep 20X2 0.25% 0.18% 31-Mar 20X3 0.27% 0.21% While discussing credit spreads, McGraw states that the bank uses reduced form models to estimate credit spreads. McGraw points out that one of the limitations of reduced form models is the assumption that the issuer has a simple balance sheet with only one class of coupon debt. Finally, McGraw states that credit analysis of ABS is different than credit analysis of corporate bonds because (1) the cash flow characteristics of the ABS differs from the cash flow characteristics of corporate bonds, (2) ABS can be viewed as credit derivatives due to distribution the waterfall, and (3) credit analysis of ABS uses probability of default instead of probability of loss as a credit risk metric. 5. Petrovich's statement 1 is most likely: A. correct. B. incorrect, because the expected loss computation uses risk-neutral probabilities. C. incorrect, because the present value of expected loss also adjusts default probabilities to capture the riskiness of the cash flows (i.e., the risk premium) 6. correct. B. 7. B. 8. B. McGraw's statement about credit ratings is most likely: A. incorrect in regards to the stability of credit ratings. C. incorrect in regards to the number of issues in each rating category. McGraw's statement about limitation of reduced form model is most likely: A. correct. incorrect, as the reduced form model assumes one class of zero- coupon debt. C. incorrect, as structural models assume a simple balance sheet. Which of the following least accurately describes an assumption of the structural model of credit analysis? A. The issuer's assets are traded in frictionless markets. The issuer's debt is traded in frictionless markets. The value of the issuer's assets at the time of the maturity of debt has a lognormal distribution. The credit spread in Figure 1 most likely includes a premium for: credit risk only. credit risk and liquidity risk only. C. credit risk, liquidity risk, and interest rate risk. Under the structural model, a long position in a debt security can be viewed as equivalent to a long position in: A. a risk-free asset and a short position in a European put option on the stock of the issuer. the assets of the issuer and short position on a risk-free asset. a risk-free asset and a short position in a European put option on the assets of the issuer. C. 9. A B. 10. B. C. 11. Which of the following statements regarding credit ratings is least accurate? A. B. Credit ratings tend to be stable over time, reducing their correlation with default probabilities over the business cycle. Credit ratings tend to be stable over time, reducing debt market price volatility. The issuer-pays model provides a strong financial incentive to credit- rating agencies to rate issuer debt accurately. 12. Suppose that the rates given in Figure 1 are continuously compounded annual rates. The present value of expected loss for the 3% Aries Corp bond is closest to: A. $4.31. B. $8.55. C. $50.13. 13. Which of the differences given by McGraw regarding the credit analysis of ABS versus credit analysis of corporate bonds is most accurate? A. (1) only. B. (1) and (2) only. C. (1), (2), and (3)Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


