Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
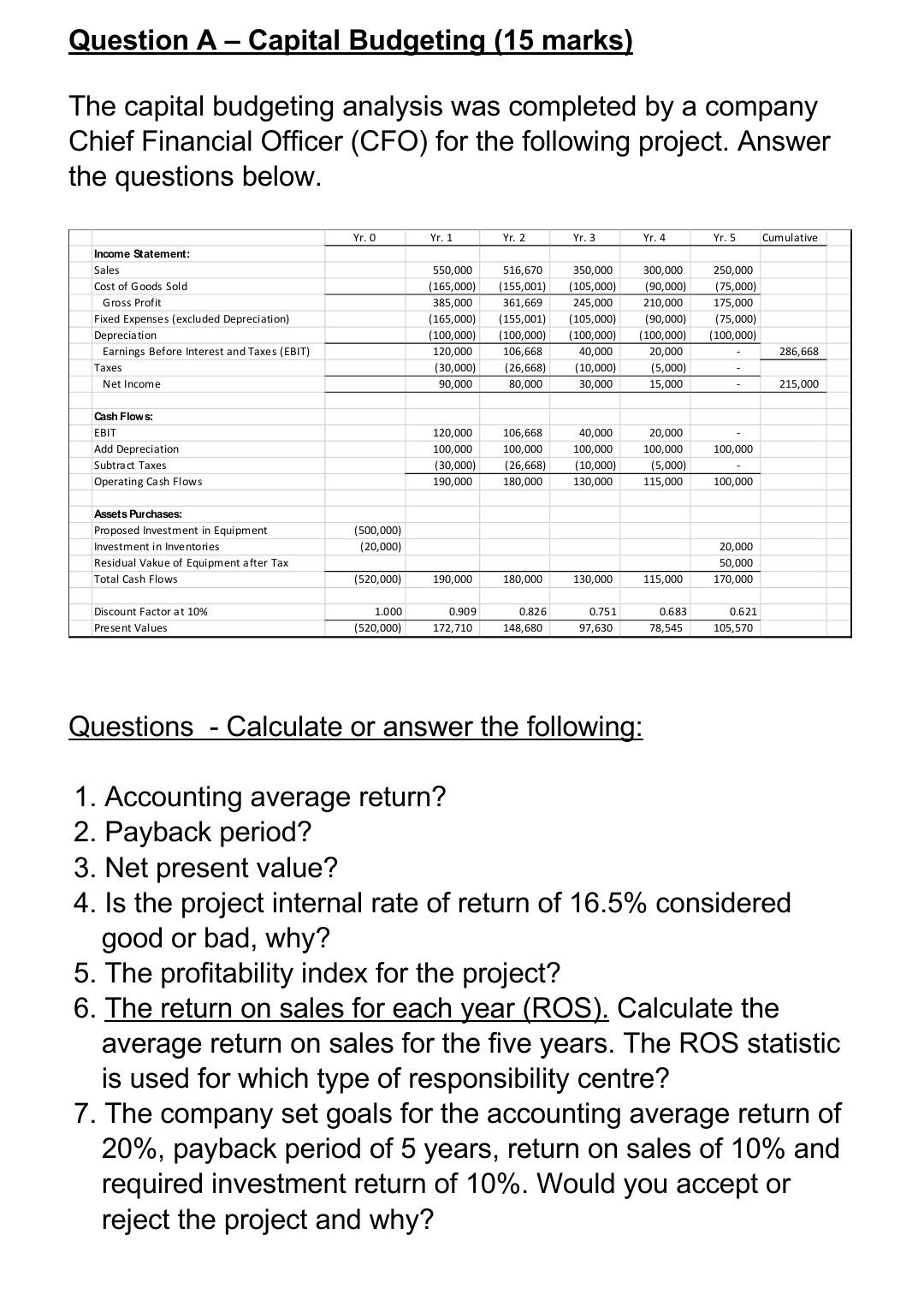
please give solution for these. Question A - Capital Budgeting (15 marks) The capital budgeting analysis was completed by a company Chief Financial Officer (CFO)
please give solution for these.
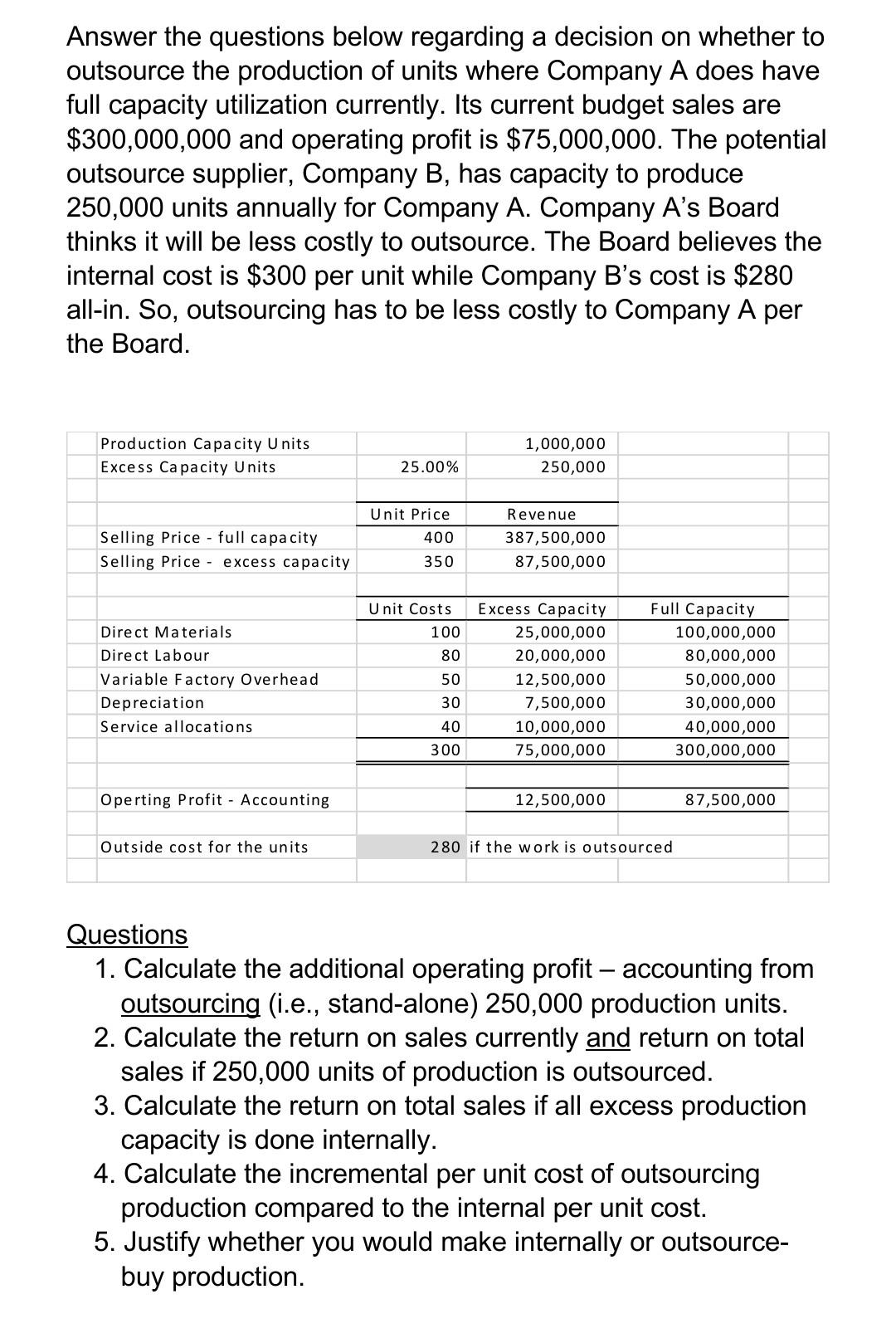
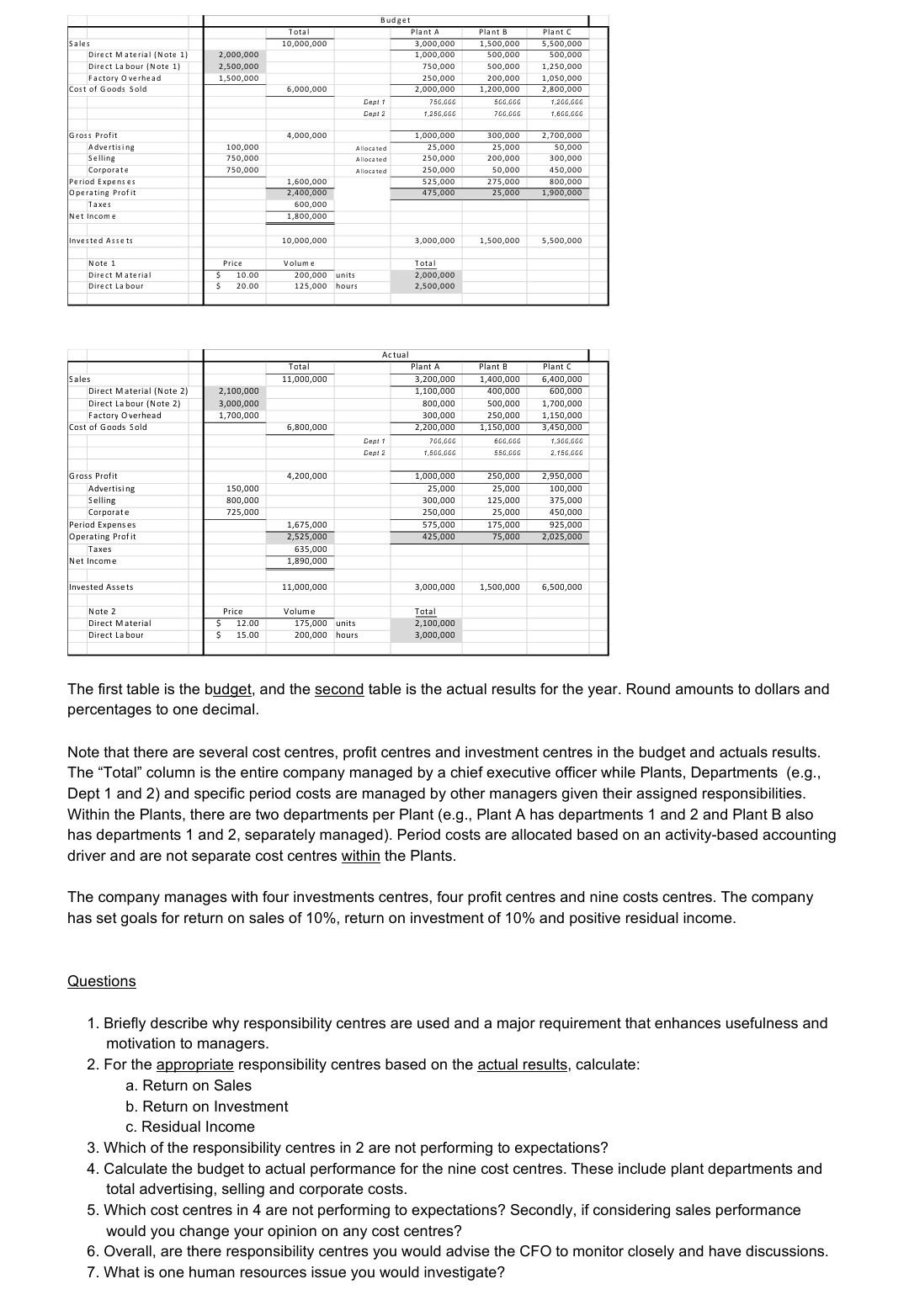
Question A - Capital Budgeting (15 marks) The capital budgeting analysis was completed by a company Chief Financial Officer (CFO) for the following project. Answer the questions below. Yr. O Yr. 1 Yr. 2 Yr. 3 Yr. 4 Yr. 5 Cumulative 250,000 (75,000) 175,000 Income Statement: Sales Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Fixed Expenses (excluded Depreciation) Depreciation Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) Taxes Net Income 550,000 (165,000) 385,000 (165,000) (100,000) 120,000 (30,000) 90,000 516,670 (155,001) 361,669 (155,001) (100,000) 106,668 (26,668) 80,000 350,000 (105,000) 245,000 (105,000) (100,000) 40,000 (10,000) 30,000 300,000 (90,000) 210,000 (90,000) (100,000) 20,000 (5,000) (75,000) (100,000) 286,668 15,000 215,000 Cash Flows: EBIT Add Depreciation Subtract Taxes Operating Cash Flows 100,000 120,000 100,000 (30,000) 190,000 106,668 100,000 (26,668) 180,000 40,000 100,000 (10,000) 130,000 20,000 100,000 (5,000) 115,000 100,000 Assets Purchases: Proposed Investment in Equipment Investment in Inventories Residual Vakue of Equipment after Tax Total Cash Flows (500,000) (20,000) 20,000 50,000 170,000 (520,000) 190,000 180,000 130,000 115,000 0.826 Discount Factor at 10% Pre sent Values 1.000 (520,000) 0.909 172,710 0.751 97,630 0.683 78,545 0.621 105,570 148,680 Questions - Calculate or answer the following: 1. Accounting average return? 2. Payback period? 3. Net present value? 4. Is the project internal rate of return of 16.5% considered good or bad, why? 5. The profitability index for the project? 6. The return on sales for each year (ROS). Calculate the average return on sales for the five years. The ROS statistic is used for which type of responsibility centre? 7. The company set goals for the accounting average return of 20%, payback period of 5 years, return on sales of 10% and required investment return of 10%. Would you accept or reject the project and why? Answer the questions below regarding a decision on whether to outsource the production of units where Company A does have full capacity utilization currently. Its current budget sales are $300,000,000 and operating profit is $75,000,000. The potential outsource supplier, Company B, has capacity to produce 250,000 units annually for Company A. Company A's Board thinks it will be less costly to outsource. The Board believes the internal cost is $300 per unit while Company B's cost is $280 all-in. So, outsourcing has to be less costly to Company A per the Board. Production Capacity Units Excess Capacity Units 1,000,000 250,000 25.00% Unit Price 400 Selling Price - full capacity Selling Price - excess capacity Revenue 387,500,000 87,500,000 350 Unit Costs 100 Direct Materials Direct Labour Variable Factory Overhead Depreciation Service allocati 80 50 Excess Capacity 25,000,000 20,000,000 12,500,000 7,500,000 10,000,000 75,000,000 Full Capacity 100,000,000 80,000,000 50,000,000 30,000,000 40,000,000 300,000,000 30 40 300 Operting Profit - Accounting 12,500,000 87,500,000 Outside cost for the units 280 if the work is outsourced Questions 1. Calculate the additional operating profit - accounting from outsourcing (i.e., stand-alone) 250,000 production units. 2. Calculate the return on sales currently and return on total sales if 250,000 units of production is outsourced. 3. Calculate the return on total sales if all excess production capacity is done internally. 4. Calculate the incremental per unit cost of outsourcing production compared to the internal per unit cost. 5. Justify whether you would make internally or outsource- buy production. Total 10,000,000 Sales Direct Material (Note 1) Direct La bour (Note 1) Factory Overhead Cost of Goods Sold 2,000,000 2,500,000 1,500,000 Budget Plant A 3,000,000 1,000,000 750,000 250,000 2,000,000 Depli 750.GGC Cept 2 1.25GGGG Plant B 1,500,000 500,000 500.000 200,000 1,200,000 SGGGGG 700.GGG Plant 5,500,000 500,000 1,250,000 1,050,000 2.800.000 1,200,000 1.6GGGGG 6,000,000 4,000,000 100,000 750.000 750,000 Allocated Allocated Allocated 300,000 25,000 200,000 Gross Profit Advertising Selling Corporate Period Expenses Operating Profit Taxes Net Income 1,000,000 25,000 250,000 250,000 525,000 475,000 50,000 2,700,000 50,000 300,000 450,000 800,000 1,900,000 275,000 25,000 1,600,000 2.400,000 600,000 1,800,000 invested Assets 10,000,000 3,000,000 1,500,000 5,500,000 Note 1 Direct Material Direct Labour Price $ 10.00 $ 20.00 Volume 200,000 units 125,000 hours Total 2,000,000 2,500,000 Total 11,000,000 Sales Direct Material (Note 2) Direct La bour (Note 2) Factory Overhead Cost of Goods Sold 2,100,000 3,000,000 1,700,000 Actual Plant A 3,200,000 1,100,000 800,000 300,000 2,200,000 Cept 1 700,000 Dept 2 1,500.GGG Plant B 1,400,000 400,000 500,000 250,000 1,150,000 600.000 550 GGG Plant C 6,400,000 600,000 1,700,000 1,150,000 3,450,000 130G,GGG 2.75G,GOG 6,800,000 4,200,000 150,000 800.000 725,000 Gross Profit Advertising Selling Corporate Period Expenses Operating Profit Taxes Net Income 1,000,000 25,000 300,000 250,000 575,000 425,000 250,000 25,000 125,000 25,000 175,000 75,000 2,950,000 100,000 375,000 450,000 925,000 2,025,000 1,675,000 2,525,000 635,000 1,890,000 Invested Assets 11,000,000 3,000,000 1,500,000 6,500,000 Note 2 Direct Material Direct Labour Price 5 12.00 $ 15.00 Volume 175,000 units 200,000 hours Total 2,100,000 3,000,000 The first table is the budget, and the second table is the actual results for the year. Round amounts to dollars and percentages to one decimal. Note that there are several cost centres, profit centres and investment centres in the budget and actuals results. The Total column is the entire company managed by a chief executive officer while Plants, Departments (e.g., Dept 1 and 2) and specific period costs are managed by other managers given their assigned responsibilities. Within the plants, there are two departments per Plant (e.g., Plant A has departments 1 and 2 and Plant B also has departments 1 and 2, separately managed). Period costs are allocated based on an activity-based accounting driver and are not separate cost centres within the plants. The company manages with four investments centres, four profit centres and nine costs centres. The company has set goals for return on sales of 10%, return on investment of 10% and positive residual income. Questions 1. Briefly describe why responsibility centres are used and a major requirement that enhances usefulness and motivation to managers. 2. For the appropriate responsibility centres based on the actual results, calculate: a. Return on Sales b. Return on Investment c. Residual Income 3. Which of the responsibility centres in 2 are not performing to expectations? 4. Calculate the budget to actual performance for the nine cost centres. These include plant departments and total advertising, selling and corporate costs. 5. Which cost centres in 4 are not performing to expectations? Secondly, if considering sales performance would you change your opinion on any cost centres? 6. Overall, are there responsibility centres you would advise the CFO to monitor closely and have discussions. 7. What is one human resources issue you would investigateStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


