Please help!
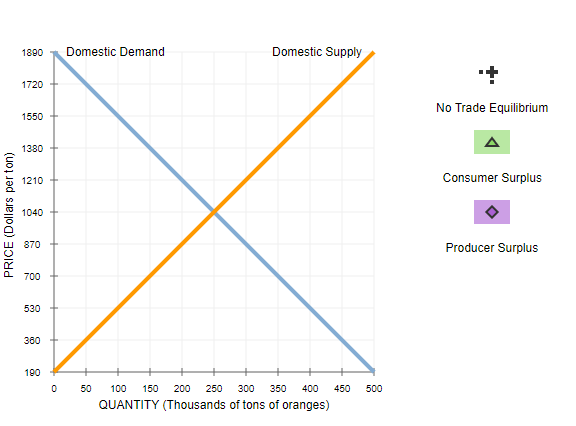
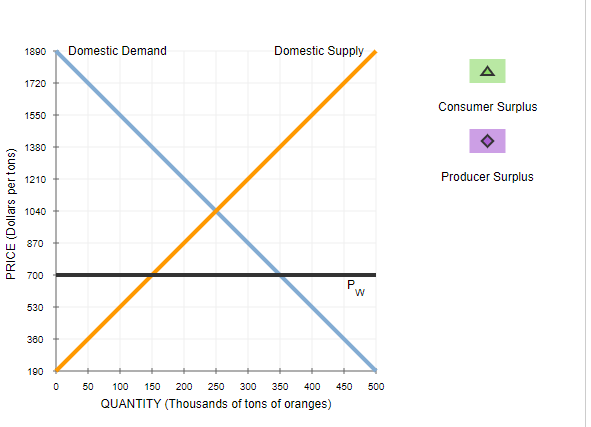
2. Welfare effects of free trade in an importing country Consider the Guatemalan market for oranges. The following graph shows the domestic demand and domestic supply curves for oranges in Guatemala. Suppose Guatemala's government currently does not allow the international trade in oranges. Use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the equilibrium price of a ton of oranges and the equilibrium quantity of oranges in Guatemala in the absence of international trade. Then, use the green point (triangle symbol) to shade the area representing consumer surplus in equilibrium. Finally, use the purple point (diamond symbol) to shade the area representing producer surplus in equilibrium. Note: Select and drag a fill area point from the palette to the graph. To fill in regions on the graph, merely drop the fill area point on the desired region.1890 Domestic Demand Domestic Supply 1720 No Trade Equilibrium 1550 A 1380 1210 Consumer Surplus 1040 PRICE (Dollars per ton) 870 Producer Surplus 700 530 360 190 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 QUANTITY (Thousands of tons of oranges)Based on the previous graph, total surplus in the absence of international trade is v The following graph shows the same domestic demand and supply curves for oranges in Guatemala. Suppose that the Guatemalan government changes its international trade policl;r to allow the free trade of oranges. The horizontal black line {13w} represents the world price of oranges at $3r'00 per ton. Assume that Guatemala's entry into the world market for oranges has no effect on the world price and there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in oranges. Also assume that domestic suppliers will satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before an}.r exporting or importing takes place. Use the green point ( triangle symbol) to shade consumer surplus, and then use the purple point {diamond symbol) to shade producer surplus. 1890 Domestic Demand Domestic Supply A 1720 Consumer Surplus 1550 1380 1210 Producer Surplus 1040 PRICE (Dollars per tons) 870 700 P W 530 380 190 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 QUANTITY (Thousands of tons of oranges)When Guatemala allows free trade of oranges, the price of a ton of oranges in Guatemala will be $700. At this price, tons of oranges will be demanded in Guatemala, and tons will be supplied by domestic suppliers. Therefore, Guatemala will import tons of oranges. Using the information from the previous tasks, complete the following table to analyze the welfare effect of allowing free trade. Without Free Trade With Free Trade (Millions of dollars) (Millions of dollars) Consumer Surplus Producer Surplus When Guatemala allows free trade, the country's consumer surplus by , and producer surplus by . So, the net effect of international trade on Guatemala's total surplus is a of