Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
please help asap! just review study guide 3. Using the phase diagram and the heating curve below, which arrow on the phase diagram corresponds to
please help asap! just review study guide 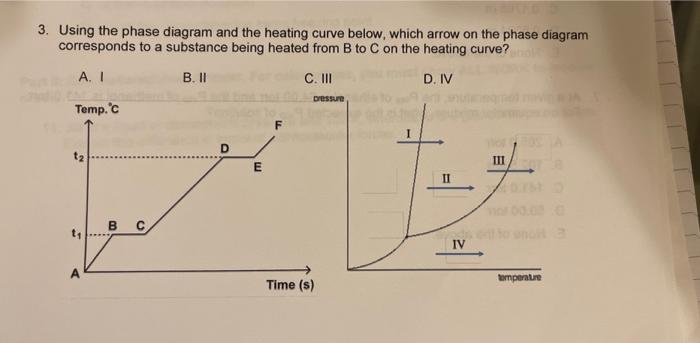


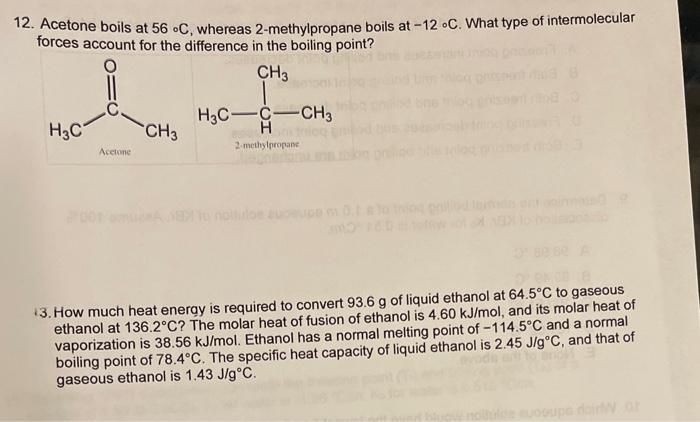


3. Using the phase diagram and the heating curve below, which arrow on the phase diagram corresponds to a substance being heated from B to C on the heating curve? 4. Hvapformercuryat25C is 59.229kJ/mol. How much heat, in kJ, would be required to vaporize 135.54g of mercury? The molar mass of mercury is 200.59g/mol. A. 0.0114kJ B. 40.021kJ C. 87.656kJ D. 8,027.9kJ E. None of the above. 5. What is the molar concentration of an aqueous solution of potassium nitrate, KNO3, with mole fraction of KNO3=0.0194 ? The solution's density is 1.0627g/mL. The molar mass of KNO3 is 101.10g/mol. A. 1.67M B. 2.04M C. 1.05M D. 0.410M E. None of the above. 6. A solution is prepared by dissolving 16.53gKI in 564.12gHH2. What is the molality (m) of KI in the solution? The molar mass of KI is 166.00g/mol. A. 0.0293m B. 0.1715m C. 0.1765m D. 0.6024m E. None of the above. 7. At a given temperature, the Pvap of ethanol is 64.00 torr and the Pvap of methanol is 141.0 torr. For an equimolar mixture, what is the expected Pvap of solution? A. 205.0 torr B. 102.5 torr C. 141.0 torr D. 50.00 torr E. None of the above. 9. Determine the normal boiling point of a 1.0m aqueous solution of KBr. Assume 100% dissociation of KBr. Kb for water is 0.51C/m. A. 98.98C B. 99.49C C. 100.51C D. 101.02C E. None of the above. 12. Acetone boils at 56C, whereas 2 -methylpropane boils at 12C. What type of intermolecular forces account for the difference in the boiling point? 13. How much heat energy is required to convert 93.6g of liquid ethanol at 64.5C to gaseous ethanol at 136.2C ? The molar heat of fusion of ethanol is 4.60kJ/mol, and its molar heat of vaporization is 38.56kJ/mol. Ethanol has a normal melting point of 114.5C and a normal boiling point of 78.4C. The specific heat capacity of liquid ethanol is 2.45J/gC, and that of gaseous ethanol is 1.43J/gC. 14. The addition of 40.0g of a nonvolatile solute to 2.27mol of benzene lowers the vapor pressure of the benzene from 107.5 torr to 94.7 torr. Calculate the molar mass of the solute. 15. Assuming 100% dissociation, calculate the freezing point (Tt) and boiling point (Tb) of a 6. Oxygen gas has a solubility in water of 0.00412g/100mL at 20C and 760mmHg. Calculate the solubility of oxygen gas in water at 20C and a pressure of 1150mmHg. 17. The concentration of lead in drinking water was found to be 6.129105M. Express this concentration in ppb and ppm. The molar mass of lead is 207.2g/mol. The density of the solution can be assumed as 1.00g/mL 





Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


